Maule MX-7 - mx-7
OCT is not the same as a computed tomography (CT) scan. OCT uses light rays to create images, and CT scans use X-ray beams.
PVD can cause a person to develop vitreous traction. This is a condition that occurs when part of the vitreous remains stuck to the macula during PVD. This part of the vitreous then pulls on the macula, causing symptoms of vitreous traction.
OCT eye test procedure
Measuring the thickness of the different layers of a person’s retina can help an ophthalmologist diagnose a number of medical conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and glaucoma.
By allowing an ophthalmologist to do all the above, OCT can help them diagnose certain eye disorders and guide specific treatments.
Abnormal OCT eye test
OCT can help an ophthalmologist see the different layers of the retina. This helps them map and measure the thickness of these layers.
During the scan, a person may focus on a target within the scanner. They may also see a red line appear during the scan.
A medical professional can use OCT to help diagnose AMD. It can be suitable for helping diagnose both early and advanced-stage AMD.
OCT can also help medical professionals diagnose optic nerve disorders. This is because an ophthalmologist can use OCT to spot changes to the fibers of the optic nerve.
In some cases, an ophthalmologist may administer dilating eye drops before the procedure. This is to help widen the pupil to make imaging easier.
OCT eye test results
They must then remain still and follow the instructions of the person carrying out the procedure. These instructions will direct the person to look in certain directions throughout the scan.
Central serous retinopathy is a condition that occurs when fluid builds up under the retina. Medical professionals may also refer to this condition as central serous chorioretinopathy.
What can an OCT scan detect
OCT can help an ophthalmologist diagnose a number of medical conditions including problems with the macula, AMD, glaucoma, and different types of retinopathy.
If a person has received dilating eye drops during OCT, their eye may be sensitive to light for several hours after the procedure.
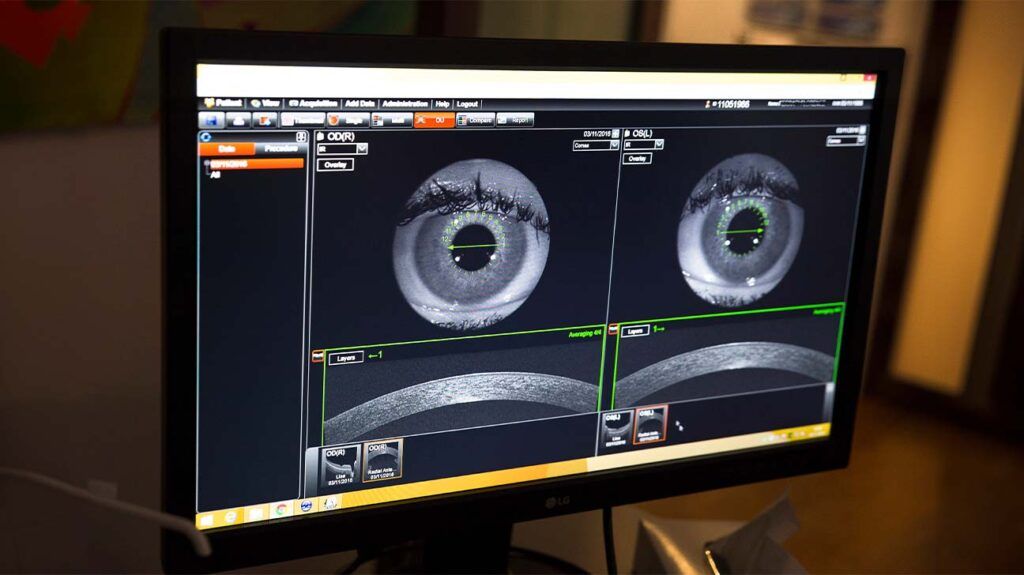
The OCT device then uses these measurements to create images of a person’s retina that are cross-sectional and three-dimensional.
OCT eye test side effects
Without treatment, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness. OCT can help a medical professional diagnose diabetic retinopathy.
Researchers say the drug aflibercept performed better in a clinical trial than bevacizumab in helping wean people off treatments for wet age-related…
Read on to learn more about how OCT works. This article also explains the conditions that OCT can help with and what happens during the procedure.
OCT eye test price
During a CT scan, a medical professional aims the X-rays at a part of the person’s body and quickly rotates them around the body. The CT scanner processes the signals that these X-rays produce. The CT scanner then creates cross-sectional images.
A person may not experience any symptoms if they have early stage glaucoma. Over time, a person may slowly experience vision loss.
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve. Glaucoma can lead to a person experiencing vision loss and blindness.
During OCT, an ophthalmologist uses a beam of light to scan an area of a person’s eye. The OCT device then measures the light that the structures within the eye have reflected back.
An ophthalmologist may use OCT to help confirm a diagnosis if a person is displaying symptoms of certain eye conditions. Below are the symptoms that may lead an ophthalmologist to use OCT.
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that causes damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Learn about its causes, symptoms, and…
Opticalcoherence tomographymachine
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a type of noninvasive imaging test. Ophthalmologists use OCT to create high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the inside of a person’s eye.
Opticalcoherence tomographyangiography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a form of noninvasive imaging test that creates high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the inside of a person’s eye.
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy usually does not cause symptoms. Some people may notice changes in their vision, such as problems seeing things that are far away.
The macula is a small area in the center of the retina. It plays a role in helping people clearly see the details of objects.
Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage the retina. This occurs when diabetes damages the blood vessels that supply the retina with blood.
There is no research to prove that exercises can help with drooping eyelids. Learn more about this here and find out about other treatment options.
Vitreous is the substance that fills the middle of the eye. Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) occurs when the vitreous pulls away from the retina.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500