Optical Prisms - prism in optics
P polarized lightapp
On an atomic scale, atoms emit light like a phased array of individual antennas. Then interference happens, and you get all the behavior of Snell’s Law, Fresnel Equations, etc.
Aug 24, 2015 — Displayed on the left, a lens with a refractive index of 1.6.It could be made from a higher index of refraction glass or plastic, such as ...
Linearlypolarized light
In photography and videography, the field of view is the angular extent of the observable scene that a lens or a camera can capture. It's often expressed in degrees or radians. A wider field of view means that more of the set is visible, useful for capturing landscapes or large groups of people. A narrower field of view is often used for telephoto shots or when photographers or video directors want to focus on a more minor subject.
The depth of field refers to the range of distances within a scene that appears acceptably sharp in an image. It is about the zone of focus where objects near and far from the camera are rendered in sharp detail. In simple terms, DoF is all about what is in focus within the image. DoF is not measured in degrees but is typically quantified regarding near and far distances from the camera (e.g., feet or meters).
Furthermore, some security cameras are designed with a wide-angle lens and have a broader FOV suitable for monitoring large areas, like parking lots or open spaces. Others have narrower lenses that are ideal for focusing on specific targets or areas in greater detail.
The camera orientation can also influence the field of view. When you change the camera's direction from landscape (horizontal) to portrait (vertical) or vice versa, it alters the FOV and the image's composition. In landscape orientation, the FOV is typically broader and suitable for capturing wide scenes. In portrait orientation, the FOV is narrower, which can help focus on a taller subject or emphasize vertical elements in the frame.
The field of view (FOV) refers to the extent of the observable world or scene that can be seen at a given moment through a particular device, such as a camera, microscope, binoculars, or the human eye. It defines the area or angle visible within the observation frame. In the case of optical devices, FoV is the maximum area that the device can capture. The broader the FOV, the more people can see, whether they're looking through a camera lens or at a screen.
The main difference between the field of view and depth of view is that the field of view is about the extent of what is seen, while DoV is about the range of distances at which objects appear in focus within that scene.
Edmund Scientific Corporation, based in Barrington, New Jersey, was founded in 1942 as a retailer of surplus optical parts like lenses.
If you've chosen a particular field of view, you can place the device strategically to optimize its effectiveness. Here are some placement tips you can follow.
As you may noticed the direction of z is default by the direction of propagation. But the x- any y-direction could have any orientation around z.
P polarized lightformula
by J Ye · 2024 · Cited by 12 — Conventionally, linear polarization is obtained by passing unpolarized light through a linear polarizer, which is typically constructed from ...
MAGNIFIER definition: 1. a device that makes objects, text, etc. look larger: 2. a device that makes objects, text, etc…. Learn more.
Several factors can affect the optical instrument's field of view. Depending on various factors, users can strategically choose the correct FOV for different applications.
The term "Field of View (FOV)" can be found in many optical devices and used in multiple scenarios. Here are some practical applications of this concept.
The field of view determines the area or angle that the camera can capture and monitor. The special FOV of security cameras can vary from one model to another. Some security cameras may have fixed lenses, which provide a constant FOV, while varifocal cameras can zoom in or out to change the FoV according to the user's needs.
Ellipticallypolarized light
For video games and virtual reality (VR) experience, the field of view is the extent of the in-game environment that can be seen on the screen. Some of these parameters can be adjusted to affect the perception of speed, realism, and the player's spatial awareness. A wider FOV can give a more immersive feeling but might require more computing power to render.
s-polarization vsppolarization
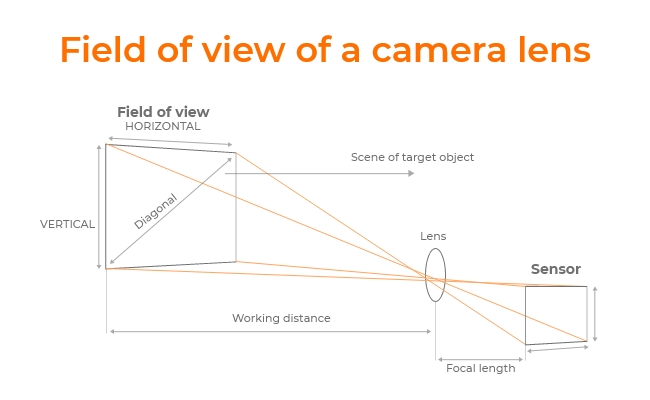
FOV: the field of view of an optical instrument in degrees. Sensor dimension: the size of the digital camera image sensor, typically measured in millimeters. Focal length: the distance from the lens to the point where parallel rays of light converge when they pass through the lens. 57.3: used to convert radians to degrees.
