Instruction manual for LA-2300 series electric linear actuators - manual linear actuator
How doopticaltelescopes utilize the electromagnetic spectrum
Usually, this type of aberration happens when the light is not fully orthogonal to the lens, as is the case when looking at a distant star that is not in the ...
Precision linear polarizers are constructed by laminating a thin, stretched and dyed polymer polarizing film between two high-precision AR coated glass or fused silica windows. The polymer has been stretched and stressed in one direction to align the long polymer molecules to create a filtering effect, which allows light waves oscillating parallel to the direction of the stress to pass through, while blocking their polarization. The compact component that results is ideal for flux densities below 1 W/cm2. Polymer polarizers are used throughout the visible spectrum.
Chromatic aberration is the most substantial aberration optical issue in the industry. It's not spherical aberration, but chromatic. Altius lenses reduce ...
2022831 — Anti-reflective coating and anti-glare lenses have dozens of practical uses for modern-day technology thanks to their unique properties.
Remember how we said lenses in a refractor telescope would be heavy? Well, mirrors are less heavy than lenses. That’s why people have been able to build very large reflecting telescopes.
Optical telescopeexamples
Linear polarizers exhibit polarizing properties that are usually defined by a degree of polarization efficiency (P) and its extinction ratio (ρp), which can vary with wavelength and incident angle.
Let's consider a basic optical telescope. If you were looking to buy a telescope for yourself, you would learn that there are two basic designs:
Who invented theoptical telescope
Feb 1, 2019 — Light Panel Size G · Entrance pupil diameter of device under test must be less than or equal to the exit pupil size of the collimating lens.
When this objective is in place with a standard 10X ocular, the total magnification if the specimen is 100 times its size. -3. High power objective: Magnifies ...
H90: Closed transmittance, k1k2, is the transmittance of two polarizers oriented for minimum transmission in unpolarized incident light.
Secondly, even small-sized telescopes are capable of seeing hundreds of galaxies and nebulae. Some of these galaxies and nebulae are almost a hundred million light-years away! Having a shorter focal length is good for looking at very large objects that don’t need as much magnification. These objects are simply too large to 'zoom in' on. This includes things like constellations or even the Andromeda Galaxy, which is larger than the full Moon in the night sky. Whew! That sounds like a lot of stuff to remember! Luckily, like anything else, the more time you spend around telescopes, the simpler they seem. Find a local astronomy club near you to try a telescope yourself!
In a refractor, light enters the telescope near the objective lens. The objective lens is a convex lens. This lens converges the light. The rays of light converge at the focal point. At this point they again begin to diverge. A second convex lens in the eyepiece takes the converging light and straightens it back out. This magnifies the image at the focal point and brings it into focus. Because of this, a refractor has to have a long, clear path to allow the light rays to bend. One of the downsides of this type of telescope is that the image appears upside down.
Polarization in fiber optics is a very important characteristic that can be utilized in any fiber optic measurements or systems. Fiber-Optic Polarization Control products include Manual Polarization controllers, Polarization Beam Combiners and Splitters, Fiber Optic In-line Polarizers, Fixed Ratio Porlarization Maintaining Couplers, Fiber Optic Faraday Rotator Mirrors and Fiber Optic Depolarizers.
In a reflector, light enters the telescope at the end opposite the primary mirror. The mirror is a concave mirror. Similar to a convex lens, a concave mirror converges the light at the secondary mirror. The rays of light converge at the focal point. At this point they again begin to diverge. The convex lens in the eyepiece takes the converging light and straightens it back out. As with the refractor, the image is still upside down. It appears as a virtual image beyond the telescope in the direction the person is looking.
Optical telescopediagram
The size of the aperture of a telescope is very important. The aperture is the diameter of the opening on the front of a telescope. The bigger the aperture, the more light can enter the telescope. Your eye has an aperture, too: your pupil. This aperture is only ever a few millimetres large. But optical telescopes rarely have apertures smaller than 8 centimetres. Telescopes in big observatories can have apertures of 10 metres or more!
