Olympus Microscope Objective Lenses - objective lenses on a microscope
f-thetalens1064nm f=160mm
Imagine a scene with a square grid. In barrel distortion, the grid would bulge outwards, making the squares appear wider on the edges. Meanwhile, in pincushion distortion, the grid would sink inwards, making the squares appear narrower on the edges. Mustache distortion would cause the grid lines to become wavy.
Diagonal Field of View (FOV) at a Specific Image Distance: Values provided at different image distances (e.g., 124° @ 10mm)
F-thetalensvs telecentric
In this blog, we break down distortion parameters in lens datasheets and the three ways in which distortion is represented.
F-Tan (Theta) method uses the tan(theta) relationship to calculate a reference height based on magnification, and the F(Theta) method uses F*theta (radians) to represent the ideal image point location based on its angular position.
f-thetalenswikipedia
TV Distortion, as the name suggests, originated in the context of television applications. It can be calculated using the following formula:
telecentric f-thetalens
Optical distortion represents the overall distortion parameter of the optical system. F-Tan theta or optical distortion can be calculated using the following formula.
F(Theta) method focuses on the angular relationship between the ideal undistorted image point and the actual distorted image point without needing magnification information.
A negative value indicates barrel distortion (objects appear smaller towards the edges). In the above example, the calculation shows a higher barrel distortion (-39.5%) at a larger image distance (10mm). As the image distance decreases (9mm and 5mm), the distortion percentages become less negative, indicating a decrease in the barrel effect.
F-ThetaLensfocal length
© 1995-2024 Healthwise, Incorporated. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
The F-Tan (Theta) method uses the tangent function to relate the angle to object size and magnification. Whereas the F(Theta) method focuses on the angular position of the image point relative to the centre. Both the methods require the focal length (F) and the diagonal FOV (degrees). But in the F(Theta) method the FOV in degrees is converted to radians.
We also provide various customization services, including camera enclosures, resolution, frame rate, and sensors of your choice, to ensure our cameras fit perfectly into your embedded vision applications.
f-thetalensdesign
F-ThetaLensPrice
F*tan(theta) calculations are used in camera calibration processes, where distortion parameters are estimated for correcting captured images. Lens designers often utilize F*tan(theta) calculations during the design phase to predict and minimize distortion in the final lens. This helps create lenses with minimal image curvature and ensures accurate image reproduction.
F-Theta lenses are specifically designed to maintain a constant image size (or spot size for lasers) across a scan field. The F-Theta calculation helps ensure the accuracy of this constant size by measuring deviations from the ideal. These lenses are used in various applications like laser marking and engraving, laser cutting, 3D printing and LiDAR.
Both methods can be used to estimate distortion, but they can be more applicable in certain situations. F-Tan (Theta) is preferred when the focus is on object size and magnification changes due to distortion. And the F(Theta) method is used to get the angular relationship of distorted image points without needing magnification information.
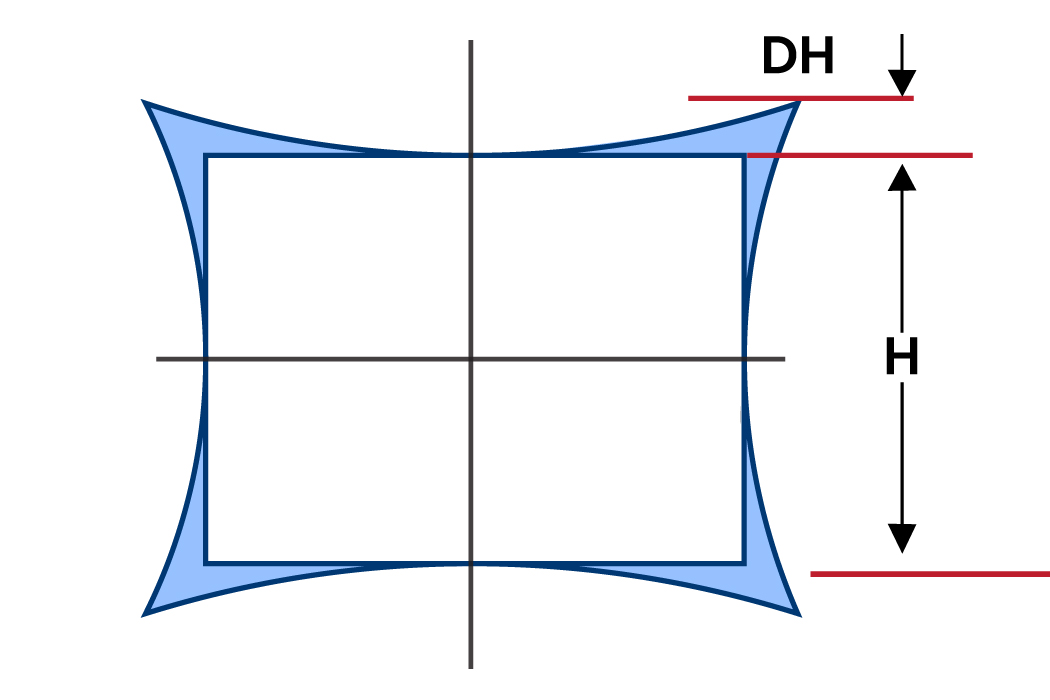
The formula calculates the difference between the expected height of an object based on the sensor size and its actual distorted height based on the distortion values and field of view. This difference is then expressed as a percentage of the vertical sensor size to provide a measure of barrel distortion.
