Manual Linear Stage - linear positioning stage
Whatis the magnification of the ocular lens

Frustratingly for optical experts and linguistic pedants alike, the discussion about “anti-glare glasses” and “anti-glare lenses” is very often littered with misused language.
The most noticeable benefit of anti-reflective coatings is the improved appearance of the lenses. Without reflections, the wearer’s eyes are more visible, making conversation and eye contact in general easier.
Reviewed & updated 06/16/2017. Creation of this web page was originally supported as part of the Southwest Environmental Health Sciences Center at the University of Arizona, NIEHS P30 ES006694.
Contrary to what you may think, an anti-reflective coating can actually make your glasses easier to clean and care for. Most AR coatings have a hydrophobic finish, which repels water and dirt, so the lenses don’t smudge so easily.
Whatdoes the stagedo on a microscope
The halos that form around bright lights are also removed from your view with an anti-reflective coating, making driving at night more comfortable. With a greater amount of light reaching your eyes, an AR coating also improves visual acuity.
Different coatings can add impact resistance, hydrophobic qualities, UV protection to your glasses, shield your eyes from blue light, and help with glare.
An anti-reflective coating is particularly useful on high-index lenses, as these can reflect up to 50% more light than other lenses. This makes an anti-reflective coating indispensable.
AR coatings are made of layers of metal oxides. Simply put, an anti-reflective coating cancels out the light reflection on the surface of the lenses and allows more light to pass through them and reach your eyes.
However, a pair of prescription polarised sunglasses is a very effective solution, although naturally not the most useful for night-time activities.
The main purpose of an anti-reflective (AR) coating is to prevent reflections on the outer surface of glasses lenses by allowing more light to pass through them.
Types ofobjective lenses
Some retailers talk about anti-glare coating for glasses, but in reality, this does not exist. It might sound like they’re the same thing, but anti-reflective coating is the correct term for this treatment.
This greatly reduces glare for the wearer, and provides much sharper vision contrast. The chemical used in the polarisation process results in heavily tinted lenses, which makes it unsuitable for eyeglasses.
Numerical Aperture (NA) is “… a critical value that indicates the light acceptance angle, which in turn determines the light gathering power, the resolving power, and depth of field of the objective.”(1) As light passes through a sample, the information describing the highest resolution information in the sample is diffracted at a very wide angle. Low magnification lenses typically have low NAs, meaning that they cannot capture the highest resolution information. To capture the widely diffracted information, high NA lenses move the front of the lens closer to the sample (increases the light acceptance angle). Dry lenses can only have NAs of up to 1.0. By using specially formulated oil and oil lenses, NAs of up to 1.4 can be achieved.
Microscopeparts
Ask your optician to recommend which cleaning products can be safely used to clean your anti-reflective glasses. The harsh chemicals in some products can damage the coating.
These pesky reflections are an aesthetic concern for some, as reflections on the front of their glasses hide their eyes from view, ruin photographs, and are also often noticeable during video calls.
Uncoated lenses allow about 92% of light to pass through them. An anti-reflective coating increases that to 99%, giving the wearer greater visual acuity.
A volunteer and collaborative effort to bring information about shared microscopy facilities to the University of Arizona and the community.
Speak to your optician for personalised recommendations on which solution is right for your specific needs, or you can ask our opticians for further advice.
Disclaimer: Anti-reflective coatings on glasses lenses can provide a more comfortable viewing experience, but do not eliminate 100% of glare.
Whatisobjectivelens inmicroscope
The “cost” of obtaining a higher NA is that the working distance (WD) of the lens becomes much shorter. Working distance is “… the distance between the objective front lens and the top of the cover glass when the specimen is in focus. In most instances, the working distance of an objective decreases as magnification increases.” (1) A smaller working distance can be a problem when you cannot see an object with a high magnification lens, even though you could see it with a low magnification lens. A 10x objective can have a WD of several millimeters (4-10mm, or 4000-10,000um). A well corrected, high NA 20x dry objective will have a WD of slightly less than 1mm (1000um). Most well corrected, high NA 40x and 60x oil objectives have working distances on the order of 0.1mm (100um).
Anti-reflective lens coatings also improve visual acuity, meaning your vision will be sharper, thanks to the extra light getting through to your eyes.
Light microscopes can, under the best conditions, resolve objects that are approximately equal to half the size of the wavelength used. In the real world this comes out to objects that are 250-300nm in size, if you are using a NA=1.4 objective lens (under optimal conditions). This means that you can make out two adjacent objects in this size range, assuming that you can see at least a 25% dip in intensity between them (Rayleigh criterion). Sample preparation is especially important when you want to resolve structures this small.
Whatare the 3objective lenses on a microscope
The more light that reaches your eyes, the more clearly you see. This is all achieved by a fairly complex scientific process called the optical interference model.
High magnification without high NA does not give the resolving power that most people expect from a research grade microscope. Using a high NA objective lens means that you are most likely sacrificing working distance (how deep into the sample that you can focus) for higher optical resolution. In most instances this is a very acceptable trade off.
When it comes to sunglasses, the dark lens tint generally negates the need for an AR coating on the outside of the lenses. It can still be applied on the inside of the lenses, however, for greater comfort when the sun is behind you.
It’s easy to avoid looking directly at a bright light source, but glare is harder to escape. Glare is defined as a strong, dazzling light.