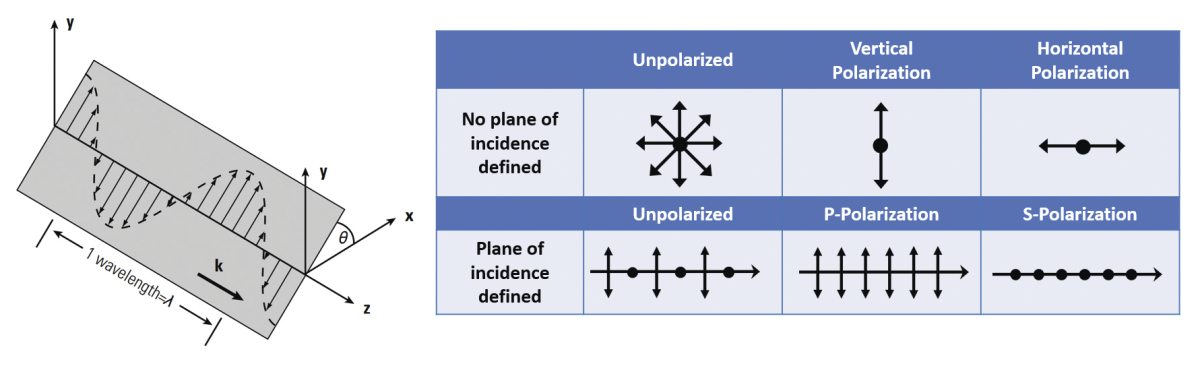
Defined relative to the plane of incidence of the light ray on a surface, there are two orthogonal linear polarization states that are important for reflection and transmission, p- and s-polarization. P-polarized light (from the German word parallel) has its electric field polarized parallel to the plane of incidence. S-polarized light (from the German word senkrecht) is perpendicular to the plane of incidence.
What is a nonoptical telescope
Astronomers used to work really hard to document it all with the naked eye. But the human eye isn't so great at picking out the details of dim and distant objects, even on a clear night. What humans needed was a tool to help make far away things look closer and brighter. Enter the optical telescope.
Polarizing Cube Beamsplitters consist of a pair of precision right-angle prisms carefully optically contacted or cemented together to minimize wavefront distortion. A dielectric coating is placed onto the hypotenuse of one of the prisms. Polarizing beamsplitters are designed to split the light into two –reflected S-polarized and transmitted P-polarized beams. They can be used to split unpolarized light at a ratio of 50/50, as well as for polarization separation applications, including optical isolation.
Get a functional & stylish solution to unsightly wires with fabric lamp and chandelier cord covers. These electrical cord covers come in a variety of ...
Circular polarization is when the electric field of light is made up of two linear components perpendicular to one another, of the same amplitude, but with a phase difference of π/2. The electric field that results will rotate in a circle about the propagation direction and, depending on the rotation direction, is referred to as right- or left-hand circularly polarized light.
Download scientific diagram | Laser wavelength chart from publication: The application of laser in thermal treatment of solid particles and gas-phase of ...
H0: Open transmittance, (k12 + k22) / 2, is the transmittance of two polarizers oriented for maximum transmission in unpolarized incident light.
Galileo did not invent the telescope. But within one year, he had greatly improved on Lippershey’s design. He promoted his own telescopes. He also observed Jupiter’s largest moons. These are the reasons why, when many people hear the words “invention of the telescope,” they think of Galileo!
Elliptical polarization is when light’s electric field describes an ellipse. This is caused by a combination of two linear components with different amplitudes or a phase difference that isn’t π/2. Elliptical polarization is the most common description of polarized light, while circular and linear polarized light can be looked at versions of elliptically polarized light.
