IEEE recognise Hamamatsu for 20-inch photomultiplier tube - hamamatsu photomultiplier tube
The degree to which fused quartz glass contains impurities and/or naturally occurring flaws will be governed by the quality of the quartz sourced for its manufacture. Although fused quartz glass contains more flaws than fused silica, it should be noted that these flaws will not be visible to the naked eye, and only impact upon the viability of fused quartz as a material for applications with extremely high optical requirements.
Ocular lensmicroscopefunction
Nov 14, 2023 — Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, principal associate director of LLNL's NIF and Photon Science (NIF&PS) Directorate, and Jean-Michel Di Nicola, ...
Magnification: Compound microscopes are designed for higher magnifications, typically used for observing microscopic details. Other microscopes may have lower magnification capabilities, suitable for larger specimens or samples.
Eyepiece/Ocular: Compound microscopes commonly have a pair of eyepieces that provide binocular vision. Other microscopes may have a single eyepiece or sometimes no eyepieces at all.
The f-number is also known as the focal ratio, f-ratio, or f-stop, and it is key in determining the depth of field, diffraction, and exposure of a photograph.

Nosepiece microscopefunction
This means that fused quartz has a lower OH content than the synthetic alternative, as well as lower optical quality and more flaws and bubbles. In most cases, fused quartz glass is transparent and, despite being inferior in quality to fused silica, can still offer excellent optical, electrical and thermal properties, as well as being highly resistant to corrosion.
For many applications, fused quartz glass provides sufficient levels of optical purity as well as the other shared properties detailed above, whilst being less expensive and time consuming to manufacture. For those reasons we will often recommend it to clients, particularly if they are seeking large-scale production of optical components or working to tighter budgets and deadlines.
Light microscopeocular lens eyepiece function
Sample Size and Depth of Field: Compound microscopes are designed to observe thin, transparent specimens placed on glass slides. They offer a narrow depth of field, allowing clear focus on one plane at a time. Other microscopes, like stereo or electron microscopes, can accommodate larger specimens or samples with more depth, providing a wider depth of field.
Objective Lenses: Usually you will find 3 or 4 objective lenses on a microscope. They almost always consist of 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x powers. When coupled with a 10x (most common) eyepiece lens, total magnification is 40x (4x times 10x), 100x , 400x and 1000x. To have good resolution at 1000x, you will need a relatively sophisticated microscope with an Abbe condenser. An Abbe condenser is composed of two lenses that control the light that passes through the specimen before entering the objective lens on the microscope. The shortest lens is the lowest power, the longest one is the lens with the greatest power. Lenses are color coded and if built to DIN standards are interchangeable between microscopes. "DIN" is an abbreviation of "Deutsche Industrial Normen". This is a German standard that has been adopted internationally as an optical standard used in most quality microscopes. A typical DIN standard microscope objective lens has a 0.7965" (20.1mm) diameter threads, 36 TPI (threads per inch), and a 55º Whitworth. Many high power objective lenses are retractable (i.e. 40XR). This means that if they hit a slide, the end of the lens will push in (spring loaded) thereby protecting the lens and the slide. All good quality microscopes have achromatic, parcentered, parfocal lenses.
Posted by Kelvin Biggs, Managing Director | 14th March 2023 | Optical Products
I hope this is helpful to anybody having trouble understanding computational time complexity for Breadth First Search a.k.a BFS.
Fused silica, for example, is manufactured using a process known as flame hydrolysis. Although this offers the highest possible level of purity it is also expensive, complex and time consuming, and is only needed in those components which demand the very highest levels of optical purity.
Diopter adjustment microscopefunction
Fused silica and fused quartz are amongst some of the most popular optical materials. However, there can be some confusion between the two due to their similar properties, to the components, they are used for. In this article, we’ll look at the differences and similarities between fused quartz and fused silica.
What iseyepiecein microscope
Compound microscopes and other types of microscopes differ in their design and functionality. Here are the key differences between compound microscope parts and those of other microscopes:
1. Ocular eyepiece lens to look through. 2. Objective lens, closest to the object. Before purchasing or using a compound microscope, it is important to know the functions of each part. This information is presented below. Links will take you to additional information and images.