F-thetalensdistortion
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
Contrast material, or contrast dye, is a substance used to make specific organs, blood vessels, or types of tissue (such as tumours) more visible on X-rays. Contrast material may also be used during a CT scan, an ultrasound, or an MRI scan.
Prabu is the Chief Technology Officer and Head of Camera Products at e-con Systems, and comes with a rich experience of more than 15 years in the embedded vision space. He brings to the table a deep knowledge in USB cameras, embedded vision cameras, vision algorithms and FPGAs. He has built 50+ camera solutions spanning various domains such as medical, industrial, agriculture, retail, biometrics, and more. He also comes with expertise in device driver development and BSP development. Currently, Prabu’s focus is to build smart camera solutions that power new age AI based applications.
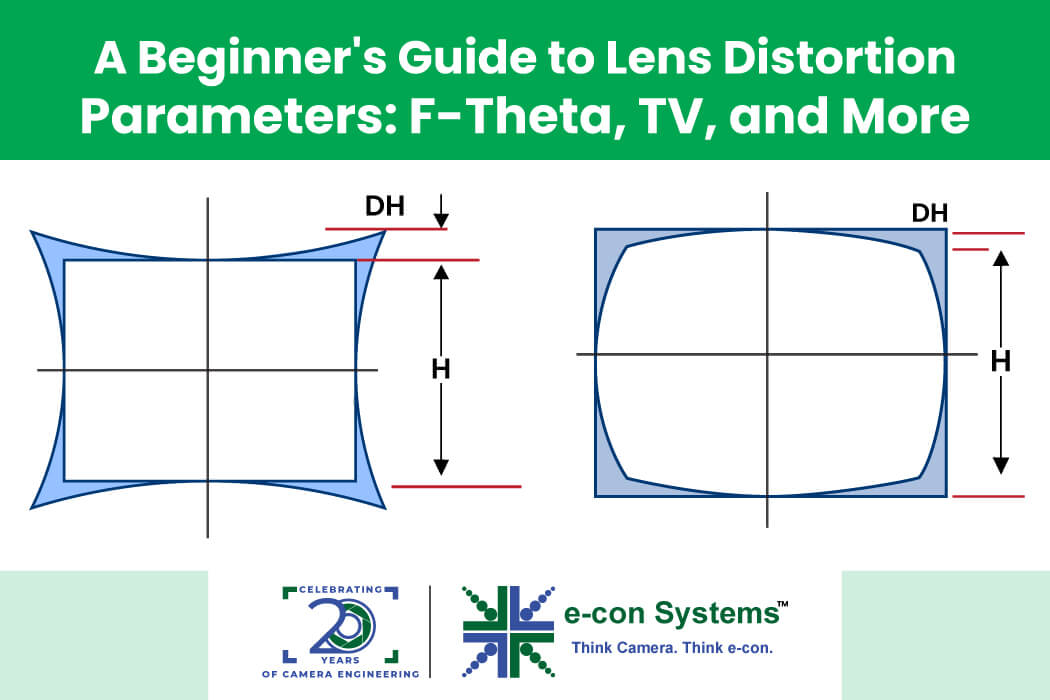
Mathematically, distortion can be represented in three different ways in the lens datasheet; let us look at each of them in detail.
Clinical Review BoardAll Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
Lens datasheets often include distortion information to help photographers and engineers understand how the lens behaves. Lens distortion refers to the phenomenon where straight lines in a scene appear curved in the final image. This happens because lenses don’t perfectly focus light from all parts of the field of view.
The F*tan(theta) method is a more general approach to calculating distortion. It’s often used for initial distortion assessment in various lenses, including photographic lenses. This method helps understand how straight lines deviate from their ideal positions due to distortion.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500