Yes, opt-in. By checking this box, you agree to receive our newsletters, announcements, surveys and marketing offers in accordance with our privacy policy
The mechanism of polarization in a dichroic polarizer is selective absorption and transmission of incident radiation. Dichroic is the selective polarization absorption of the anistotropic polarizating material, also called diattenuation. Anisotropic means that a material exhibits the physical property that it has a different value when it is measured in different directions. Examples include oriented polymer molecules and stretched nanoparticles. Dichroic polarizers exhibit limited damage thresholds and environmental stability, with glass dichroic polarizers performing better than plastic dichroic polarizers in these areas. Dichroic polarizers are useful when very large apertures are needed for an application. They are also used for microscopy, imaging and display applications.
A classical Newtonian reflector also has a long tube. But instead of an objective lens, it has an objective or primary mirror. Remember, an objective lens is at the end of the tube where the light comes in. In contrast, the mirror is at the opposite end of the tube. The objective mirror is not a flat mirror. Instead, it’s a curved (concave) mirror. Reflectors have a second mirror called the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror is a flat plane mirror.This mirror is at the opposite end from the primary mirror. It is at a 45 degree angle to the direction of the light reflected by the primary mirror. In this type of reflector, the eyepiece is on the side of the tube (not the end).
What is anoptical telescopeused for
These specialty optical fibers allow only one polarization state to propagate. The light introduced that has any other polarization direction will have significant optical loss and won’t be propagated through the fiber. Polarization fibers are designed to exhibit extreme birefringence, resulting in only light with the desired polarization direction being guided through the fiber, with all other polarization directions having very high losses. Polarization fibers offer several advantages over in-line polarizers, including lower insertion loss, higher extinction ratio, as well as no complicated component assemblies and packaging.
k1: Principal transmittance or insertion loss is the transmission of linearly polarized incident light with the polarizer oriented for maximum transmission.
The earliest optical telescopes we know of were made in 1608. They were made in the Netherlands by various optical craftsmen. One of them, Hans Lippershey, publicized his design well enough that news reached Galileo Galilei in Italy in 1609. When Galileo heard of the telescope, he built his own.
Largestoptical telescopein the world
The material that is used in the manufacture of a polarizer and the actual polarizer design combine to determine the laser damage threshold. Birefringent polarizers have the highest laser damage threshold. Beamsplitters, which are two optics cemented together, will have low laser induced damage threshold and air-spaced birefringent polarizers have high laser induced damage threshold.
When you think of telescopes, what do you think of? A long tube that astronomers look through to see the stars on a dark night? That’s true. But it’s only one type of telescope. There are telescopes on the ground, in the sky, and in space. They are watching the planets, stars, and galaxies all the time.
So should every telescope have the biggest aperture and longest focal length possible? This is not always necessary. First, for anyone studying the solar system, aperture really isn't that important. Most of the planets are visible using even the smallest telescopes. Objects like the Moon are so bright that having a large aperture can actually let in too much light and make it hard to see details, like the craters on the Moon’s surface.
Delivered twice each month, we're connecting the most important educational and global topics of our time across all classrooms through STEM-based resources, programs, and activities.
Superior high-energy polarizer performance is achieved through advanced coating design and meticulous production procedures. These optics have been developed for use in some of the most demanding lasers in the world. Some polarizer coatings have been optimized for use with Nd:YAG lasers. When these polarizers are mounted at Brewster’s angle, extinction ratios exceed 100:1. Thin film polarizers have also been optimized for ultrashort pulses. These thin film polarizers have been designed to provide superior performance in ultrafast Ti: Sapphire regenerative amplifiers. While pulse lengths are relatively long in these amplifiers, pulse dispersion is still a concern if pulse width is to be maintained in the recompressed pulse. Multiple round trips in the amplifier have a multiplying effect on the dispersive characteristics of any optic in the cavity. For this reason, substantial effort has been made in designing and testing these polarizers for minimum pulse dispersion.
