Lenses | Sony - zoom lens
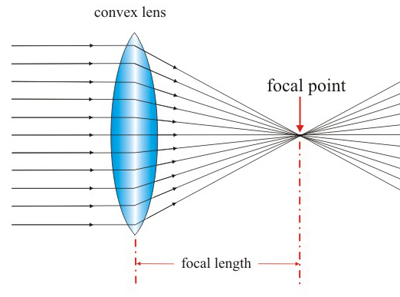
When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens the refracted rays converge at one point called the principal focus.
Concave concave lensvsconcave lens
Convex lenses are thicker at the middle. Rays of light that pass through the lens are brought closer together (they converge). A convex lens is a converging lens.
Concave lenses are thinner at the middle. Rays of light that pass through the lens are spread out (they diverge). A concave lens is a diverging lens.
Concave concave lensuses
When parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens the refracted rays diverge so that they appear to come from one point called the principal focus.
A magnifying glass produces an upright, magnified virtual image. The virtual image produced is on the same side of the lens as the object. For a magnified image to be observed the distance between the object and the lens must be shorter than the focal length of the lens.
Concave lensray diagram
Available perforated and non-perforated, our Low Temperature Release Film makes for an easy release of vacuum bagging materials from your part once the process is complete. When used directly next to your laminate, it generally produces a smoother, glossy surface finish for your part (although it can be used on top of peel ply within a set-up). This Release Film is suited for use in temperatures up to 315°F.
For a magnified image to be observed the distance between the object and the lens has to be shorter than the focal length of the lens. The image formed is upright, magnified and virtual.
As this is a ratio between heights it has no units. A magnification of 2 means the image is twice the size of the object and a magnification of 1 indicates an image size being the same as the object size.
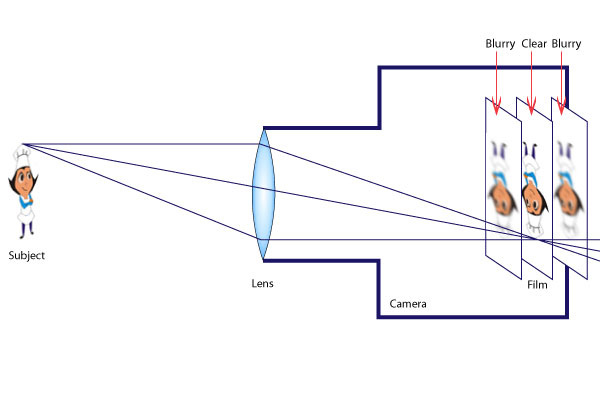
The image formed is said to be real because the rays of lighted from the object pass through the film and inverted (upside down).
Concave concave lensexamples
The angle at which the light enters the lens depends on the distance of the object from the lens. If the object is close to the lens the light rays enter at a sharper angled. This results in the rays converging away from the lens. As the lens can only bend the light to a certain agree the image needs to be focussed in order to form on the film. This is achieved by moving the lens away from the film.
Thus the real image of a closer object forms further away from the lens than the real image of a distant object and the action of focusing is the moving of the lens to get the real image to fall on the film.
The rays of light from the person are converged by the convex lens forming an image on the film or charged couple device in the case of a digital camera.
Similarly, if the object is away from the lens the rays enter at a wider angle. This results in the rays being refracted at a sharper angle and the image forming closer to the lens. In this case the lens needs to be positioned closer to the film to get a focused image.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500