Lithium fluoride, 98.5%, Thermo Scientific Chemicals - lithium and fluoride
This Open Source Physics animation helps you visualize the electric field vectors as light encounters a polarizing filter. You can rotate the filter—note that the angle displayed is in radians. You can also rotate the animation for 3D visualization.
Pastel-pink, round-eye frames with gorgeous polished gold metal interior and sides. The tips are a semi-translucent pink acetate-plastic.

GlowbackLED specializes in LED accessories such as LED light controllers from top manufacturers. We stock Nicolaudie, OMNI, DMXPRO Series ...
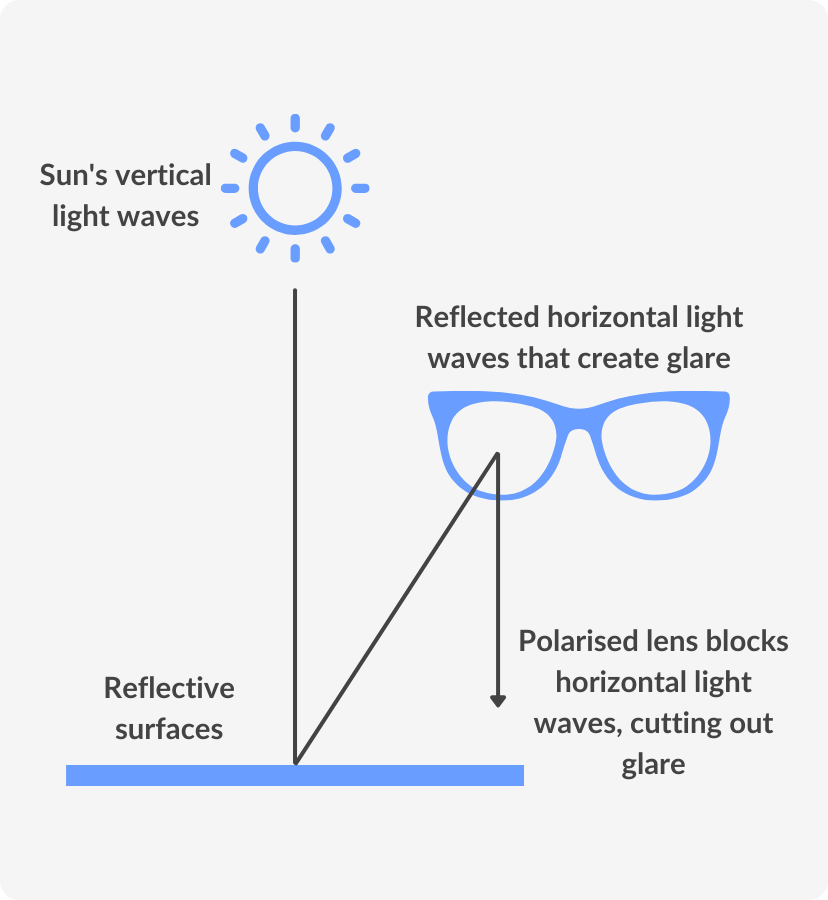
The most effective anti-glare glasses are those fitted with polarised lenses. Polarised lenses work by filtering out horizontal light waves, while allowing vertical light waves through.
A 5V power supply is a device that converts AC voltage to DC voltage with a voltage output of 5 volts. This type of power supply is commonly used in ...
Only the component of the EM wave parallel to the axis of a filter is passed. Let us call the angle between the direction of polarization and the axis of a filter θ. If the electric field has an amplitude E, then the transmitted part of the wave has an amplitude \(E\cos θ \) (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). Since the intensity of a wave is proportional to its amplitude squared, the intensity I of the transmitted wave is related to the incident wave by
Another interesting phenomenon associated with polarized light is the ability of some crystals to split an unpolarized beam of light into two polarized beams. This occurs because the crystal has one value for the index of refraction of polarized light but a different value for the index of refraction of light polarized in the perpendicular direction, so that each component has its own angle of refraction. Such crystals are said to be birefringent, and, when aligned properly, two perpendicularly polarized beams will emerge from the crystal (Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)). Birefringent crystals can be used to produce polarized beams from unpolarized light. Some birefringent materials preferentially absorb one of the polarizations. These materials are called dichroic and can produce polarization by this preferential absorption. This is fundamentally how polarizing filters and other polarizers work.
