Limits to Resolution in the Electron Microscope - limit of resolution

Anti glare and antireflective glasses
The construction of a beam and block floor is similar to that of a suspended timber floor, but uses small pre-cast, pre-stressed inverted concrete T-beams with aircrete blocks laid between the beams.
Antireflective vsAnti GlareLenovo
AR glass is optically coated on one or both sides. The anti-reflective coating is usually a di-electric coating and can be applied to the glass in a single layer or multiple layers. When this invisible optical coating is applied to a glass substrate it accomplishes the following:
Because the floors are suspended, minimal groundwork is required when used to construct ground floors. Further, the installation of a beam and block floor is not usually weather dependent and can reduce site delays that other floor construction methods may encounter. The speed of construction means the floor can be used to provide a working platform for early access of follow-on trades.
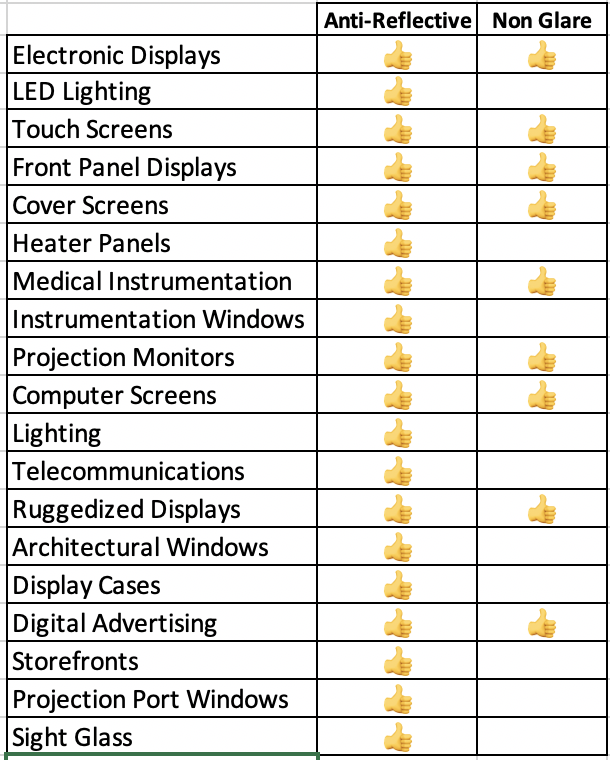
Non Glare Glass. There is an inverse relationship between the amount of diffusion of the non-glare glass and the resolution of the display. Now that we have explored how both Non-Glare and Ant-reflective glass are produced, let’s look at their typical applications. The matrix below can help steer you in the right direction when deciding between Anti-Reflective and Non-Glare Glass.
Anti glare and anti reflectionfor glasses
Anti-Reflective Coatings can be applied to just about any glass substrate including: Gorilla Glass, Borofloat, Ultra Clear Low Iron Float Glass, Ultra Thin Glass (Schott AS-87, Schott D263, AGC EN-A1)
Let’s start with a detailed description of both anti-reflective glass and non-glare glass. After defining both glass types we will list how each is used.
Anti glarevsAntiReflective TV
Anti glarevsantireflective for night driving
A differentiator of Anti-Reflective glass – when compared to Non-Glare glass – is the ability to customize the coating for specific wavelengths of light. AR coatings can be customized for visible light, UV and or NIR spectral bands.
It is suitable for the construction of both ground floor and intermediate floors of homes and commercial buildings, but without the shrinkage, flexing, bouncing or squeaking associated with timber floors. The system can also be used for the construction of floors of domestic garages
Anti glare and anti reflectioncost
For ground floors, insulation is usually positioned on top of the beam and aircrete block floor and covered by a sand cement screed, the choice of insulation material will determine the insulation thickness required to meet Part L of the Building Regulations. Depending on the floor covering used, a vapour control layer may be required to keep the moist room air on the warm side of the insulation.
Now that we have explored how both Non-Glare and Ant-reflective glass are produced, let’s look at their typical applications. The matrix below can help steer you in the right direction when deciding between Anti-Reflective and Non-Glare Glass.
Difference betweenanti glare and antireflective glasses
Beam and aircrete block floors are a quick, easy and economical solution to installing suspended floors. Depending on the pre-stressed concrete beams used, beam and block floors can generally span further than timber joists, typically 6m, potentially reducing foundation costs.
Non-Glare is measured in gloss units and is available in numerous gloss (etching) levels. The gloss levels range from 60 to 140. Non-Glare Glass is available in both Low Iron a Soda Lime gloat glass. The challenge with finding the right gloss level is balancing the amount of glare reduction (diffusion) with the resolution of the display behind the glass. The environment of the application, ambient light, thickness of the glass and brightness of the underlying display all play a part in the performance of the
Beams are typically spaced 440mm apart for a standard floor, or they can be placed 215mm apart to allow the blocks to be placed sideways to accommodate higher loads and/or longer spans
The precast concrete beams are laid in rows supported by the perimeter walls and on internal load bearing walls. Celcon Block Standard Grade 440 x 215 x 100mm is ideal as an infill between the precast concrete beams.
The ventilated void beneath the ground floor should be at least 150mm. In some areas of the country where radon gas occurs, a gas membrane will also be required to stop the gas entering the building and the ground floor will need to be ventilated. In the England and Wales the Building Regulations Approved Document C provides guidance on some of the requirements of suspended ground floors.
Difference betweenAnti glare and antireflective laptop screen
The jargon of the glass industry is not always clear when it comes to anti-reflective glass. The terms anti-reflective glass and non-glare glass are often used interchangeably; but in reality, they are very different types of glass. In this post we will explain how these two different glass types serve a similar purpose and also help you determine which might be best suited for your specific application.
Non-Glare Glass is produced by etching (via acid bath) one or both surfaces of the glass. The etching process is very precise and leaves the glass with an incredibly consistent etched finish across the entire surface. This etched surface disperses light as it hits the surface of the glass, virtually eliminating glare. This allows the end user to see transmitted images and videos very clearly – even in direct sunlight. Non-Glare Glass works best with high resolution displays.
For upper floors, in addition to their robustness the solidity of beam and block offers several advantages over timber floors including: excellent acoustic separation between floors, better fire, and concrete's thermal mass can help reduce summer overheating.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500