Plate Beamsplitters - EMF Corp - Omega Optical - plate beam splitter
The longevity and upkeep of optical systems are important factors when choosing between spherical and aspheric lenses. Each type offers different maintenance challenges and durability characteristics.
In the field of photography, aspheric lenses are prized for their ability to minimize distortion and provide high image clarity, making them essential in professional-grade cameras and high-end smartphones. They help achieve sharp images with accurate focus, important for detailed photography and videography. Spherical lenses, while not as advanced in reducing aberrations, are commonly used in entry-level cameras where cost-efficiency is a priority.
Aspheric lenses, due to their complex manufacturing process and materials, can be more delicate and susceptible to damage if not handled properly. They require careful handling and storage to maintain their precision and performance. On the other hand, spherical lenses, being simpler in design and construction, tend to be more robust and less prone to damage, making them a durable option for rugged applications and environments.
Both spherical and aspheric lenses play significant roles in consumer electronics, each bringing distinct advantages to various devices.
The primary reason why sapphire is often chosen as the material for optical windows rather than other materials such as silica and quartz is that it is the hardest oxide material in existence, and one of the hardest crystals available, second only to diamond.
In display technologies such as projectors and augmented reality displays, the choice between spherical and aspheric lenses can impact image quality and device compactness. Aspheric lenses help in producing uniform and high-quality images across the entire display surface, while spherical lenses might be used in more cost-effective solutions where high precision is not as important.
In technical terms, sapphire windows or sapphire plates that have been cut to ‘C’ axis have been cut to provide an optical axis that runs perpendicular to the plane of the sapphire substrate itself. It is also referred to as a ‘Z’ cut or 0° plane cut.
Aspherical lens designs offer several advantages that outweigh their challenges, including enhanced optical performance or more compact lens configurations.
Aspheric lenses feature more intricate profiles with changing curvatures from center to edge that enable more precise focusing and less distortion from spherical distortion, resulting in clearer images with sharper contrast. Although aspherics lenses may cost more and be harder to produce than regular lens designs, their superior optical performance make it worthwhile in high precision applications.
Hardness of this kind means that sapphire windows are highly resistant to wear and tear and scratching, no matter how potentially damaging the environment in which they are utilised is.
Posted by Kelvin Biggs, Managing Director | 14th February 2023 | Optical Products
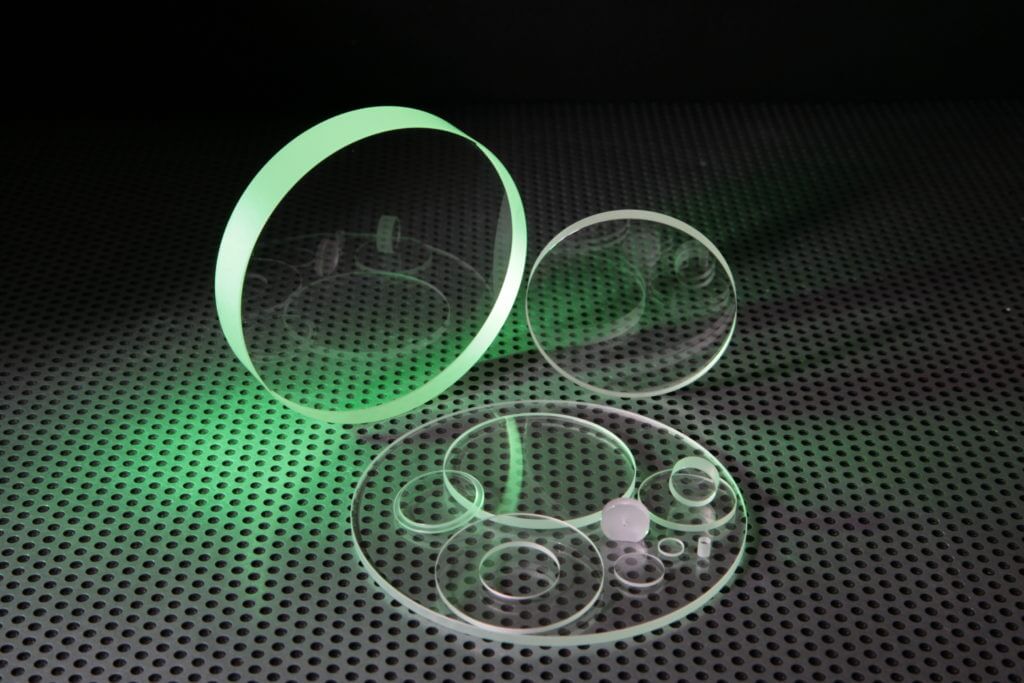
When supplied as standard, sapphire windows and sapphire plates are cut to a random optical axis, which offers all of the advantages listed above in terms of durability, strength, and versatility, while the sapphire windows can also be AR coated on one or both sides.