Polarizing filters have a polarization axis that acts as a slit. This slit passes EM waves (often visible light) that have an electric field parallel to the axis. This is accomplished with long molecules aligned perpendicular to the axis, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\).
Is an anti-reflective coating worth the investment? If improving the appearance of your glasses is a priority for you, then absolutely.
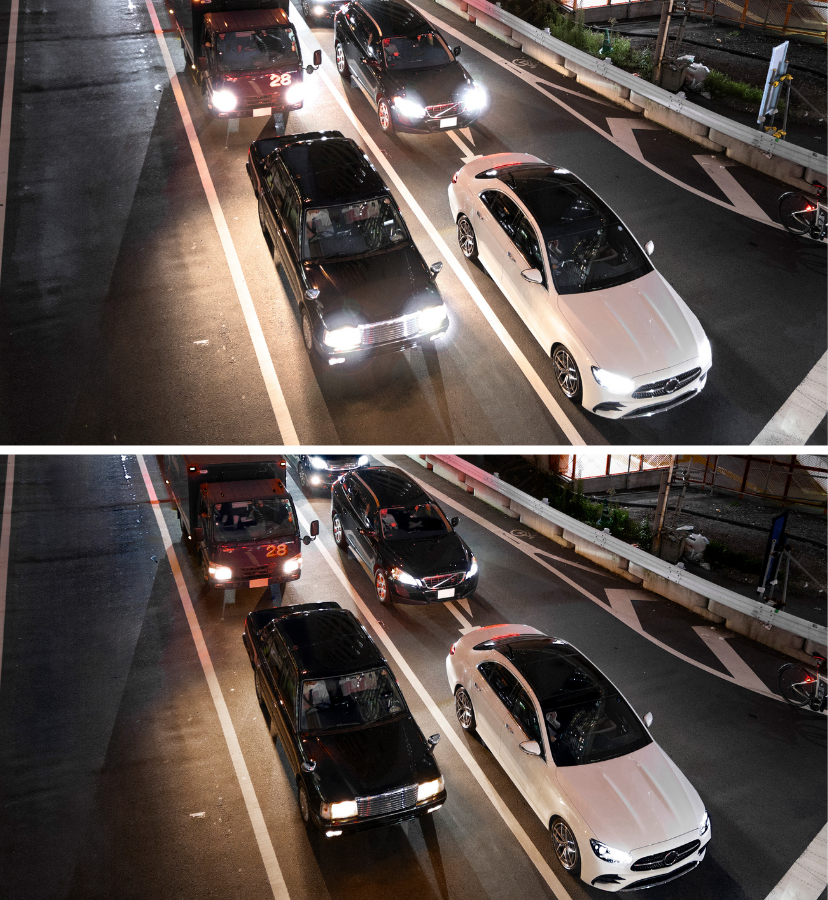
By now, you can probably guess that polarizing sunglasses cut the glare in reflected light, because that light is polarized. You can check this for yourself by holding polarizing sunglasses in front of you and rotating them while looking at light reflected from water or glass. As you rotate the sunglasses, you will notice the light gets bright and dim, but not completely black. This implies the reflected light is partially polarized and cannot be completely blocked by a polarizing filter.
Anti-reflective lens coatings also improve visual acuity, meaning your vision will be sharper, thanks to the extra light getting through to your eyes.
All we need to solve these problems are the indices of refraction. Air has n1=1.00, water has n2=1.333, and crown glass has n′2=1.520. The equation \(tan \, θ_b=\frac{n_2}{n_1}\) can be directly applied to find θb in each case.
