Optical Engineering Services | Optical Design Engineers - optical engineering
Diffractivelens
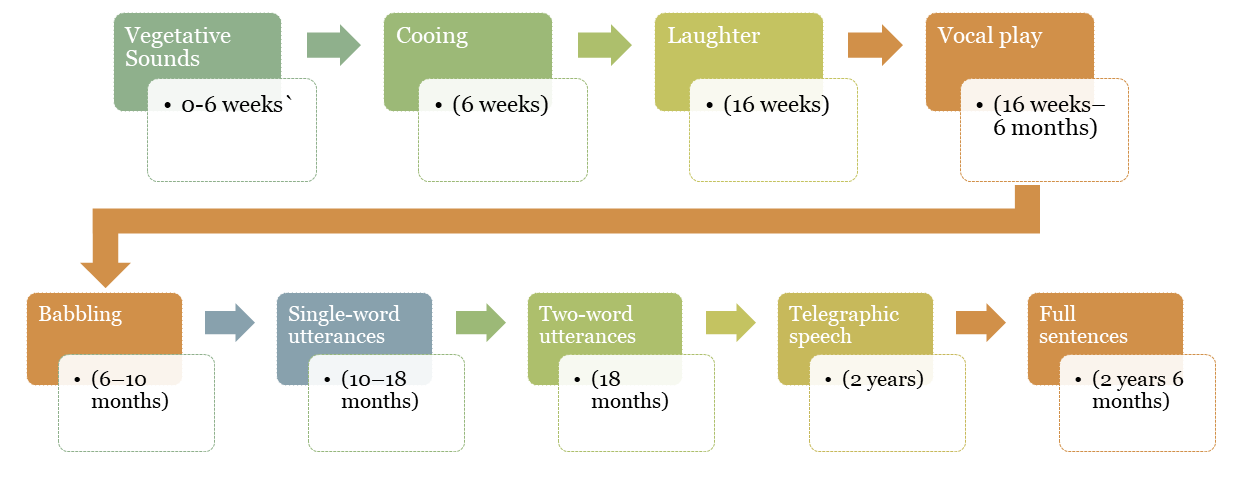
As seen in Figure 5.1, infants make vegetative sounds from birth. These include crying, sucking noises and burps. At around 6 weeks, we start getting cooing sounds followed by vocal play between 16 weeks and 6 months (Stark, 1986). This vocal play involves sounds that appear similar to speech but containing no meaning. Babbling is observed between 6 to 9 months. This is different from vocal play in that it contains true syllables (generally CV syllables as in ‘wa wa’ for ‘water’). Children produce single-word utterances around 10 to 11 months followed by an extraordinary expansion of vocabulary around 18 months. At the same time, we start to get two-word utterances. We also start to get telegraphic speech. These are utterances which lack grammatical elements (Brown & Bellugi, 1964). Grammatically complex utterances emerge around two and a half years.
IOL implantation after cataract extraction or as part of refractive lens exchange is a relatively safe procedure but carries the risks that come with invasive eye surgery. These surgical complications include, but are not limited to infection, increased IOP, corneal edema, posterior capsular rupture, vitreous loss, posterior capsule opacification (PCO), IOL decentration, and retinal detachment.
Diffractivemeaning
Chomsky demonstrated that children acquire linguistic rules or grammar without an inexhaustive sample of the acquired language. In other words, children cannot learn the rules of grammar by mere exposure to a language (Chomsky, 1965). For one thing, children hear an imperfect input. Adult speech is full of slips-of-the-tongue, false starts and errors. Sometimes there are contractions such as gonna and wanna and words are not necessarily separated in continuous speech. There is also a lack of examples of all the grammatical structures in a language for children to derive all linguistic rules from analysing the input. All of these phenomena are often labelled the “poverty of the stimulus” (Berwick, Pietroski, Yankama, & Chomsky, 2011). Poverty of the stimulus is often used as an argument for universal grammar. This is the claim that all languages have some underlying common structure within which all surface structures of language emerge.