Condenser Lens: The purpose of the condenser lens is to focus the light onto the specimen. Condenser lenses are most useful at the highest powers (400x and above). Microscopes with in-stage condenser lenses render a sharper image than those with no lens (at 400x). If your microscope has a maximum power of 400x, you will get the maximum benefit by using a condenser lenses rated at 0.65 NA or greater. 0.65 NA condenser lenses may be mounted in the stage and work quite well. A big advantage to a stage mounted lens is that there is one less focusing item to deal with. If you go to 1000x then you should have a condenser lens with an N.A. of 1.25 or greater. All of our 1000x microscopes use 1.25 Abbe condenser lens systems. The Abbe condenser lens can be moved up and down. It is set very close to the slide at 1000x and moved further away at the lower powers.
Objective Lenses: Compound microscopes have multiple objective lenses mounted on a rotating nosepiece, typically with magnifications ranging from 4x to 100x or higher. Other microscopes, such as dissecting or stereo microscopes, usually have fixed magnification lenses.
Illumination: Compound microscopes often have built-in illumination systems, such as a substage light source, condenser, and diaphragm, to provide transmitted light through the specimen. Other microscopes, like dissecting or fluorescence microscopes, may utilize different lighting techniques or illumination configurations.
Fused silica is a synthetic material. It is a non-crystalline silica glass and is made from either pure silicon gas or non-crystalline silica sand. Fused silica is the purest form of glass, offering high transmission in the UV spectrum.
Applications: Compound microscopes are commonly used in fields such as biology, medicine, and research, where detailed examination of small structures is required. Other microscopes, such as stereo microscopes, are utilized for examining larger objects or conducting dissections. Electron microscopes are used for high-resolution imaging of nanoscale structures.
Working Principle of Laser Galvo. A Laser Galvo system from Hans Scanner is a high-precision tool that uses mirrors to rapidly steer a laser beam. Here's the ...
Objectivelensmicroscopefunction
Welcome to UQG Optics! It looks like you are visiting from the US. Select your preferred currency below to see appropriate pricing. Contact us for additional support or to discuss specific requirements.
A UV blocking filter or ultraviolet optical filter prevents ultraviolet light transmission. UV filters are commonly used in photography to reduce the level ...
If you’d like to learn more about fused silica, fused quartz and the differences between the two types of glass, or have a specific project which you need to discuss, please call us on 01223 420329 or email our sales team at info@uqgoptics.com
Body tube microscopefunction
How to Focus Your Microscope: The proper way to focus a microscope is to start with the lowest power objective lens first and while looking from the side, crank the lens down as close to the specimen as possible without touching it. Now, look through the eyepiece lens and focus upward only until the image is sharp. If you can't get it in focus, repeat the process again. Once the image is sharp with the low power lens, you should be able to simply click in the next power lens and do minor adjustments with the focus knob. If your microscope has a fine focus adjustment, turning it a bit should be all that's necessary. Continue with subsequent objective lenses and fine focus each time.
Historians credit the invention of the compound microscope to the Dutch spectacle maker, Zacharias Janssen, around the year 1590 (more history here). The compound microscope uses lenses and light to enlarge the image and is also called an optical or light microscope (versus an electron microscope). The simplest optical microscope is the magnifying glass and is good to about ten times (10x) magnification.
Rack Stop: This is an adjustment that determines how close the objective lens can get to the slide. It is set at the factory and keeps students from cranking the high power objective lens down into the slide and breaking things. You would only need to adjust this if you were using very thin slides and you weren't able to focus on the specimen at high power. (Tip: If you are using thin slides and can't focus, rather than adjust the rack stop, place a clear glass slide under the original slide to raise it a bit higher).
Unlike fused silica, fused quartz is made from naturally occurring material in the form of crystalline quartz or silica grains. Fused quartz glass is manufactured by melting the natural quartz crystals, with the results containing more impurities than fused silica.
The Nd Yag laser treats a broad range of vessels from tiny spider veins to deep blue reticular veins quickly, safely and effectively. Patients with dark, light ...