As you’re undoubtedly well aware, the main function of glasses is to allow you to enjoy a clear, sharp field of vision, and therefore live your life in greater comfort.
If you struggle with the headlights of oncoming traffic when driving at night, an AR coating would also help in that regard. If your goal is to have anti-glare glasses, then polarised sunglasses will do a great job of achieving that.
Light is one type of electromagnetic (EM) wave. EM waves are transverse waves consisting of varying electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). However, in general, there are no specific directions for the oscillations of the electric and magnetic fields; they vibrate in any randomly oriented plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Polarization is the attribute that a wave’s oscillations do have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave. (This is not the same type of polarization as that discussed for the separation of charges.) Waves having such a direction are said to be polarized. For an EM wave, we define the direction of polarization to be the direction parallel to the electric field. Thus, we can think of the electric field arrows as showing the direction of polarization, as in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\).
Since the part of the light that is not reflected is refracted, the amount of polarization depends on the indices of refraction of the media involved. It can be shown that reflected light is completely polarized at an angle of reflection θb given by
When it comes to sunglasses, the dark lens tint generally negates the need for an AR coating on the outside of the lenses. It can still be applied on the inside of the lenses, however, for greater comfort when the sun is behind you.
The most noticeable benefit of anti-reflective coatings is the improved appearance of the lenses. Without reflections, the wearer’s eyes are more visible, making conversation and eye contact in general easier.
If you hold your polarizing sunglasses in front of you and rotate them while looking at blue sky, you will see the sky get bright and dim. This is a clear indication that light scattered by air is partially polarized. Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) helps illustrate how this happens. Since light is a transverse EM wave, it vibrates the electrons of air molecules perpendicular to the direction that it is traveling. The electrons then radiate like small antennae. Since they are oscillating perpendicular to the direction of the light ray, they produce EM radiation that is polarized perpendicular to the direction of the ray. When viewing the light along a line perpendicular to the original ray, as in the figure, there can be no polarization in the scattered light parallel to the original ray, because that would require the original ray to be a longitudinal wave. Along other directions, a component of the other polarization can be projected along the line of sight, and the scattered light is only partially polarized. Furthermore, multiple scattering can bring light to your eyes from other directions and can contain different polarizations.
polarization中文
Many crystals and solutions rotate the plane of polarization of light passing through them. Such substances are said to be optically active. Examples include sugar water, insulin, and collagen (Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\)). In addition to depending on the type of substance, the amount and direction of rotation depend on several other factors. Among these is the concentration of the substance, the distance the light travels through it, and the wavelength of light. Optical activity is due to the asymmetrical shape of molecules in the substance, such as being helical. Measurements of the rotation of polarized light passing through substances can thus be used to measure concentrations, a standard technique for sugars. It can also give information on the shapes of molecules, such as proteins, and factors that affect their shapes, such as temperature and pH.
Ellipticalpolarization
where \(I_0\) is the intensity of the polarized wave before passing through the filter. This equation is known as Malus’s law.
where n1 is the medium in which the incident and reflected light travel and n2 is the index of refraction of the medium that forms the interface that reflects the light. This equation is known as Brewster’s law and θb is known as Brewster’s angle, named after the nineteenth-century Scottish physicist who discovered them.
An anti-reflective coating is particularly useful on high-index lenses, as these can reflect up to 50% more light than other lenses. This makes an anti-reflective coating indispensable.
AR coatings are made of layers of metal oxides. Simply put, an anti-reflective coating cancels out the light reflection on the surface of the lenses and allows more light to pass through them and reach your eyes.
Frustratingly for optical experts and linguistic pedants alike, the discussion about “anti-glare glasses” and “anti-glare lenses” is very often littered with misused language.
Polarization
Oct 11, 2012 — Roataions in edit mode affect the relationship of the geometry to the local axes of the object inworld. Rotations in Object mode do not affect ...