Due to their properties, sapphire windows are often used in difficult environments that involve factors such as high temperatures or pressure or the presence of corrosive substances.
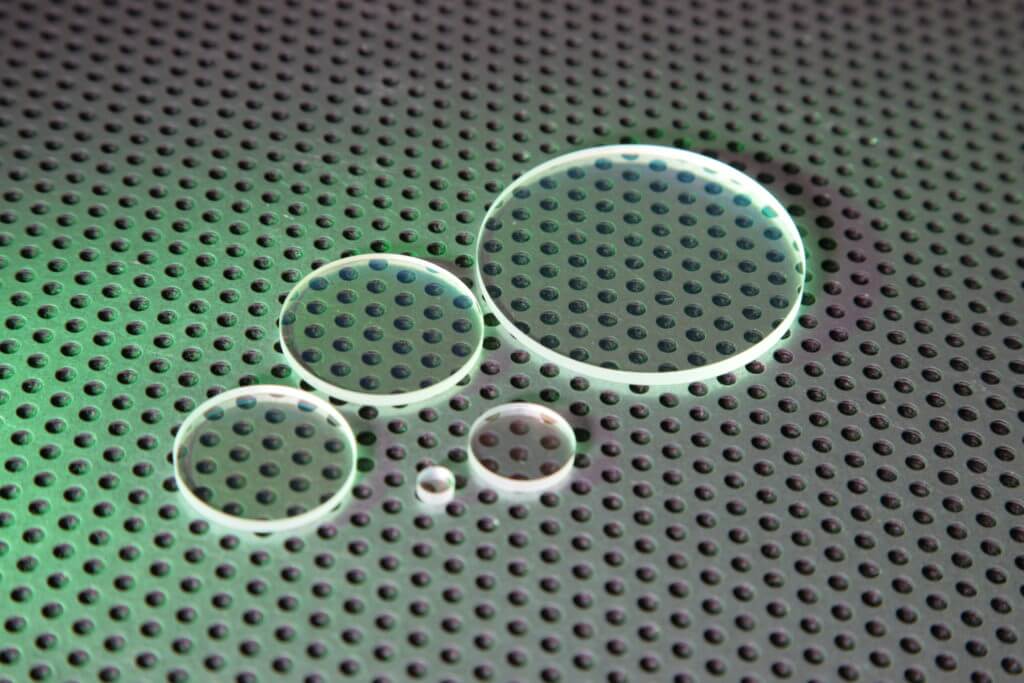
Spherical and aspherical lenses should be selected based on your application requirements, including optical performance, design complexity and cost considerations. Aspherical lenses offer higher precision while at the same time remaining an affordable solution for many general-purpose uses; on the contrary aspherical lenses tend to offer superior image quality than their spherical counterparts.
Welcome to UQG Optics! It looks like you are visiting from the US. Select your preferred currency below to see appropriate pricing. Contact us for additional support or to discuss specific requirements.
Refraction occurs when light rays pass through spherical lenses which bend them as they pass. Their basic principle lies within their circular design: light entering such lenses interact with its curvilinear surface, leading them either towards convergence (convex lenses) or divergence (concave lenses).
While Sapphire windows cut to random orientation still involves a high degree of precision and tolerance, it may not be exact enough for particular optical components, which is why some sapphire windows are cut to C axis.
Finding an aspherical or spherical lens suitable to your needs requires considering several key aspects, particularly within photonics. Photonics is an expansive field that encompasses everything from telecom systems and laser beam systems through medical photonics as well as sensors requiring lenses – this comprehensive guide can assist in selecting an appropriate type of lens in photonics applications.
Focusing the light through a spherical lens depends upon its curvature, refractive indices of materials used in its construction and wavelengths of light that pass through it. Spherical lenses suffer from distortion due to their uniform curve; light hitting their edges being refracted more than those striking its center, thus leading to different focus locations along an optical axis.
