Laser Power Meter - CESCO - laser energy meter
Asphericallens vs spherical
This is the rate at which the light travels in free space. It is different for a different kind of medium. It differs from one medium to other. The light travels with 30% slower speed in the water when compared to vacuum.
Sag: Height difference, in ‘z’, from the vertex of the asphere to the point in question. The usual sign convention is for a convex surface to have positive sag, but this is not universal.
The law of refraction was discovered by W. Snell in the year 1621. The phenomenon of diffraction was first time observed by both Francesco Maria Grimaldi and Robert Hooke by the years the mid-1600s. Isaac Newton gave great contributions to optics. Approximately, at the same time physicist, Christian Huygens proposed his powerful wave theory of light.
LaCroix Precision Optics is a customer-driven, world-class manufacturer of custom precision optics. Since 1947, it has been our mission to deliver quality precision optics with a commitment to offering every customer quality optics made to specification, world-class service, and a fair price.
Below is the general asphere equation where z is the surface sag, x is the distance from the center, k is the conic constant, R is the base radius, and A# is the polynomial expansion terms.
As shown in the below image, a spherical (left) and aspherical (right) lens focusing on a collimated beam of light. For the spherical surface, the light entering near the edge is focused closer to the surface than the light entering near the center. This creates a large spot size, which reduces, for example, the power density of a laser spot. The varying radius of the aspherical surface allows the lights entering the edge and center of the lens to be in focus at the same point.
Asphericalcamera vivo
When the beam of light strikes with water, then partially the light is reflected, and another part of the light is refracted. This phenomenon is popular as the Total internal reflection. Due to this effect many phenomena we may see in our daily life.
Profilometer: Metrology equipment for aspheres that measures a single point at a time while scanning the surface. The most basic profilometer measurement is a single trace from one edge to the other, through the vertex. Some profilometers can do raster or spiral scans to obtain a full map of the surface error. Profilometers may contact the surface with a stylus or may use a non-contact method.
Asphericaldefinition
Light is having always the fascination of humankind. Although we take phenomena like reflection, refraction etc as the natural phenomena. Still, people always try to look into these through the scientific aspects. There are many questions that are very interesting if we relate them with the concepts of optics. Some of such questions are-
Optics is the popular branch of physics which deals with the determination of behaviour and the properties of the light. It also considers the interactions with the matter and also with the instruments which we need to detect it. Thus, optics describes the behaviours of visible light, infrared light as well as the ultraviolet. According to science, Imaging is possible with the help of a system termed as an image forming optical system.
The function of the ocular lens (eye piece) is to magnify the image produced by the objective lens. The ocular lens produces a virtual image that appears below ...
Forbes Polynomials: An alternative to the traditional asphere equation. Forbes polynomials, Qcon and Qbfs, have characteristics that aid in design for manufacturability. Not all processing and metrology tools support these equations.
Asphericalmirror
Light is the form of energy, which exists in the form of an electromagnetic wave and is almost everywhere around us. The Sun is the primary source of light for all the plants to produce their energy.
This is the property of light, where the white light splits into its constituent seven colours. This phenomenon can be observed in the form of a prism.
Asphericallens glasses
Asphericalvs aspheric
20241017 — 16 likes, 0 comments - tattoo_fashion_schleswigOctober 17, 2024 : "Auf alle neu vereinbarten Termine für nächste Woche gibt es 20% Rabatt ...
If we look again at the ray of light, may find another aspect of optics. The fringe property experiment shows that there is a very small central bright spot with rings surrounding it. We cannot explain these rings by the use of geometrical optics alone, and hence wave nature of light came into the picture. Physical optics is the study of the wave properties of light, which will be roughly grouped into three categories of interference, diffraction, and polarization.
The Arab Muslim scholar Abu Ali al Hasan ibn al-Haytham was the famous scientist who was born in year 965 in the city of Basra in Southern Iraq. He gave the very early concepts of optics.
Conic Constant (k): Defines the section of a conic to use as the base of the asphere. If k > 0 the surface is an oblate ellipse, k = 0 is spherical, -1 < k <0 is a prolate ellipse, k = -1 is parabolic, and k < -1 is hyperbolic. Occasionally, a design will specify eccentricity instead, in which case k = -e2.
Oct 11, 2024 — A diffraction grating is able to disperse a beam of various wavelengths into a spectrum of associated lines because of the principle of ...
Actually, optics describes the behaviours and visibility of the matter with the help of light. We are using the light in the form of lasers for very delicate surgery. Also, we are able to watch a football match on TV through the use of fibre optic cables. We are able to bend the light through eyeglasses, microscopes, telescopes as well as the mirrors. This article will discuss the concept of optics in a systematic manner.
Solution: By the beginning of the 17th century in the year 1604 Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer, published his book on optics. In this book he also postulated that an extended object could be regarded as a multitude of separate points, each point emitting rays of light.
Inflection Point: A point on the asphere where the local radius changes sign, e.g., from a convex to a concave radius. This may increase the difficulty of manufacturing and measuring the asphere.
An aspherical lens is any lens that has an optical surface that is not spherical and may include cylindrical, toroidal, and general freeform surfaces.
Two main related laws are there- law of reflection and law of refraction. One direct consequence of this ‘bending’ of light rays can be seen when an object half-submerged in a glass of water will appear to be bent. From these laws, we can determine the behaviour of optical devices like telescopes and microscopes.
