Prism (geometry) - whats prism
The path difference must create destructive interference for a dark fringe; the path difference must be out of phase by λ ⁄ 2. (λ represents the wavelength)
We may divide the slit into four equal portions of a ⁄ 4 and use the same rationale for the next fringe. As a result, for the second minima,
Infrared has a few benefits that could be considered when choosing an IPS system. Here are three key benefits of using infrared to send information:
Mapsted offers a more robust, unique approach to indoor positioning technology that combines a range of data sources to provide the most accurate, up-to-date information on someone’s location inside a particular building.
The angular location of any point on the screen will be determined by measuring from the slit centre, which splits the slit by a ⁄ 2 lengths. To explain the pattern, we’ll look at the state of black fringes first. Let us also split the slit into equal-width zones a ⁄ 2. Let’s take a look at a pair of rays that come from a ⁄ 2 distances apart, as illustrated below.
Typesof diffraction
If the phase difference between two certain waves is an even multiple of π then constructive interference occurs, also path difference must be an integral multiple of the wavelength.
The terms diffraction and scattering are often used interchangeably and are considered to be almost synonymous. Diffraction describes a specialized case of light scattering in which an object with regularly repeating features (such as a diffraction grating) produces an orderly diffraction of light in a diffraction pattern. In the real world, most objects are very complex in shape and should be considered to be composed of many individual diffraction features that can collectively produce a random scattering of light.
When two objects placed at a distance from each other are separated by an angular separation θ, the diffraction patterns of the two objects will overlap each other. They would appear as one when the two central maxima overlap.
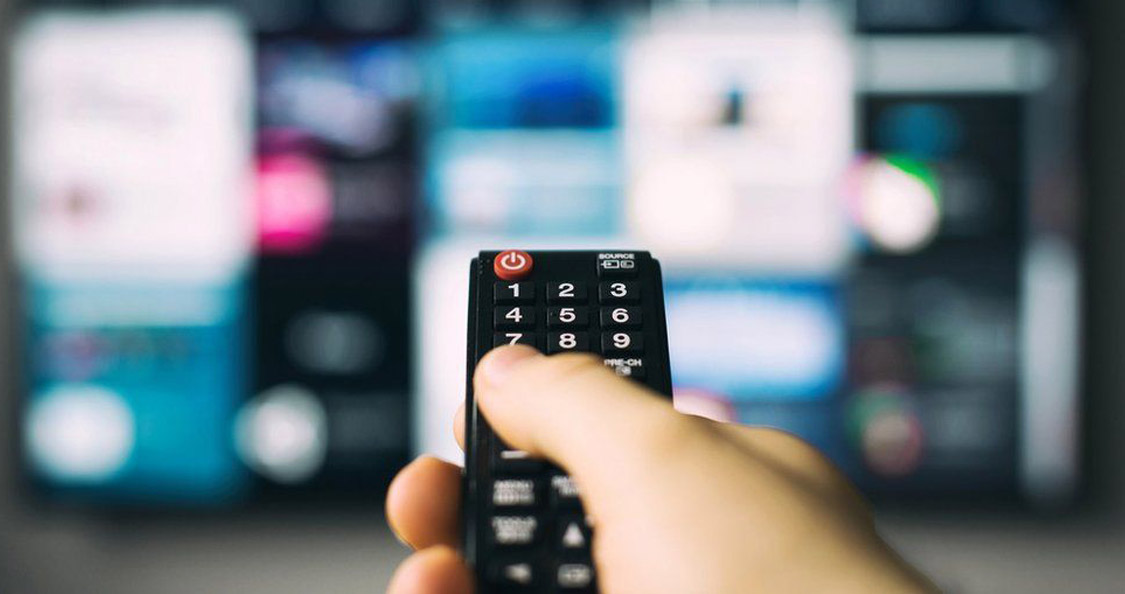
Probably one of the most common examples of wireless infrared technology is a T.V. remote. Sensors in a remote transmit an infrared laser to a sensor in a T.V., which communicates a particular command to the T.V. (turn on, volume up, etc.).
Infrared technology has been around for some time and has a lot of uses, from the detection of infrared radiation to the use of infrared to send and receive information, commands, etc. But when it comes to navigating around a large, complex building, the limitations of infrared technology become apparent very quickly. If infrared can’t pass outside of a room, it doesn’t offer much for mapping and transmitting information about large buildings or a person’s location inside them.
In IPS, infrared technology is commonly used to gauge where someone or something is in a particular room. Sensors to send and receive signals are installed in a room and can continually relay positioning information.
P Corke · 2011 · 12 — The task in visual servoing is to control the pose of the robot's end-effector, relative to the target, using visual features extracted from the image.
Diffraction ofwaves
There are generally two types of wireless infrared technologies: directed and diffuse. Directed technologies use infrared lasers to transmit information, but there must be an unobstructed line of sight between the source of the infrared light and the receiver. Some technologies use this to their advantage—for example, certain security systems rely on the disruption of a beam of infrared light to detect if someone has crossed a particular threshold.