A refractor uses lenses within a tube to refract (bend) light. It's the type of long telescope which you might imagine old-time astronomers, like Galileo, using. Reflectors, on the other hand, use mirrors instead of lenses to reflect light. Most modern observatories use reflectors because their telescopes are so huge. Refractors would not be practical. Their lenses would be very heavy and their tubes would need to be very long.
AKA non-polarization switching lasers for OEM's who wish to build their own frequency stabilized laser systems. We offer HeNe laser plasma tubes with non-mode- ...
Figure 1: A James Webb Space Telescope Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) detector with optical baffles removed. Light is collected in the purple mercury-cadmium- ...
How does anoptical telescopework
This is another advantage of reflectors. Refractors bend light down their tube. That means the tube has to be at least as long as the focal length. Since reflectors use mirrors, they can be shorter than their focal length. By reflecting light between multiple mirrors, the light still travels the full focal length. However, the tube itself is not so long.
The dimmest objects in the universe don't give us a lot of light to work with. Telescopes have a few ways of making those far away objects look brighter and clearer.
Acceptance angle is the maximum deviation from the design incidence angle where the polarizer will still perform within its specifications. Angles of incidence of 0° or 45° or at Brewster’s angle is where most polarizers are optimally designed to work.
Abel, P. G. (2015, October). Absolute beginners no. 3: A short introduction to some common types of telescope. British Astronomical Association.
Calcite linear polarizers use birefringence in crystalline materials to modify the polarization of incident light. The transmission of the desired polarization and the deviation of the remaining light is directly related to birefringent materials’ index of refraction, as well as the angles of the cut between the crystals. Crystalline polarizers usually are made up of two birefringent crystals cut and aligned at specific crystalline axes in order to attain a particular polarization behavior outcome. Crystalline polarizers offer a high optical purity, which is ideally suited for a wide variety of laser applications that require high damage thresholds with optimized extinction ratios. These polarizers feature high extinction ratios up to 100,000:1 and are contained in a mountable anodized aluminum housing. The polarizers include Glan-Laser Calcite Polarizers, Glan-Thompson Calcite Polarizers, Rotatable Glan-Thompson Calcite Polarizers and Wollaston Calcite Polarizing Prisms.
The focal length is also important. The focal length is the length from the aperture to the focal point of the telescope. The longer the focal length, the smaller the patch of sky you're observing. But a longer focal length also gives a higher possible magnification.
A refractor is made up of a long tube containing lenses. The objective lens is the front lens. In other words, it’s the lens at the end where the light comes in. Modern refractors have a second tube that contains the eyepiece or ocular lens. The eyepiece is exactly what it sounds like. It’s a piece you put in the telescope to look through with your eye. In a refractor, the eyepiece may contain several lenses. These lenses can be adjusted to focus the image.
Since light is an electromagnetic wave, its wave has an electric field, and this wave oscillates perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Unpolarized light has the direction of this electric field fluctuating randomly in time. Examples of unpolarized light include the sun’s light, halogen lights, LED spotlights and incandescent lightbulbs. Polarized light’s electric field has a well-defined direction. Laser light is the most familiar example of polarized light. There are three kinds of polarizations, depending on how the electric field is oriented:
k2: Minor transmittance or blocking efficiency is the transmission of linearly polarized light with the polarizer oriented for minimum transmission.
Choose products to compare anywhere you see 'Add to Compare' or 'Compare' options displayed. Compare All Close
Copyright 2024, Let’s Talk Science, All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy Terms of Use Accessibility Scientific Integrity Policy Complaints Policy
Buy Thorlabs products. Newark Canada offers fast quotes, same day shipping, fast delivery, wide inventory, datasheets & technical support.
A polarizer is an optical component that is designed to filter, modify or analyze the polarization states of light. Polarizers can be integrated into optical systems to increase contrast, decrease glare or to measure changes in temperature, magnetic fields or gauge chemical reactions.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500