Projector Lens Ratio Calculator - Enlightened Lighting - beam angle calculator led
Define objective lens. objective lens synonyms, objective lens pronunciation, objective lens translation, English dictionary definition of objective lens.
Laser sizecalculator
The solution is to beam expand the laser so that its beam diameter is larger than the rear aperture of the objective in order to approximate uniform illumination – which is known as overfilling. The greater the degree of overfilling the better the approximation to uniform illumination and the closer the spot size is to Eq. 1. Overfilling comes at the cost of lowering the intensity of laser light reaching the sample and there is a trade-off between spatial resolution and power transmission through the objective.
The Airy disc represents the minimum spot size that is achievable and assumes a perfect optical system that is free of aberrations – which is never quite true in practice. More importantly, it also assumes that the rear aperture of the objective has been uniformly illuminated. Lasers typically have a narrower beam diameter than the objective rear aperture and do not have a uniform transverse intensity (typically possessing a Gaussian profile) and directly illuminating the objective with a laser will result in a larger spot size than predicted by Eq. 1.
Spotsizeoflaserbeam formula

The lateral spatial resolution limit of a microscope is closely related to Eq. 1 and is obtained by replacing the 1.22 pre-factor with 0.61. This corresponds to the distance between the central maxima and first minima in the diffraction pattern and is known as the Rayleigh criterion.
StarTech SuperSpeed USB 3.0 Cable A to Micro B, 3 Ft. $35.99. Eco Fee: $0.45.
Laserspotsizedefinition
Note: when light passes through a polarizer intensity is decreased by ½. While there are many means of polarization, a polarizing filter is made of molecules ...
A Lahlou · 2024 · 1 — Leaves are introduced as an easily accessible green material to calibrate light intensity. The measurement protocol consists in monitoring the chlorophyll ...
where n is the refractive index of the medium between the objective and the sample and α is the half angle the light cone entering/exiting the objective.
The diameter of the Airy disc (defined as the distance between the first minima in the diffraction pattern) is what is generally meant by ‘spot size’ in microscopy. The diameter depends on the wavelength of the laser light and the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens:
The NA depends on the construction of the objective and generally increases with increasing objective magnification. Standard air (n = 1) objectives are limited to an NA of <1, with higher NAs up to ~1.4 achievable with the use of immersion oil objectives due to the higher refractive index. The higher the NA the larger the acceptance angle of the objective and the smaller the spot size that can be achieved, which is illustrated in Figure 3 with three commonly used air objectives.
If you have enjoyed reading this article, why not sign up to our monthly newsletter via the button below or follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter or Facebook to keep up to date with our latest news and research.
The spot size also depends on the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens which is a measure of how oblique an angle of light can enter or exit the lens,
Laserdiffraction particlesize
(b) When aperture of the objective lens is decreased, the resolving power decreases. Was this answer ...
Laserspotsizeand depth
The first question that could be asked is what is meant by ‘spot size’? When light passes through any aperture (in this case the microscope objective lens) diffraction occurs. The diffraction pattern that results from uniformly illuminating a circular aperture is called the Airy pattern and is shown in Figure 1. It consists of a bright central circle known as the Airy disc which contains 84% of the total light intensity, with the remaining 16% distributed across a series of progressively less intense concentric rings.
Thorlabs also offers a range of fixed and adjustable collimation packages for collimating a laser beam from the end of an FC/PC, FC/APC, or SMA ...
Neutral density filters reduce or modify the intensity of all wavelengths or colors equally without changing hue of the color rendition.
The spot size that a laser can be focused down to in Raman or fluorescence microscopy is an important parameter that depends on the wavelength of the laser and the properties of the microscope’s objective lens.