It’s easy to avoid looking directly at a bright light source, but glare is harder to escape. Glare is defined as a strong, dazzling light.
Circularly polarized light
This is what they were designed for, but innovation and technological advancements mean that glasses can also improve your visual experience in other ways, such as blocking out blue light or reducing glare.
This page titled 1.8: Polarization is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) illustrates what happens when unpolarized light is reflected from a surface. Vertically polarized light is preferentially refracted at the surface, so the reflected light is left more horizontally polarized. The reasons for this phenomenon are beyond the scope of this text, but a convenient mnemonic for remembering this is to imagine the polarization direction to be like an arrow. Vertical polarization is like an arrow perpendicular to the surface and is more likely to stick and not be reflected. Horizontal polarization is like an arrow bouncing on its side and is more likely to be reflected. Sunglasses with vertical axes thus block more reflected light than unpolarized light from other sources.
A hex key (also known as Allen key and Allen wrench) is a simple driver for screws or bolts that have a hexagonal recess, as opposed to the typical Phillips ...
Optik K&R has been providing exceptional quality optical products and customer service solutions for over 30 years. Our newly expanded 30,000 sq. ft. optical ...
Basically, the layers of the anti-reflective coating work together to introduce “destructive” light waves, that, as their name suggests, destroy reflections on the lenses.
The Sun and many other light sources produce waves that have the electric fields in random directions (Figure \(\PageIndex{1a}\)). Such light is said to be unpolarized, because it is composed of many waves with all possible directions of polarization. Polaroid materials—which were invented by the founder of the Polaroid Corporation, Edwin Land—act as a polarizing slit for light, allowing only polarization in one direction to pass through. Polarizing filters are composed of long molecules aligned in one direction. If we think of the molecules as many slits, analogous to those for the oscillating ropes, we can understand why only light with a specific polarization can get through. The axis of a polarizing filter is the direction along which the filter passes the electric field of an EM wave.
The difference between polarised lenses and anti-reflective coating is that polarisation prevents you from seeing glare at the source, while an anti-reflective coating prevents you from seeing glare reflected on your lens surface.
The more light that reaches your eyes, the more clearly you see. This is all achieved by a fairly complex scientific process called the optical interference model.
While there are different methods of introducing anti-glare properties, it’s important to use the right names for them in order to avoid confusion.

Surfaces like glass, water, snow, and certain metals are highly reflective, so we often experience glare from them, making it more difficult to view other objects close to where the glare is coming from.
Speak to your optician for personalised recommendations on which solution is right for your specific needs, or you can ask our opticians for further advice.
Politicalpolarization
A secondary advantage of AR coatings is that they generally have a hydrophobic finish to seal all of their layers, making them water-repellent and easier to clean.
Choose Anti-Reflective lenses to reduce glare & reflection for when you see starburst effects. Prescription available online and insurance plans accepted.
By default, the SciChart3DSurface.Camera is set to a new CameraController instance. This defines the Position, Target (in world coordinates) of the camera, and ...
Both polarised lenses and anti-reflective coating have their benefits, with one potentially more suited than the other to the types of settings you’ll most often find yourself in.
Solving Malus's law (Equation \ref{Malus's Law}) for \(\cos θ\) and substituting with the relationship between I and I0 gives
Circularpolarization
A fairly large angle between the direction of polarization and the filter axis is needed to reduce the intensity to 10.0% of its original value. This seems reasonable based on experimenting with polarizing films. It is interesting that at an angle of 45°, the intensity is reduced to 50% of its original value. Note that 71.6° is 18.4° from reducing the intensity to zero, and that at an angle of 18.4°, the intensity is reduced to 90.0% of its original value, giving evidence of symmetry.
Polarizing sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). They have this ability because of a wave characteristic of light called polarization. What is polarization? How is it produced? What are some of its uses? The answers to these questions are related to the wave character of light.
A positive focal length optical lens always introduces positive spherical aberration. This is evident from its transmitted wavefront error (WFE) profile and ...