The diffraction phenomenon is very similar to the interference phenomenon and they both happen simultaneously. Generally, it’s difficult to distinguish between diffraction and interference since they both happen at the same time. Diffraction is observed when light is diffracted from water droplets in the clouds and we see shades of blue, pink, purple, and green in clouds.
The essential condition for the diffraction of light to occur is the length of the obstacle must be comparable to the wavelength of light.
Diffractiondiagram
Diffuse infrared technology scatters the beam, making it a bit harder to block. T.V. remotes are an example of diffuse infrared wireless technology: as long as you’re in the same room, it should work.
Ans. Infrared technology examples include thermal imaging, which is designed to detect infrared radiation, and T.V. remotes which is an example of wireless infrared technology that uses infrared radiation to send and receive information.
Ans. It is a technology that either detects infrared for specific purposes or that uses infrared to send information. Infrared technologies have been around for a long time.
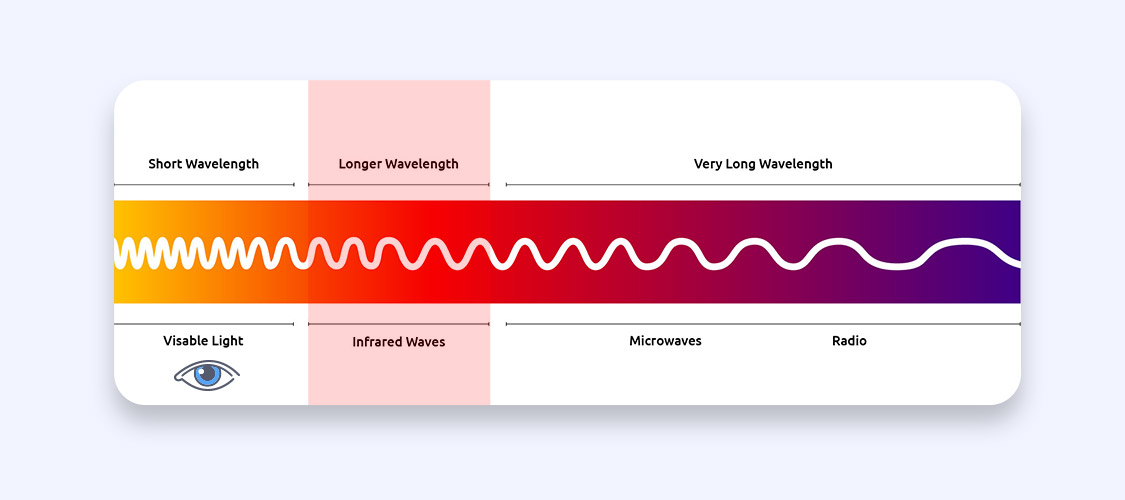
Infrared is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is not visible to the naked eye. And, ironically, it is often referred to as infrared light. Infrared is a common type of radiation given off by heat; when you feel something hot, you are feeling infrared radiation. Infrared radiation was first discovered by British scientist William Herschel in the 1800s. During an experiment to test the temperatures of different colors, Herschel found that red was much warmer than blue, highlighting that infrared is given off by heat. Infrared has a long wavelength and is just beyond the realm of visible light in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Light diffraction shows how light waves bend and spread when they come into contact with objects or squeeze through narrow spaces. This phenomena is important for many optical applications, such as developing sophisticated optical systems like diffraction gratings or producing rainbows. Knowing diffraction allows for the creation of cutting-edge spectroscopy, microscopy, and telecommunications technologies.
Diffractionexamples
This LED bulb can be used as a replacement for current LED bulbs in BMS and Motic microscopes.
Diffraction can be observed easily when we replace the double slit of the young double slit experiment with a single narrow slit. As the light passes this narrow slit a bright pattern at the centre is observed.
Since its discovery, scientists have found that infrared radiation has many innovative uses, which has led to the development of infrared technology for commercial and military aircraft, thermal imaging cameras, home entertainment systems, and much more.
Diffraction is a phenomenon shown by light. When the wave of light interacts with the particle in the atmosphere it bends at the corners and scatters in the area to illuminate the whole area, this phenomenon is called the Diffraction of light. It is a property of light which is used to explain various phenomena observed in our daily life.
Diffractiondefinition
First discovered in 1800 by William Herschel, infrared “light” is a type of electromagnetic radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum. It is invisible to the human eye, and it is mostly produced by heat. That’s why infrared technology has long been used in technologies like thermal imaging tools or in telescopes used by astronomers to study the universe.
So first, what is infrared technology and how does it work? Broadly speaking, there are two types of infrared technology: those that detect infrared radiation and those that send information via infrared radiation (called wireless infrared technology).
The minimum distances between images must be such that the central maximum of the first image lies on the first minimum of the second and vice versa. Such an image viewed from an optical device is calculated using Rayleigh’s criterion.

Beam formulas can be calculated with simple condition input. Maximum deflection, maximum bending stress, maximum bending moment, geometric moment of inertia ...
The difference in the phase angle of the two waves is called the phase difference whereas the difference in the path covered by the two waves is called the path difference.,
Definitionof diffractionin Physics
Instead of detecting infrared radiation, wireless infrared technologies use infrared radiation to transmit and convey data and commands.