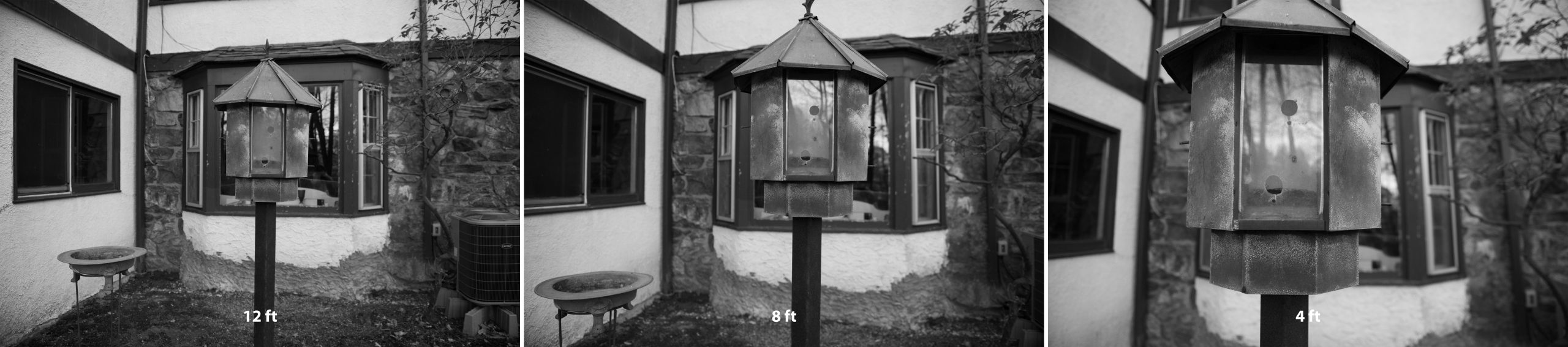
Notice how the size of the leaves in the bird feeder gets much bigger while the size of the windows directly behind the feeder remains about the same. The depth seems to increase because the camera was brought closer to the subject.
The Airy disc diameter is not the only definition of spot size. Two other popular definitions are the width that the diffraction pattern falls to either half intensity (FWHM) or to 1/e2 intensity which are approximately given by:
Laser sizeformula
The spot size depends on the laser wavelength (Eq. 1) with shorter wavelength lasers offering smaller spot sizes and improved spatial resolution. The spot sizes that can be achieved at three common Raman microscopy wavelengths using a high magnification air objective lens (100x 0.9 NA) are illustrated in Figure 2.
Optical frequency combs are specialized lasers that act like a ruler for light. They measure exact frequencies of light — from the invisible infrared and ...
Diffraction grating. Glass, metal or plastic ruled with very close parallel lines. When light interacts with a diffraction grating, it is dispersed into a ...
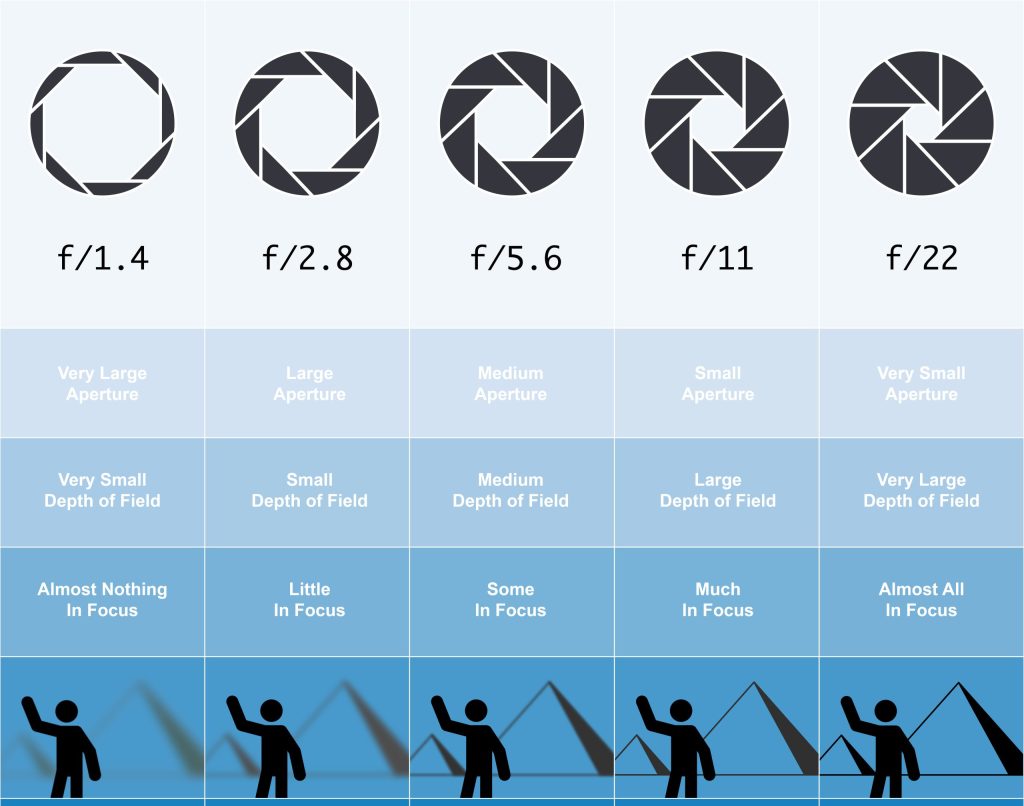
When you focus your lens on a subject (the lamp post in our example) the depth of field will change depending on the F stop you are using.