Extended depth of focus (EDF) IOLs are a newer category of IOLs that aims to give an elongated focus of vision without compromising distance visual acuity[7]. The Symfony IOL (Johnson & Johnson Vision/AMO, ZXR00) is an example of an EDF lens that extends the depth of focus through a combination of effects from its echelette design, reduced chromatic aberration and negative spherical aberration. Intermediate vision is improved compared to standard bifocal multifocal IOLs, but near vision may only be modestly improved. Additionally, while patients may have better levels of contrast sensitivity and less ocular aberrations, they may experience a unique visual phenomenon typically described as "starbursts."[7][6] The Vivity IOL (Alcon) is a non-diffractive EDF IOL offers distance, intermediate and near vision.
The only accommodative IOL to be FDA-approved is the Crystalens IOL (Bausch and Lomb), a 4.5 mm optic (AO and HD variants have 5mm optic) with two haptic plates and four polyimide loops that help fix it into place within the capsular bag.[8] Its placement within the capsular bag allows it to simulate the natural accommodative process in the eye by changing power in response to ciliary muscle contraction.[8] The Crystalens accommodative IOL provides good distance vision and the advantage of fewer visual disturbances compared to multifocal IOLs.[8] As this lens is made of silicone, it should be avoided in patients with asteroid hyalosis, and patients who may require retinal surgery with silicone oil injection.
Accommodating IOLvsmultifocal IOL
May 31, 2024 — With multiple display splits, telescopic shaped display, uniform technology display screen high definition without distortion, super advertising ...
Sensor type: Sony IMX183 · ZWO · ZWO · ZWO · ZWO · ToupTek. Camera 183 CA Color. RRP: $ 999.00 ...
The other major side effect experienced by patients after IOL implantation are visual disturbances. Reduced visual quality and visual phenomena such as halos, glare, and starbursts are characteristic of multifocal IOLs due to the light scatter that naturally occurs when transitioning between near and far zones .[14] Patients with monofocal IOLs experienced less visual distortions and halos compared to patients with multifocal IOLs.[15]In a prospective study of 95 eyes comparing multifocal IOLs to monofocal IOLs, 29% of multifocal patients reported glare while 25% reported halos, compared to 19% and 12% in the monofocal group, respectively.[16]Accommodative IOLs as a whole produce less visual disturbances compared to multifocal IOLs. This can be explained by the design of the accommodative lens which contains a smooth central surface and acts to enhance near vision through movement in conjunction with ciliary muscle contraction. This is in contrast with multiple zones of optical power in a multifocal IOL that can result in scattering of light and visual disturbances. EDF lenses, while providing preserved visual quality with fewer halos, can still produce a relatively unique photic phenomenon generally described as starbursts.
Language development is perhaps one of the greatest mysteries in psycholinguistics. The rapidity of first language acquisition is astounding to anyone who has tried to learn a second language as an adult. This process can be broadly divided into stages based on the characteristics of the infants’ output. However, we must note that output doesn’t always assure us a clear picture of the cognitive processes that are going on within the infants’ minds.
Intraocular lenses produce high levels of satisfaction and freedom from spectacles. ReSTOR IOLs produced high levels of patient satisfaction, with 93.1% of patients reporting a positive change in vision, 88.2% reporting better postoperative vision, and 78% reporting resolution of their vision problems.[17]In addition, spectacle-free rate improved significantly from just 6.4% preoperatively to 87.2% after ReSTOR implantation.[17] Another prospective study using the ReSTOR IOL after bilateral refractive lens exchange, found that all patients reported satisfaction with their visual outcomes, but rated intermediate vision lowest.[18] A study comparing the Tecnis diffractive IOL to the ReZoom refractive IOL found higher levels of patient satisfaction and less visual disturbances in the Tecnis group, but less reported problems with intermediate vision in the ReZoom group, despite no differences in near or distance uncorrected vision between the two groups.[3]This may be explained by the nature of the two lenses, with diffractive lenses producing clear images at near and far with less-than-optimal intermediate vision, and refractive lenses improving vision at all distances. The Crystalens accommodative IOL produced good patient satisfaction with patients reporting adequate vision at all distances in order to complete activities of daily living, with the exception of needing reading glasses for fine newspaper print.[19]
Difference betweenrefractiveanddiffractivemultifocal IOL
Apr 28, 2022 — Still have questions? magnify glass. Find more answers. Ask your question. imp.