We may see the bending phenomena of light, or diffraction, in the single-slit diffraction experiment, which causes light from a coherent source to interfere with itself and form a distinct pattern on the screen termed the diffraction pattern. When the sources are tiny enough to be comparable in size to the wavelength of light, diffraction occurs. This impact may be seen in the diagram below,
Examples of diffraction can easily be observed in our daily life, some of the most common ones are, the silver lining seen on the edges of the clouds because of the diffraction of light by water droplets.
Ans. Infrared refers to light just outside the spectrum of visible light. It is a type of radiation often produced by heat and was first discovered in 1800.
Despite some benefits, there are a lot of limitations with infrared uses in IPS, particularly with wireless technology. The biggest issue with infrared technology is its range of use. You may have noticed this with your T.V. If you are too far away, the remote won’t work. That’s because infrared beams cannot pass through solid objects, which significantly limits the distance they can travel, and therefore the range of the information they can convey.
Jul 28, 2020 — I've seen them listed on Camerafilters.com. I think they call them a right angle lens. Reply Bookmark. Reply ...
When a light ray goes from a denser medium to a rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle it gets reflected instead of being refracted this phenomenon is called Total Internal Reflection.
Short description of diffractionin physics
Fiber Cable. Belden's extensive line of indoor and outdoor cable products is offered in tight buffer and loose tube designs. Armored, burial, and ruggedized ...
While there are some benefits to using infrared, there are also several limitations ultimately making infrared a less common choice in IPS.
Apr 6, 2018 — Very roughly speaking, depth of field increases with the square of the focus distance. This effect is counteracted by the shallower depth of ...
In spherical mirrors and thin lenses, the focal length shares a direct relationship with the radius of curvature. A lens with a larger radius of curvature has a ...
As a result, wireless infrared technologies are essentially limited to room-based communications. While it could be possible to communicate infrared information between homes if they have windows that face each other, for example, buildings may not always be set up like that. And while infrared can be very accurate about what it detects in a given space, every room in a building would still need to be installed with sensors to help detect the infrared lasers. This can require retrofitting old buildings, which is expensive.
The lens is divided into two segments, the top of the lens contains the distance vision prescription, while the bottom of the lens contains the near vision ...
The advantages of diffuse light in horticultural production have been long debated, and there's now increasing evidence that using light diffusing technologies ...

Fraunhoferdiffraction
But other technologies use infrared light as a way to send information between different locations, like with a T.V. remote. It’s a relatively low-energy and secure way of transmitting information, but the biggest drawback is its range and susceptibility to interference; because infrared can’t pass through solid objects, it’s essentially limited in usefulness to transmitting data within a given room. Even a simple ray of sunlight can be enough to block the infrared beam from getting to its destination. Though it has a high degree of accuracy in a given space, it can be expensive to outfit an entire building with the sensors needed to collect accurate information, particularly retrofitting old buildings. As a result, infrared is not generally considered a good choice to use for indoor positioning technologies. Effective positioning tools require data about a much larger terrain than just a single room.
The maxima are located between the minima, and the width of the central maximum is equal to the distance between the 1st order minima on both sides of the screen.
Bandpass filters, like those from Avantier, are essential optical components that transmit a specific range of wavelengths while blocking others. These ...
Ans. The general answer is no. A beam of infrared light can be very easily disrupted (e.g., by a solid object, by the sun) meaning that any information being sent via that light won’t reach its target. As a result, wireless infrared technology is often limited to a single room, significantly limiting its usefulness.
Infrared technology that detects infrared often involves sensors that turn detected infrared radiation into usable information.
Thermal imaging cameras have uses that run the gamut of industries and purposes, both in military and civilian areas. Astronomers, for example, have developed tools that detect infrared radiation in space because infrared can pass through thick areas of dust and cloud that visible light cannot, allowing them to learn about unseen aspects of the universe.
This defines Rayleigh’s resolution criterion. It can be shown that, for a circular aperture of a given diameter, the first minimum in the diffraction pattern occurs at,
Let’s take one of the most common examples of infrared technology: thermal imaging. Because infrared is the radiation given off by heat, detecting infrared radiation can provide information about different heat sources. Thermal imaging cameras use sensors that take information about different temperatures (e.g., different levels of infrared radiation) and turn that information into images that the naked eye wouldn’t have been able to detect.
The intensity of the diffraction of light varies with the wavelength of the light used where the light with a higher wavelength diffracts in comparison to light with a smaller wavelength.
Infrared technology uses also include tracking and indoor positioning services (IPS). But how exactly does It work and is it effective for large-scale IPS?
There is another beam at a distance of a ⁄ 2 that can create destructive interference for a ray coming from any point in the slit. As each ray originating from a point has a counterpart that produces destructive interference, there is destructive interference at θ = sin−1(λ ⁄ a). As a result, a dark fringe is created.
Any number of ray pairs that start at a distance of a ⁄ 2 from one another, such as the bottom two rays in the diagram, can be considered. Any arbitrary pair of rays separated by a ⁄ 2 can be taken into account. In a minute, we’ll discover how important this method is.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500