The distance to the subject can affect the perceived field of view (FOV), but it doesn't directly alter the physical FOV of the camera or lens. Instead, it influences the composition and perspective of the image. If you move closer to the subject, you may need to use a wider-angle lens to encompass the subject within the frame, making the FOV appear wider. Conversely, if you move farther from the subject, you might need to use a longer focal length lens (telephoto) to frame the subject as desired, making the FOV appear narrower.
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Lens aperture doesn't directly affect the field of view, but it will change the composition of different images. The lens aperture significantly affects the depth of field, which is the range of distances in the scene that appears acceptably sharp in the picture. A wider aperture (e.g., a lower f-number like f/1.8) will result in a shallower depth of field. This depth of field usually makes the background and foreground more out of focus. The image appears to have a narrower FOV, even though the FOV itself remains the same.
Light as part of the electromagnetic radiation consists of photons. These quanta have an oscillating electric field component and an oscillating magnetic field component, both perpendicular to the direction of propagation. In vacuum the electric and the magnetic field components are exact perpendicular to each over. To make it imaginable for you, take a Cartesian coordinate system, orient z to the direction of propagation. The directions x and y are the directions of the E-field and the B-field.
Now consider p-polarised light. The electric field is polarised in the plane of incidence and causes the dipoles to oscillate in the same plane. However, at a certain angle, the Brewster angle, the reflected light would need to be produced by electric dipoles oscillating along the line defined by the direction of the reflected ray. But no electric field is seen in this direction because it is the axis of oscillation for the dipoles. Thus no reflected p-polarised light is seen at the Brewster angle.
After reading this, do you understand the FOV meaning? Is it important? Let us know your thoughts in the comment section below, and share this article with your family and friends if you find it useful!
Astronomy enthusiasts and scientists often use telescopes or binoculars to observe the infinite sky. For astronomical devices, the field of view describes the area of the sky that can be observed through a telescope or binoculars. It is often measured in degrees, and a larger field of view allows for a broader view of celestial objects. A narrower field of view helps focus on specific astronomical objects.
Shining light perpendicular to a surface does not influence the random oriented E- and B-field. But shining light not-perpendicular, the surface influences the orientation of the lights field components. (BTW, the same happens with light in front of a polarizing foil or at the boundary of slits.)
In microscopy, the field of view refers to the area visible through the microscope's eyepiece or on a digital display. The field of view can vary depending on the objective lens used, with higher magnification objectives typically having a smaller field of view.
To turn off Magnifier, press the Windows logo key + Esc. If you prefer using a mouse, select Start > Settings > Accessibility > Magnifier, and then turn on the ...

The maximum human field of vision, also known as the human visual field, is approximately 200 degrees horizontally and about 135 degrees vertically. This field of vision can vary slightly from person to person due to factors like genetics and individual differences in eye anatomy.
Circularlypolarized light
Lenses with short focal lengths have more curved shapes and cause light rays to converge more quickly. As a result, they bring distant objects into focus and capture a wider area within the camera's FOV. In contrast, lenses with long focal lengths have flatter or less curved shapes and cause light rays to converge more slowly. As a result, long focal length lenses capture a narrower FOV.
It would help if you determined what you intend to capture with the camera. Different purposes may require distinct FOV. For example, if you are looking for a security camera, you need to map out the places you want to monitor and choose between a wide FOV (larger space) or a narrow FOV (rich details).
The term "field of view" can be found in different scenarios. This parameter has become a fundamental element for enhanced visual experience, from photography and videography to surveillance and immersive technologies. With the knowledge gained from this article, we truly hope you can harness the power of the field of view in the future!
The field of view of a security camera refers to the area or angle that the camera can capture and monitor. It is measured in degrees vertically and horizontally. The wider the field of view, the larger the area the camera can capture.