The maintenance requirements for aspheric lenses are typically higher due to their complex surface profiles, which can make cleaning and alignment more challenging. Special tools and techniques might be needed to ensure they remain in optimal condition. Spherical lenses, with their simpler curvature, are easier to clean and maintain, reducing the time and cost associated with their upkeep.
Optical window
In terms of replacement and repair, spherical lenses offer more straightforward solutions. Their widespread use and simpler design mean that replacements are generally more readily available and less expensive. Aspheric lenses, due to their specialized nature, might involve longer lead times for replacements and higher costs, especially if custom designs are required.
We use optional cookies to review analytics that help us to improve our website experience. By clicking accept, you are giving consent for us to do this. You can find out more and manage cookies in our privacy policy.
Visible window
Selecting an aspherical or spherical lens for photonics applications involves careful consideration of application requirements, design factors, cost versus performance considerations and supplier collaboration – to achieve desired performance from your photonics system through lens selection in an organized manner.
Put your optical component needs in the hands of Chineselens Optics and our dedicated marketing team will quickly provide you with a customised response and solution.
VR and AR systems demand lenses that can deliver a wide field of view with minimal distortion. Aspheric lenses are well-suited for these applications due to their ability to provide clear and immersive visuals, enhancing the user experience. The precision in aspheric lenses ensures that users perceive virtual objects with minimal optical flaws, which is critical for maintaining realism and immersion in VR and AR environments.
Sapphire windows and plates are optical components that can be utilised in a wide range of applications. Their ability to transmit light with a specific wavelength at the same time as protecting the rest of the system from the impact of the environment makes them particularly useful. Sapphire windows and plates used for optical products can be supplied in several ways including, ‘C’ cut, random orientation, and AR coated – we review the key differences and benefits between them.
Selecting the right lens type for your imaging application involves a thorough understanding of the specific requirements and constraints of your project. Spherical lenses offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for less demanding applications, while aspheric lenses provide superior optical performance for high-precision tasks. By considering factors such as clarity, field of view, compactness, cost, and supplier capabilities, you can make an informed decision that meets your needs. Innovations in lens technology continue to expand the possibilities, making it an exciting time for developments in optical systems.
Here at UQG we provide sapphire windows and plates in a range of standard shapes and sizes as well as manufacturing custom solutions when required. In some cases, the sapphire windows or sapphire plates might have additional coatings applied to deliver necessary effects, such as reducing reflection or protecting the component from light at the infra-red or ultra-violet ends of the spectrum.
To find out more about Sapphire Windows and Plates from UQG Optics, or any of our other optical products call us on 01223 420329 or email our sales team at info@uqgoptics.com
Sapphire windows have exceptional surface hardness, acid, alkali, and other chemical endurance and scratch resistance, and they are frequently employed in the UV, visible, and near infrared bandwidth ranges.
Aspherical lenses work by controlling the direction that light rays pass through through a process known as refraction, similar to how spherical ones do, yet feature significant variations in surface curvature; their profiles tend to be more complex than spherical ones which typically feature uniform curvatures; as such they’re better at correcting aberrations (especially spherical) more effectively due to non-uniform surface curvatures; as such they focus light more precisely onto one focal point; correct aberrations while correct aberrations more effectively due to non-uniform surface curvatures as opposed to uniform curvatures featured by their counterparts spherical counterparts which feature uniform curvatures; they also focus light more efficiently onto one point when focused onto one point than traditional counterparts would allow.
Selecting the right lens for your imaging application is important to achieving optimal performance. Lenses come in various shapes and forms, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Understanding the differences between spherical and aspheric lenses can help you make an informed decision that meets your specific needs. In this blog, you will learn more about the intricacies of both lenses, including their design, how they work, their applications, and the main considerations in choosing the right lens for an optical system.