DiffractiveIOL
Skinner (1957) argued that language acquisition happens through the same mechanisms of operant conditioning that operated on other human and animal behaviour. However, adults generally do not encourage children to speak like them. On the contrary, adults often imitate the childish speech of children when speaking to them. If any correction is made, it is regarding the accuracy of the statements rather than their syntax.
Refractive IOLs such as ReZoom (AMO) and Array (AMO) function by creating multiple focal points that allow for viewing at all distances.[3]The Array zonal progressive silicone IOL consists of five concentric zones alternating between distance- and near- dominant.[2] The ReZoom IOL is a second-generation refractive IOL, that enhanced some aspects of the Array design, such as enlargement of the second and third zones, reduction of the fourth and fifth zones and an aspheric transition between zones so that visual disturbances could be reduced.[1]While refractive IOLs produce good quality distance, intermediate, and near vision, they are limited by pupillary diameter because of the zonal design of the lens.[4]
Patients with diffractive and refractive multifocal lenses have better near vision than those with accommodating lenses and monofocal lenses.[9] In a prospective randomized study comparing Crystalens, ReSTOR, and Tecnis IOLs, the ReSTOR demonstrated better UNVA compared with Crystalens and Tecnis, with the Crystalens accommodating IOL demonstrating better intermediate and low-contrast distance-corrected vision compared to ReSTOR and Tecnis.[10],[11] However, there was no difference in uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA) between the three groups.[10]A meta-analysis of 20 clinical trials looking at 11 monofocal and 35 multifocal IOLs, also found that patients with the ReSTOR IOL had significantly better UNVA than all other multifocal IOLs.[12]
Focal length determines angle of view and magnification. When light enters a lens, glass elements within the lens serve to converge the light to a single point, ...
Trifocal IOLs are popular presbyopia-correcting IOLs in many areas outside of the United States, and have recently become available in the US with the introduction of the Alcon PanOptix Trifocal IOL. Compared to the bifocal diffractive IOL, the trifocal IOL improves intermediate vision by providing a third focus. The higher order aberrations and visual quality have been shown in many studies to be similar to that of bifocal diffractive intraocular lenses; however, in bench testing, they are associated with increased halos and reduced distance visual quality when compared to bifocal diffractive IOLs.[5][6]
The images provided by optical coherence tomography are used to diagnose retinal conditions such as macularholes, macular edema, wet age-related macular ...
Diffractive vs refractiveIOL
InfraRed is an international infrastructure investment manager investing in assets that are critical to the functioning of societies.
Another observation that learning theories cannot predict is the pattern of acquisition of irregular verb and noun forms. Saying *gived instead of gave or *gooses instead of geese are some examples of this. Children generally show a pattern of correct imitation of the stem but then incorrect production. These incorrect productions are usually because of over-regularization of the past tense or plural forms of the stems. Finally, children produce the correct forms. This is an example of U-shaped development: performance starting off well, then deteriorating before improving. In essence, language acquisition appears to be based on learning rules rather than learning associations.
Refractivemultifocal IOL
5.1 Language Development Copyright © 2021 by Dinesh Ramoo is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Chomsky (1965) argued for the existence of a language acquisition device (LAD). This is hypothesized to be an innate structure separate from intellectual ability or cognition. If the poverty of the stimulus is true, then children need something in additional to language exposure to arrive at language competency. The language acquisition device was later replaced by the concept of universal grammar. According to this idea, the child has innate rules of inference that enable them to learn a language. This would be a set of parameters that constrain and guide language acquisition. As languages vary in terms of their grammar, syntax and morphology, Chomsky hypothesized that language learning was essentially setting parameters using input from exposure to a language that in turn set other parameters automatically. In other words, languages cannot vary in any way possible with infinite variety. There are basic parameters that influence each other.
