Laser Speed M6R - Specter Solutions - laser speed ir laser
Pdc The section height level difference for the primary profile Wdc The section height level difference for the waviness profile
The M² factor is calculated by dividing the product of the actual beam's beam width and the divergence angle by the product of the ideal beam's beam width and the divergence angle, where the ideal beam is defined by the fundamental mode Gaussian beam, and the beam width is defined by the second moment. It can be proved that when the laser beam passes through the aberration-free optical system, its M² factor is a transmission invariant, and M²≥1; the farther M² deviates from 1, the worse the laser beam quality.
This parameter expands the profile (line roughness) parameter Rz three dimensionally. The maximum height Sz is equivalent to the sum of the maximum peak height Sp and maximum valley depth Sv.
Motif parameters are used for the evaluation of surface contact status based on the enveloped features of the sample surface.
Note This is one of the most widely used parameters and is also referred to as the RMS value. The parameter Rq corresponds to the standard deviation of the height distribution. The parameter generates good statistics and enables stable results since the parameter is not significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise.
Note This parameter is suitable for evaluating friction and abrasion. It is also used to evaluate lubricity for engine cylinder surfaces.
Sku=3: Normal distribution Sku>3: Height distribution is sharp Sku<3: Height distribution is even
This parameter expands the material ratio curve parameters (Rk, Rpk, Rvk, Mr1, and Mr2) of the profile parameter three dimensionally.
Note This parameter relates to the tip geometry of peaks and valleys and is suitable for analyzing the degree of contact between two objects.
What isbeam qualityin radiography
Note These parameters are suited to evaluating the slippage of lubrication mechanisms and contact surfaces, such as gaskets.
The average value of the heights of the five peaks with the largest global peak height added to the average value of the heights of the five pits with the largest global pit height.
Rsk=0: Symmetric against the mean line (normal distribution) Rsk>0: Deviation beneath the mean line Rsk<0: Deviation above the mean line
Rmr indicates the material ratio determined by the difference Rδc between the referential section height level C0 and the profile section height level.
Laser beam qualitytest
Note This is one of the most widely used parameters and is also referred to as the RMS value. The parameter Rq 7corresponds to the standard deviation of the height distribution. The parameter provides for easy statistical handling and enables stable results as the parameter is not significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise.
AR Mean spacing of roughness motifs: the arithmetic mean of roughness motifs ARi calculated from the evaluation length R Mean depth of roughness motifs: the arithmetic mean of the roughness motif depth Hj calculated from the evaluation length Rx Maximum depth of roughness motifs: the maximum value of the Hj calculated from the evaluation length AW Mean spacing of waviness motifs: the arithmetic mean of the waviness motif AWi calculated from the evaluation length W Mean depth of waviness motifs: the arithmetic mean of the waviness motif depth HWj calculated from the evaluation length Wx Maximum depth of waviness motifs: the maximum value of the HWj calculated from the evaluation length
Note This function is used to evaluate friction and abrasion. It is also used to evaluate the lubricity of engine cylinder surfaces.
Rk, Mr1, and Mr2 values are calculated from the linear curve (equivalent linear curve) minimizing the sectional inclination corresponding to 40% of the material ratio curve. Draw a triangle with the area equivalent to the protrusion of the material ratio curve segmented by the breadth of the parameter Rk and calculate parameters Rpk and Rvk.
This parameter expands the profile (line roughness) parameter Rsk three dimensionally; parameter Rsk, is used to evaluate deviations in the height distribution.
Represents the sum of the mean value for the height of the five tallest peaks and the mean of the depth of the five deepest valleys of a profile within the sampling length.
At present, regarding the quality of laser beams, there are two standards currently being implemented in my country, namely, the evaluation and testing method of laser beam quality for manufacturing (GB/T 27666-2011) and the evaluation and testing method of high-energy laser beam quality (GB/T 32831). -2016), in which the latter includes relevant specification documents for the β factor.
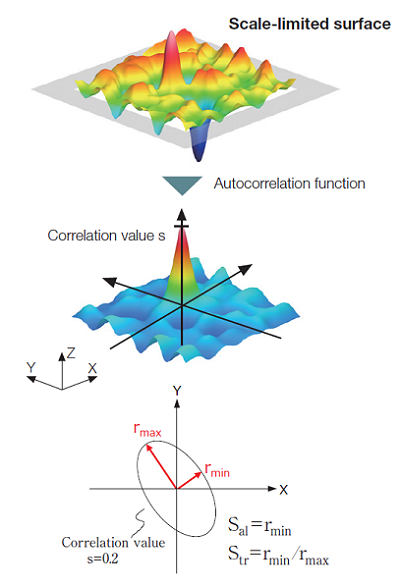
The horizontal distance of the autocorrelation function that has the fastest decay to a specified value s (0≤ s < 1). Unless otherwise specified, the parameter is specified as = 0.2.
Pmr (c) The material length rate of the primary profile (formerly tp) Wmr (c) The material length rate of the waviness
Laser beam qualityM2
Note Although frequently used, this parameter is significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise due to its utilization of peak values.
The difference in height between the p and q material ratio. Unless specified otherwise, the values p=2.5%, q=50% shall be applied.
The Str value ranges from 0 to 1; normally Str > 0.5 indicates a strong isotropy while Str < 0.3 is strongly anisotropic.
This is the number of peaks per unit area. Only peaks that exceed a designated size are counted. Unless otherwise specified, the designated size is determined to be 5% of the maximum height Sz.
how to (maybe) measurelaser beam quality
Indicates the ratio of the material length Ml(c) of the profile element to the evaluation length for the section height level c (% or μm).
This parameter expands the profile (line roughness) parameter Rku three dimensionally; Rku, is used to evaluate sharpness in the height distribution.