What angle is needed between the direction of polarized light and the axis of a polarizing filter to reduce its intensity by 90.0%?
However, a pair of prescription polarised sunglasses is a very effective solution, although naturally not the most useful for night-time activities.
This greatly reduces glare for the wearer, and provides much sharper vision contrast. The chemical used in the polarisation process results in heavily tinted lenses, which makes it unsuitable for eyeglasses.
Ask your optician to recommend which cleaning products can be safely used to clean your anti-reflective glasses. The harsh chemicals in some products can damage the coating.
The halos that form around bright lights are also removed from your view with an anti-reflective coating, making driving at night more comfortable. With a greater amount of light reaching your eyes, an AR coating also improves visual acuity.
These pesky reflections are an aesthetic concern for some, as reflections on the front of their glasses hide their eyes from view, ruin photographs, and are also often noticeable during video calls.
Photographs of the sky can be darkened by polarizing filters, a trick used by many photographers to make clouds brighter by contrast. Scattering from other particles, such as smoke or dust, can also polarize light. Detecting polarization in scattered EM waves can be a useful analytical tool in determining the scattering source.
The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Legal. Accessibility Statement For more information contact us at info@libretexts.org.
Different coatings can add impact resistance, hydrophobic qualities, UV protection to your glasses, shield your eyes from blue light, and help with glare.
Light reflected at these angles could be completely blocked by a good polarizing filter held with its axis vertical. Brewster’s angle for water and air are similar to those for glass and air, so that sunglasses are equally effective for light reflected from either water or glass under similar circumstances. Light that is not reflected is refracted into these media. Therefore, at an incident angle equal to Brewster’s angle, the refracted light is slightly polarized vertically. It is not completely polarized vertically, because only a small fraction of the incident light is reflected, so a significant amount of horizontally polarized light is refracted.
As is usually the case when it comes to eyewear choices, your own vision requirements and lifestyle will dictate what the best option for you is.
Glass and plastic become optically active when stressed: the greater the stress, the greater the effect. Optical stress analysis on complicated shapes can be performed by making plastic models of them and observing them through crossed filters, as seen in Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\). It is apparent that the effect depends on wavelength as well as stress. The wavelength dependence is sometimes also used for artistic purposes.
When the intensity is reduced by 90.0%, it is 10.0% or 0.100 times its original value. That is, I=0.100I0. Using this information, the equation I=I0cos2θ can be used to solve for the needed angle.
In flat screen LCD televisions, a large light is generated at the back of the TV. The light travels to the front screen through millions of tiny units called pixels (picture elements). One of these is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\). Each unit has three cells, with red, blue, or green filters, each controlled independently. When the voltage across a liquid crystal is switched off, the liquid crystal passes the light through the particular filter. We can vary the picture contrast by varying the strength of the voltage applied to the liquid crystal.
A range of optical effects are used in sunglasses. Besides being polarizing, sunglasses may have colored pigments embedded in them, whereas others use either a nonreflective or reflective coating. A recent development is photochromic lenses, which darken in the sunlight and become clear indoors. Photochromic lenses are embedded with organic microcrystalline molecules that change their properties when exposed to UV in sunlight, but become clear in artificial lighting with no UV.
(a) At what angle will light traveling in air be completely polarized horizontally when reflected from water? (b) From glass?
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) shows the effect of two polarizing filters on originally unpolarized light. The first filter polarizes the light along its axis. When the axes of the first and second filters are aligned (parallel), then all of the polarized light passed by the first filter is also passed by the second filter. If the second polarizing filter is rotated, only the component of the light parallel to the second filter’s axis is passed. When the axes are perpendicular, no light is passed by the second filter.
For the wearer, the absence of reflections on their lenses is less distracting, especially in situations such as driving at night, working in a brightly lit environment, or in front of digital screens. Your eyes are put under less strain as a result.
polarization极化
Like with any glasses, always use a microfibre cloth to clean anti-reflective lenses instead of a t-shirt, tissue, or other type of material that could cause tiny abrasions.