Planepolarized light
If the reflected light ray is either side of the Brewster angle, then the oscillating dipoles would be viewed at an angle (less then 90 degrees) to the oscillation direction. Thus there would be some electric field produced in that direction, but not as much as for the case of s-polarised light, where the dipole oscillation direction is always perpendicular to the reflected ray.
The sensor aspect ratio is the sensor's width-to-height ratio. The sensor aspect ratio can affect the field of view (FOV) and the composition of an image by determining how much of the scene is captured horizontally and vertically, especially when using lenses designed for a specific aspect ratio. A camera with a 3:2 or 16:9 aspect ratio captures a slightly wider FOV than a 4:3 aspect ratio.
The focal length of a camera lens can affect the field of view because it determines how light rays are refracted and focused onto the image sensor (or film plane) within the camera. When light rays pass through a lens, their paths are bent due to their curved shape. These rays can either converge or diverge. The extent to which they converge or diverge depends on the curvature of the lens.
I cannot understand the physics behind the reflection and polarization-reflection on an atomic scale. What exactly happens at the boundary of two surfaces? I was studying Brewster's law and thus this doubt came.
This small, yet effective angle bracket can support a static load up to 160 lbs. The ¼-inch holes act as hangers, allowing installers to make chain or wire ...
In the end, the amount of polarized light depends on the angle of light propagation to the surface. The surface influences the orientation of the E and B field at most for a certain Brewster angle.
The field of view of a camera or optical instrument depends on the focal length of the lens or eyepiece, the sensor size (for digital cameras), and the distance between the lens or eyepiece and the object of interest. Here is a simplified formula:
Oct 15, 2018 — Well suited for projects that include the need for a stable wavelength reference device as a stand alone component, or to be used in tandem with ...
s-polarised light causes these dipoles to oscillate perpendicular to the plane of incidence, in the same direction as the oscillating electric field of the incoming light.
Tilting the camera up or down (pitch) and panning it left or right (yaw) also affects the FOV. Tilted upward, the FOV may emphasize the sky or tall objects, while tilting downward highlights the ground or low objects.
Visual experiences play significant roles in daily life thanks to the rapid development of different digital devices. Whether through the lens of a camera, the eye of a microscope, or the immersive screens of our favorite video games, the concept of "Field of View (FoV)" dramatically impacts how people see the world. This article will help you understand the FOV meaning, its practical applications, and how it can significantly impact the performance and coverage of your security cameras.
P polarized lightmeaning
Editor from Reolink. Interested in new technology trends and willing to share tips about home security. Her goal is to make security cameras and smart home systems easy to understand for everyone.
4K 8MP UHD, Wide-Angle & Telephoto Lenses, Pan-Tilt-Zoom, Auto-Tracking, Person/Vehicle Detection, 2.4/5 GHz Dual-Band WiFi, Two-Way Audio.
The size of the image sensor directly affects how the camera captures and records the light coming through the lens, which in turn impacts the FOV. Large image sensors will allow more light to pass through than smaller sensors. Smaller sensors tend to result in a narrower FOV and can magnify the image, while larger sensors provide a wider FOV.
MTF Chart. MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) is one of the ... MTF Chart · Camera / Camera Lens · Camera / Camera Lens : Top · Lineup · Information ...
Selecting the appropriate field of view for security cameras is essential for an effective surveillance system. So why is the field of view so crucial for security camera selection? This part may give you the answer.
For example, the Reolink TrackMix series combines a telephoto and wide-angle lens to provide comprehensive coverage, allowing users to view close-up and wide-angle perspectives simultaneously. This series offers various models, including WiFi, PoE, 4G, and battery-powered options. The TrackMix WiFi supports dual-band 2.4/5GHz WiFi and integrates seamlessly with Reolink NVR systems.
The Midori™ fiber-optic LED light source series combines state-of-the-art, solid-state illumination technology with Ushio's distinctive optical design to create ...
The oscillating electric field produced by an oscillating electric dipole is maximised at right angles to the oscillation direction. i.e. in the plane of incidence for s-polarised light. It is zero along the axis of oscillation.
Microscope lenses, also known as objective lenses or microscope objectives, play a crucial role in magnifying specimens for observation. · Different types of ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500