Note These parameters are used to evaluate the horizontal size and complexity of parallel grooves and grains instead of the height parameters.
Note This parameter concerns the height distribution and is suitable for evaluating the abrasion and oil sump of lubricants for slide planes.
This parameter is defined as the ratio of the horizontal distance of the autocorrelation function that has the fastest decay to a specified value s to the horizontal distance of the autocorrelation function that has the slowest decay to s (0 ≤ s < 1) and indicates the isotropic/anisotropic strength of the surface.
Note This parameter relates to the tip geometry of peaks and valleys and is suited to analyzing the contact between two objects.
This parameter expands the profile (line roughness) parameter Rp three dimensionally. It is the maximum value for peak height.
This signifies the rate of an increase in the surface area. The increase rate is calculated from the surface area A1 derived by the projected area A0.
Rku=3: Normal distribution Rku>3: The height distribution is sharp Rku<3: The height distribution is even
Terms Of Use | Privacy Notice | Cookies | Cookie Settings | About Us | Careers | Careers | Sitemap
Minimum height discrimination: 10% of the Rz value Minimum length discrimination: 1% of the reference length
Note Rzjis is equivalent to the parameter Rz of the obsolete JIS standard B0601:1994. Although ten-point mean roughness was deleted from current ISO standards, it was popularly used in Japan and was retained within the JIS standard as the parameter Rzjis.
Represents the sum of the maximum peak height Zp and the maximum valley depth Zv of a profile within the reference length.
Minimum height discrimination: 10% of the Rz value Minimum length discrimination: 1% of the reference length
Rk Core roughness depth Rpk Reduced peak height Rvk Reduced valley depth Mr1, Mr2 Material portion
Terms Of Use | Privacy Notice | Cookies | Cookie Settings | About Us | Imprint | Careers | Careers | Sitemap
Beamparameter product
Material ratio curves signify the ratio of materiality derived as a mathematical function of parameter c, where c represents the height of severance for a specific sample. This is also referred to as the bearing curve (BAC) or Abbott curve. Probability density curves signify the probability of occurrence for height Zx. The parameter is equivalent to the height distribution histogram.
Sk Core height: the difference between the upper and lower levels of the core Spk Reduced peak height: the mean height of the protruding peaks above the core Svk Reduced valley height: the mean height of the protruding dales beneath the core Smr1 The areal material ratio segmenting protruding peaks from the core (indicated as a percentage) Smr2 Areal material ratio segmenting protruding valleys from the core (indicated as percentage)
Note One of the most widely used parameters is the mean of the average height difference for the average surface. It provides for stable results as the parameter is not significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise.
Laser beam qualityfactor
This parameter expands the profile (line roughness) parameter Rdq three dimensionally. It indicates the mean magnitude of the local gradient (slope) of the surface. The surface is more steeply inclined as the value of the parameter Sdq becomes larger.
Pt The maximum total height of the profile (Rmax in the case of JIS’82) Wt The maximum total height of the waviness
Note Rt is a stricter standard than Rz in that the measurement is conducted against the evaluation length. It should be noted that the parameter is significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise due to its utilization of peak values.
Note Std represents the angle for the strongest orientation, although the second and third strongest angles can also be defined on the directional chart.
This parameter expands the profile (line roughness) parameter Rv three dimensionally. It is the maximum value for the valley’s depth.
Unlike core parameters such as line width and power, the basic concepts and related knowledge of beam quality have not yet been fully popularized. And unlike the definition and measurement method parameters of laser "power" and "line width", the definition of "beam quality" is relatively abstract and has a certain degree of difficulty.
The ELITE Bios series of highly stable lasers are mainly used in the fields of drain cytometer, Raman spectrometer, confocal microscope, etc. The beam quality factor is a very important factor for customer testing. At present, we can achieve ≤1.2. It can basically meet the requirements of customers, which is also a major advantage of this product.
Laser beam qualitycalculator
Note This parameter concerns height distribution. It is suitable for evaluating the abrasion and oil sump of lubricants for slide planes.
Spc indicates the mean principle curvature (average sharpness) of the peaks. Only peaks that exceed a designated curvature are taken into consideration.
The material volume and void volume are calculated from a material ratio curve as indicated in the diagram. The position that corresponds to a material ratio of 10% and 80% is regarded as the threshold segmenting the peak, core, and dale.
Beam qualitycalculator
Note Although frequently used, max height is significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise due to its reliance on peak values.
Beam Quality is one of the core parameters of laser beam characteristics. People usually use "high directivity, high brightness, high coherence" and other words to summarize the characteristics of laser beams, and the line width of the laser determines the time coherence of the laser to a certain extent, and the power of the laser and the brightness of the laser is highly positive. The correlation is similar, the beam quality of the laser is closely related to the directionality of the laser. Therefore, the beam quality of the laser has an important influence on the application effects in the fields of laser communication, remote energy transmission, and laser manufacturing.
Pmr The relative material length rate of the primary profile Wmr The relative material length rate of the waviness profile
Represents the sum of the maximum peak height Zp and the maximum valley depth Zv of a profile within the evaluation length, not sampling length.
Note This parameter is used to evaluate the horizontal size of parallel grooves and grains instead of the height parameters.
This parameter indicates the direction angle of the texture (parallel groove orientation, etc.). It is derived from the angle maximizing the angle spectrum of two-dimensional Fourier transformation images.
Ssk=0: Symmetric against the mean line Ssk>0: Deviation beneath the mean line Ssk<0: Deviation above the mean line
Note This is one of the most widely used parameters and is the mean of the average height difference for the average plane. It provides stable results since the parameter is not significantly influenced by scratches, contamination, and measurement noise.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500