Although you are undoubtedly aware of liquid crystal displays (LCDs) found in watches, calculators, computer screens, cellphones, flat screen televisions, and many other places, you may not be aware that they are based on polarization. Liquid crystals are so named because their molecules can be aligned even though they are in a liquid. Liquid crystals have the property that they can rotate the polarization of light passing through them by 90°. Furthermore, this property can be turned off by the application of a voltage, as illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\). It is possible to manipulate this characteristic quickly and in small, well-defined regions to create the contrast patterns we see in so many LCD devices.
Uncoated lenses allow about 92% of light to pass through them. An anti-reflective coating increases that to 99%, giving the wearer greater visual acuity.
Electricpolarization
Although we did not specify the direction in Example \(\PageIndex{1}\), let’s say the polarizing filter was rotated clockwise by 71.6° to reduce the light intensity by 90.0%. What would be the intensity reduction if the polarizing filter were rotated counterclockwise by 71.6°?
Disclaimer: Anti-reflective coatings on glasses lenses can provide a more comfortable viewing experience, but do not eliminate 100% of glare.
Some retailers talk about anti-glare coating for glasses, but in reality, this does not exist. It might sound like they’re the same thing, but anti-reflective coating is the correct term for this treatment.
The main purpose of an anti-reflective (AR) coating is to prevent reflections on the outer surface of glasses lenses by allowing more light to pass through them.
This Open Source Physics animation shows incident, reflected, and refracted light as rays and EM waves. Try rotating the animation for 3D visualization and also change the angle of incidence. Near Brewster’s angle, the reflected light becomes highly polarized.
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\) illustrates how the component of the electric field parallel to the long molecules is absorbed. An EM wave is composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The electric field is strong compared with the magnetic field and is more effective in exerting force on charges in the molecules. The most affected charged particles are the electrons, since electron masses are small. If an electron is forced to oscillate, it can absorb energy from the EM wave. This reduces the field in the wave and, hence, reduces its intensity. In long molecules, electrons can more easily oscillate parallel to the molecule than in the perpendicular direction. The electrons are bound to the molecule and are more restricted in their movement perpendicular to the molecule. Thus, the electrons can absorb EM waves that have a component of their electric field parallel to the molecule. The electrons are much less responsive to electric fields perpendicular to the molecule and allow these fields to pass. Thus, the axis of the polarizing filter is perpendicular to the length of the molecule.
Despite this, usage of the term “anti-glare coating” persists. The lens technology that most accurately fits the description of “anti-glare glasses” would be polarization, although it is only available for sunglasses lenses.
To examine this further, consider the transverse waves in the ropes shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). The oscillations in one rope are in a vertical plane and are said to be vertically polarized. Those in the other rope are in a horizontal plane and are horizontally polarized. If a vertical slit is placed on the first rope, the waves pass through. However, a vertical slit blocks the horizontally polarized waves. For EM waves, the direction of the electric field is analogous to the disturbances on the ropes.
Light is essential for vision, but too much light causes problems for our eyesight. We don’t tend to look directly at sources of light, as it can hurt our eyes and cause discomfort.
Every anti-reflective coating gives the lenses it’s applied to a very subtle tint. This tint is most often either green, brown or yellow.
Contrary to what you may think, an anti-reflective coating can actually make your glasses easier to clean and care for. Most AR coatings have a hydrophobic finish, which repels water and dirt, so the lenses don’t smudge so easily.
SmartBuyGlasses™ is a leading independent retailer of the world’s best designer eyewear since 2006 and is not owned by or affiliated with the brands it sells unless stated otherwise. All trademarks and brand names shown on our pages are the property of their respective companies which retain all rights.
Easily Magnify The Sewing Area In Front Of The Needle Creating Greater Visibility When Threading And Doing Detailed Sewing This set of magnifying lenses ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500