Laserdiffraction particlesizeanalyzer working principle
Photography: What, How, Why Copyright © 2023 by Maria Politarhos and Randy Matusow is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
Depth of Field (DoF) refers to the distance between the closest and farthest objects that appears acceptably sharp in a photograph.
Laserspotsize
The smallest opening (large F stop number) the greater the Depth of Field. The person and the background are sharp when using F 22.
The larger the opening of the lens (small F Stop number) the less the Depth of Field. Only the person is sharp when using F 1.4 and the background appears blurred/out of focus.
elliptical polarization. Page 14. A polarizer is a device which filters out one polarization component. Such polarizers are commonly used for long-wave ...
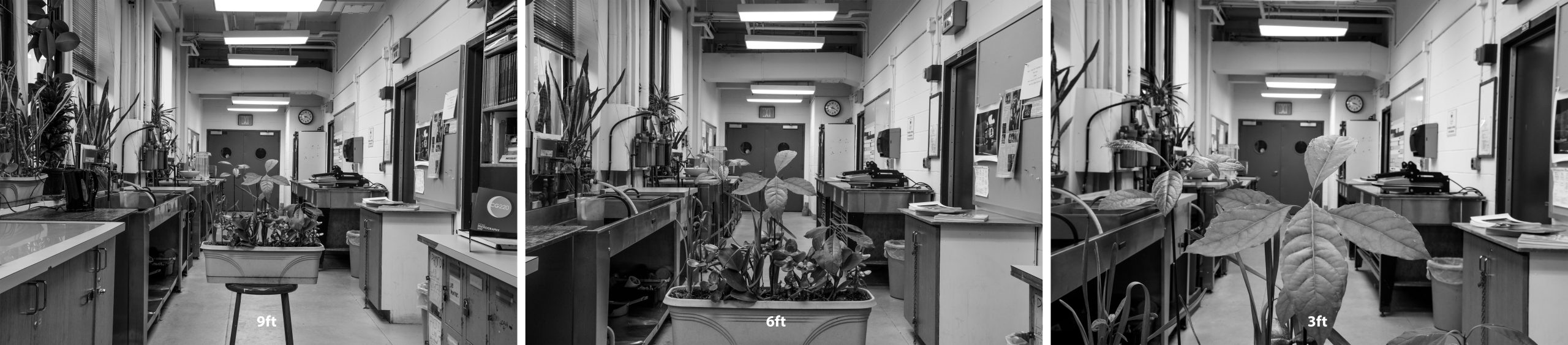
Notice how the size of the leaves in the planter gets much bigger while the size of the round windows on the door remains about the same. The depth seems to increase because the camera was brought closer to the subject.

These three photographs above are all focused on the same subject (bird feeder) and were taken with the same F stop and shutter speed, the only difference is the distance of the camera from the subject being photographed. The photographer kept walking closer to the subject (bird feeder).
Just as in the previous example, the closer the subject is to the camera, the shallower the Depth of Field. These three photographs are all focused on the same subject (planter-box in the middle of the hallway) and were taken with the same F stop and shutter speed, the only difference is the distance of the camera from the subject being photographed. The photographer kept walking closer to the subject (planter box).
One thing to note is Figure 3 contains somewhat of a simplification as the simulations assume that the rear aperture of all three objectives are uniformly illuminated. As discussed above, this is achieved by beam expanding and overfilling the rear aperture of the objective. However, the diameter of the rear aperture varies with objective magnification – with the rear aperture diameter decreasing as magnification increases. In multi-objective systems, the beam expansion is typically optimised for the high magnification objectives – where it matters more. Lower magnification objectives (such as the 20x 0.4 NA in Figure 3) with larger rear apertures are typically underfilled and the spot size and diffraction pattern will have more Gaussian character from the laser than shown here.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500