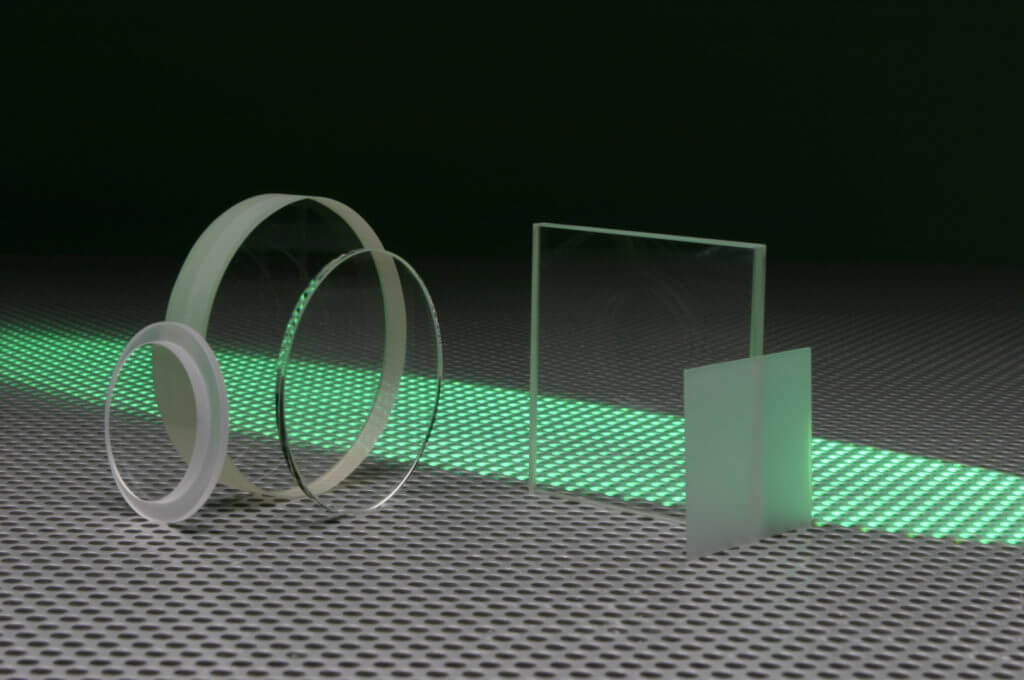
This is one of the things that makes sapphire windows and plates of this kind particularly useful within camera systems, optical equipment, and medical components.
Sapphire windows and plates that are optically AR coated on one or both sides maximise the transmission of light. Sapphire windows and sapphire plates that have been treated in this manner are extremely transparent in a range running from UV visible to mid IR.
Consider all requirements of your application when choosing lenses, including image quality, field of view requirements, compactness of lens design and cost. Aspheric lenses tend to perform better for applications involving aberrations; spherical ones might suffice if less demanding or cost-conscious applications exist.
Welcome to UQG Optics! It looks like you are visiting from outside the UK. Select your preferred currency below to see appropriate pricing. Contact us for additional support or to discuss specific requirements.
Standard AR coatings of this kind include UV 250nm-400nm, visible range 400nm-700nm and IR 700nm-1100nm, and 3-5 microns. AR coatings can also be applied to apply to a single specified wavelength and coatings of this kind – on one or both sides of a sapphire window or plate – are often utilised in imaging applications, cameras and lasers.
The strength of sapphire is also an advantage because it enables sapphire windows to be manufactured to extremely tight tolerances and thicknesses, therefore meeting the requirements of high-precision optical components across a wide range of different industries.
“C”-cut sapphire windows have the added benefit of reducing any birefringence that may exist in sapphire windows cut to a random axis. Birefringence refers to the fact that a ray of light passing through an optical plate or window splits into two rays, and while it is only a slight effect in sapphire windows cut to a random orientation it is reduced further in ‘C’ cut sapphire windows.
Edmund window
The durability, precision, and strength of sapphire windows and plates make them the solution of choice across a range of sectors and industries, including the following:
Aspherical and spherical optical lenses differ both in terms of shape and light handling capabilities, creating different advantages and disadvantages depending on which application the lens will be used in. Here is a detailed comparison.
Additionally, they offer great transmission, high strength, and temperature resistance properties. Due to this, they are frequently used in optical instrumentation and equipment deployed in tough environmental situations where excessive temperatures, pressures, moisture, chemicals, or other factors must not impair optical performance because to their thermal stability features.
A sphere-shaped lens features an even curvature across its entire surface and is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, aspherics being more so. However, Spherical lenses may suffer from an effect called Spherical Aberration which causes light rays passing through their edges not focusing correctly in comparison with those passing through its center; images produced can appear blurry due to this phenomenon using wider apertures or high magnification magnification levels.
Here at UQG we offer sapphire windows and plates which are AR coated on one or both sides, cut to a random orientation, or cut to ‘C’ axis.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500