OCT System dOCTor™ for Optical Coherence Tomography - oct system
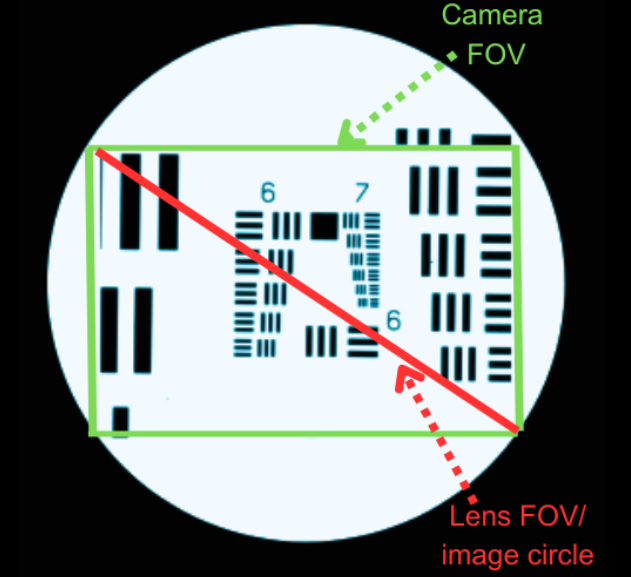
The camera lens captures the extent of the observable area in a single shot, known as the Field of View (FOV). This encompasses what one can see through the eyes or an optical device. In photography, the FOV determines “what we are seeing in our image” and “how much of the scene we are seeing.” As light passes through the camera lens, it focuses on the subject being imaged by converging the light. Shorter focal lengths intensify the convergence of light to focus on the subject being imaged.
Objective microscope definitionand function
Numerical Aperture: A dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light, influencing the resolving power of an objective lens.
VIETNAM:Alpha Industrial Park, Tu ThonVillage, Yen My District, HungYen Province 17721+84 221-730-8668sales-vn@avantierinc.com
Stagemicroscope definition
An objective lens is a crucial component of a microscope that gathers light from the specimen and focuses it to create a magnified image. The quality and type of objective lens used can significantly affect the clarity, resolution, and overall detail of the observed specimen. Objective lenses come in various magnifications, typically ranging from low to high power, allowing for different levels of detail when examining cellular structures.

Objective microscopefunction
Conversely, shorter focal lengths focus the image by converging the light more intensely. The determination of the focal length distance depends on how strongly the lens converges the light to focus the subject being imaged. This, in turn, affects the angle from the horizontal of the light captured by the lens. Referred to as the angular field of view (AFOV), it is necessary for determining the overall FOV. The FOV is expressed in either angular or size terms, with the former indicating the full angle in degrees and the latter denoting the length in millimeters or meters.

The lens focal length and sensor size influence the FOV, necessitating a wider FOV for a larger sensor if the lens focal length remains fixed. Typically measured horizontally due to the rectangular shape of sensors, FOV is usually expressed in millimeters. Optical tests commonly determine the FOV of UV, visible, and infrared cameras. These tests involve focusing light from a black body (an object that absorbs all light that falls on it) onto a test target at the focal place. A set of mirrors creates a virtual image at an infinitely far distance during the test.
Resolution: The ability of a microscope to distinguish two close points as separate, which is essential for observing fine details.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500