Light is essential for vision, but too much light causes problems for our eyesight. We don’t tend to look directly at sources of light, as it can hurt our eyes and cause discomfort.
This is what they were designed for, but innovation and technological advancements mean that glasses can also improve your visual experience in other ways, such as blocking out blue light or reducing glare.
As is usually the case when it comes to eyewear choices, your own vision requirements and lifestyle will dictate what the best option for you is.
If you struggle with the headlights of oncoming traffic when driving at night, an AR coating would also help in that regard. If your goal is to have anti-glare glasses, then polarised sunglasses will do a great job of achieving that.
We respectfully acknowledge the University of Arizona is on the land and territories of Indigenous peoples. Today, Arizona is home to 22 federally recognized tribes, with Tucson being home to the O’odham and the Yaqui. Committed to diversity and inclusion, the University strives to build sustainable relationships with sovereign Native Nations and Indigenous communities through education offerings, partnerships, and community service.
While there are different methods of introducing anti-glare properties, it’s important to use the right names for them in order to avoid confusion.
The UArizona Microscopy Alliance is a volunteer and collaborative effort to bring information about shared microscopy facilities to the University of Arizona and the community.
High powerobjective microscopefunction
Surfaces like glass, water, snow, and certain metals are highly reflective, so we often experience glare from them, making it more difficult to view other objects close to where the glare is coming from.
As you’re undoubtedly well aware, the main function of glasses is to allow you to enjoy a clear, sharp field of vision, and therefore live your life in greater comfort.
Both polarised lenses and anti-reflective coating have their benefits, with one potentially more suited than the other to the types of settings you’ll most often find yourself in.
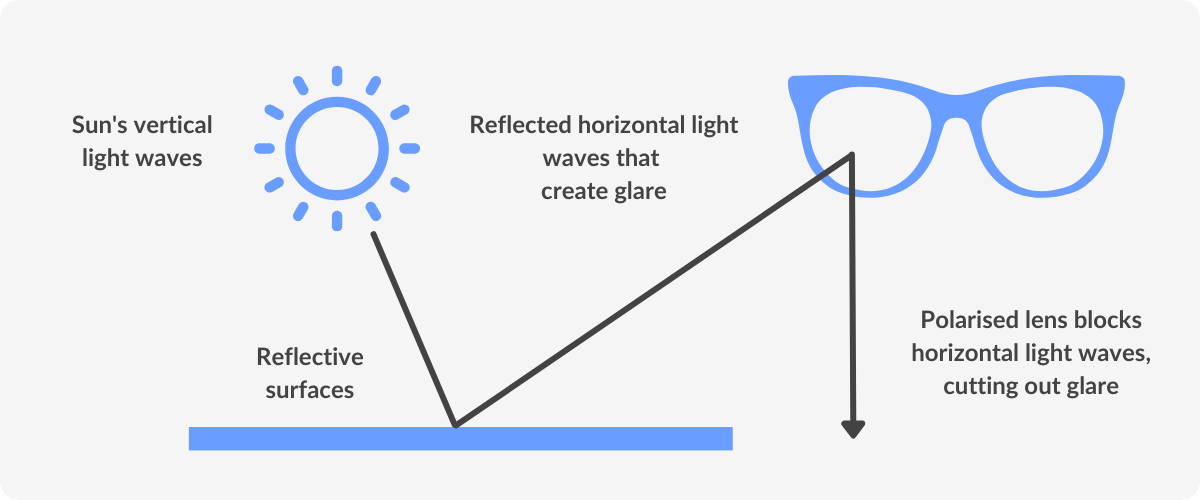
The most effective anti-glare glasses are those fitted with polarised lenses. Polarised lenses work by filtering out horizontal light waves, while allowing vertical light waves through.
The difference between polarised lenses and anti-reflective coating is that polarisation prevents you from seeing glare at the source, while an anti-reflective coating prevents you from seeing glare reflected on your lens surface.
Objectivelens function

Is an anti-reflective coating worth the investment? If improving the appearance of your glasses is a priority for you, then absolutely.
Basically, the layers of the anti-reflective coating work together to introduce “destructive” light waves, that, as their name suggests, destroy reflections on the lenses.
Despite this, usage of the term “anti-glare coating” persists. The lens technology that most accurately fits the description of “anti-glare glasses” would be polarization, although it is only available for sunglasses lenses.
For the wearer, the absence of reflections on their lenses is less distracting, especially in situations such as driving at night, working in a brightly lit environment, or in front of digital screens. Your eyes are put under less strain as a result.
Every anti-reflective coating gives the lenses it’s applied to a very subtle tint. This tint is most often either green, brown or yellow.
Many of us have looked though the eyepiece of a department store microscope and seen a fuzzy looking “something” with the highest magnification objective lens. It’s not completely surprising that an inexpensive lens would give a blurry image. There are many optical aberrations that need to be corrected to manufacture the expensive lenses that are used on research grade microscopes.
A secondary advantage of AR coatings is that they generally have a hydrophobic finish to seal all of their layers, making them water-repellent and easier to clean.
SmartBuyGlasses™ is a leading independent retailer of the world’s best designer eyewear since 2006 and is not owned by or affiliated with the brands it sells unless stated otherwise. All trademarks and brand names shown on our pages are the property of their respective companies which retain all rights.
Like with any glasses, always use a microfibre cloth to clean anti-reflective lenses instead of a t-shirt, tissue, or other type of material that could cause tiny abrasions.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500