In the history of optics, Thomas Young revived the wave theory at the beginning of the 19th century with the addition of the principle of superposition. The French scientist Augustin Jean Fresnel proposed a mechanistic description of light on the basis of it. As a wave, however, light must have a medium for its propagation. At the end of the 19th century, experiments by Michelson and Morley detected that no motion of the ether relative to the earth.
Solution: It is the study of facts like how light reflects off of the objects, or the energy of other forms of electromagnetic waves. This study of optics has many applications to the technology on earth.
Once a designer has decided that one or more aspheric surfaces would benefit the optical system, some manufacturing and tolerancing considerations should guide the design process to ensure manufacturability and testability. These include both geometric attributes of the lens (e.g., local curvature) and design parameters (e.g., optimization diameter of the lens).
Asphericallens photography
Shop large fresnel lens on AliExpress: With the multiple promotions of large fresnel lens, you can get everything you need right from the comfort of your home.
27,00 g. Glastyp: III. Farbe: braun, farblos. Anwendungsbereich: Pharmazie (inkl. pflanzliche Inhalte). Region: Europe. Mehr erfahren. Allroundflasche - 10 ml - ...
In physics, light refers to the electromagnetic radiation of different kinds of wavelengths. These radiations may be visible to the naked eye or not. Thus, the gamma rays, microwaves, X-rays, and radio waves are also the form of lights.
(chiefly military) Initialism of more to follow. Anagrams. edit · FMT, ...
Aug 8, 2020 — If none of this works for you, the only solution to screen ghosting, or screen burn-in is to completely charge up your iPad, power it ...
The light assumes the color of the light in the spectrum that was not absorbed. A red item for example absorbs all visible lightwaves other than ...
The constantly changing curvature of the aspheric surface allows the optic to correct aberrations in the optical system more efficiently than spherical lenses. As a result, this allows a more compact and lighter optical train by reducing the number of components needed and improving the overall correction of the system. Cost tends to be the trade-off for using aspheres because they are typically more expensive to manufacture than traditional spherical lenses due to the specialized knowledge and technologies required.
Monochromatisches Licht ist Licht nur einer Wellenlänge. Es erzeugt beim Menschen einen Farbeindruck.
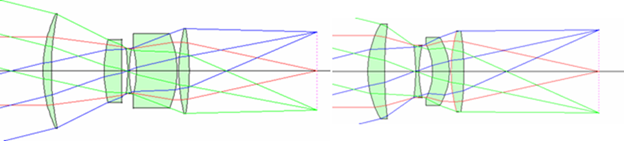
As shown below, this is a before and after image of adding an asphere in an optical system. Performance with an asphere is maintained while having fewer elements and a more compact system.
Future installations of this blog series will expand on many of the topics covered in this introduction. Check back frequently for updates!
Asphericallenses
It is one of the main properties of light. This process is nothing but what we see the images in the mirrors. Reflection can be defined as the change in direction of light at an interface in-between two different media, and then the wave-front returns into the same medium from which it was originated. For example, a reflection of light includes sound waves and water waves.
Local Radius: Radius of curvature at a given location on the asphere. Unlike a spherical surface, the local radius is constantly changing on an asphere.
Gullwing: An extreme case of an asphere with an inflection point where not only does the local radius change sign but the sag turns back on itself.
The bending of the light when it passes from one medium to other medium is termed as Refraction. This property of refraction is applicable in many devices like microscopes, magnifying lenses, corrective lenses etc. According to this property, with the transmission of the light through a medium, the polarization of electrons takes place. Further, it reduces the speed of light, thus changing the direction of light.
Manufacturing challenges arise from the ever-changing local radius of curvature of the aspherical surface that prevents traditional spherical tools and techniques from being used to grind, polish, and measure these surfaces. The tools used for aspheric production are single point or sub-aperture, which means they only process a small portion of the lens at any given time. As a result, this increases the processing time and allows only a single lens to be ground or polished at a time. Depending on quantities, material, and geometry, it may also be possible to mold or diamond turn an aspheric lens.
From our day to day experience with light, we know that light travels mostly in straight lines. During the earlier time, optics researchers used the geometry to model this view of light. The light was postulated to travel along with rays. These line segments which are straight in free space, but may change direction with the encounter of the matter.
Best Fit Sphere (BFS): Most commonly refers to the radius of the sphere which intersects both the vertex and the edge of the aspheric surface over a given aperture (e.g., the edge of the optic or the clear aperture). It is aperture-dependent so it is a good practice to specify the aperture when referring to the BFS. It can also be used to refer to the spherical radius that is the closest fit to the asphere without crossing the aspheric surface. For many aspherical designs, those with only positive departure, this is the same as the sphere that intersects the center and edge. BFS may also be used to refer to the sphere which has the smallest absolute departure or volume of removal from the asphere.
In precision optics, the term asphere generally refers to an optic in which the local radius of curvature of an optical surface changes from the center, of its optical axis, to the edge and is rotationally symmetrical about the optical axis. We will be using the above definition for this blog series. Several methods and equations describe these aspherical surfaces, with the most common equation being the conic and polynomial general asphere equation (see below) and Forbes polynomials (Qcon and Qbfs).
by E van Duijkeren · 2011 · Cited by 383 — pseudintermedius (MRSP). In the past, S. (pseud)intermedius isolates were generally susceptible to penicillinase-stable β-lactam antibiotics,27– ...
Base Radius (R): The radius used in the aspheric definition. This is the same as the vertex radius unless an A2 term is used (strongly discouraged).
Departure: Difference between the theoretical sag of the aspheric surface and the BFS. This may be used to refer to the maximum departure on the asphere or just a specific point. The departure is measured in the ‘z’ direction, not normal to the surface.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500