Light of this type is termed non-polarized. In addition, there exist several states of elliptically polarized light that lie between linear and non-polarized ...
Diffractiveoptics
It is engineered with anti-reflective fully multi-coated optical surfaces to ensure bright and clear high-contrast images with true color transmission across ...
Multifocal IOLs consist of multiple zones of lens power that produce more than one focal point, allowing for enhanced vision at both near and far.[2] The multifocal IOLs can be further subdivided into diffractive and refractive lenses.
The simplest form of language acquisition would be simple imitation of adult language. While children do imitate adult behaviour to some extent, this alone cannot account for language development. The sentences produced by children acquiring language do not show imitation of adults. Children often make errors that adults don’t make. However, imitation may play a role in the acquisition of accents, speech mannerisms and specialized vocabulary.
Intraocular lens implants (IOLs) are used in both refractive lens exchange and cataract surgery to replace the natural lens of the eyes and correct for refractive errors. Over recent years, many improvements in intraocular lenses have allowed for the development of a wide-spectrum of lenses beyond the traditional monofocal lens implants. These developments include presbyopia-correcting IOLs which provide a treatment option for presbyopic patients who do not qualify for laser refractive surgery and do not want to rely on reading glasses.[1] Presbyopia-correcting lenses can be divided into three broad categories: multifocal IOLs, extended depth of focus IOLs, and accommodative IOLs.
Some universals may be an innate part of grammar. For example, there is not obvious rationale for having all SVO languages putting question words at the beginning of their sentences. It is also possible that the external environment in which we evolved may play a role in the development of universals. Languages often note a difference between animate and inanimate object of sentient and non-sentient beings. However, there is some criticism about the idea that true universals, common to all languages, might exist.
When multifocal IOLs are compared to other treatment modalities such as laser in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK) monovision, they demonstrate significantly better UNVA.[13] LASIK monovision, however, produces better uncorrected intermediate visual acuity (UIVA) and UDVA than multifocal IOLs as well as less visual disturbances.[13]
The polarising effect of your filter is at its greatest when you shoot at a 90-degree angle to the sun, so it is perfect to use for compositions with side- ...
Polymer optical fibers (POF) have a number of advantages over glass fibers, such as low cost, flexibility, low weight, electromagnetic immunity, good bandwidth, ...
We can look at some examples of parameter setting across language. For example, if a language has subject-verb-object (SVO) word order, then question words (what, where, who, how) would come at the beginning of the sentence while a language that is subject-object-verb (SOV) would put them at the end.
Research methods that we can employ with adults is not always possible with infants. One technique is the sucking habituation paradigm. This paradigm measures the rate of sucking an artificial pacifier as a measure of interest by the infant in a novel stimulus. It has been observed that babies prefer novel stimuli as opposed to stimuli that are familiar. If they are presented with habituated (or familiar) stimuli and then a novel stimulus pops up, the rate of sucking increases. This can be used to see whether an infant can detect the difference between who stimuli. Another technique is the preferential looking technique. Here children look longer at scene that are consistent with what they are hearing. Using such techniques (and others), psycholinguists try to determine at what age children understand the difference between phonemes, morphemes and understand syntax.
Despite the high level of patient satisfaction with IOLs, studies have demonstrated that patients are no more satisfied with IOLs than with other correction strategies. In a meta-analysis of 20 clinical trials comparing multifocal and monofocal lenses, patients with multifocal IOLs were 3.6 times less likely to require spectacles compared to patients with monofocal IOLs.[12] However, there was no difference in patient satisfaction between patients in the monofocal and multifocal groups.[12],[15] A prospective study comparing refractive lens exchange with multifocal IOL implantation to LASIK-induced monovision, found no significant difference in patient satisfaction or spectacle dependency between the two groups.[13] Although the new generation multifocal IOLs are an effective means of presbyopic correction, patients seem to be no more satisfied with them than other corrective modalities.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500