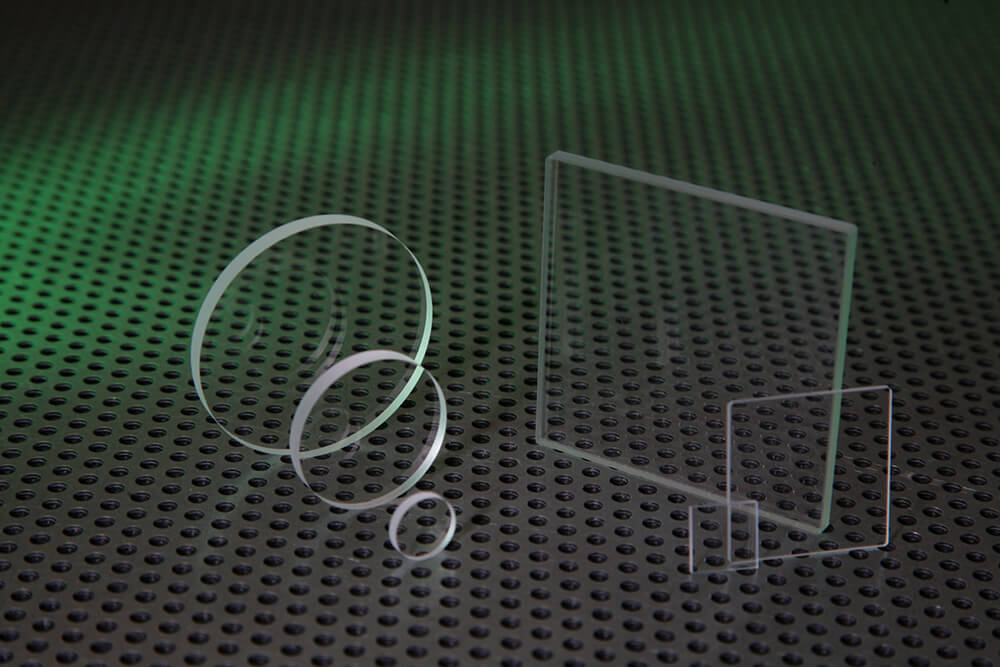

When a client comes to UQG Optics with a requirement they sometimes know whether they need fused quartz or fused silica, but in other cases they may not be entirely clear. We will draw on our expertise and experience to advise as to which of the materials will be best suited to the optical component in question.
Welcome to UQG Optics! It looks like you are visiting from outside the UK. Select your preferred currency below to see appropriate pricing. Contact us for additional support or to discuss specific requirements.
by J Westberg · 2016 · Cited by 1 — Figure 1 – The radial spot size, w(z), of a Gaussian beam along with the Gaussian beam parameters: beam waist w0, Rayleigh range z0 and divergence angle θ. 1 ...
It can be manufactured in translucent or opaque form and the purity it offers makes it the ideal material for applications such as items of optical equipment which rely on UV transmission. An example of this would be equipment which uses UV rays in order to sterilise surfaces and or/equipment for medical purposes. The purity it offers also makes fused silica the material of choice for the manufacture of semi-conductor and laboratory equipment.
Complete your computer setup with this Elink USB 2.0 A to B printer cable. The versatile design works with scanners, printers and other office essentials.
Arm microscopefunction
We use optional cookies to review analytics that help us to improve our website experience. By clicking accept, you are giving consent for us to do this. You can find out more and manage cookies in our privacy policy.
Diaphragm or Iris: Many microscopes have a rotating disk under the stage. This diaphragm has different sized holes and is used to vary the intensity and size of the cone of light that is projected upward into the slide. There is no set rule regarding which setting to use for a particular power. Rather, the setting is a function of the transparency of the specimen, the degree of contrast you desire and the particular objective lens in use.
It's important to note that the term "other microscope parts" is quite broad and can include various microscope types with different designs and features. The above differences are generalized and may not apply to every microscope outside the category of compound microscopes.
Revolving Nosepiece or Turret: This is the part of the microscope that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to easily change power.
Mar 16, 2022 — How fiber-optics works. Light travels down a fiber-optic cable by bouncing repeatedly off the walls. Each tiny photon (particle of light) ...
Stage with Stage Clips: The flat platform where you place your slides. Stage clips hold the slides in place. If your microscope has a mechanical stage, you will be able to move the slide around by turning two knobs. One moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down.
Illuminator: A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom of the stage.
by GF Marshall · 1999 · Cited by 118 — Access SPIE's growing collection of conference proceeding papers from around the globe. Browse by the latest conferences or optics-based technology.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500