How to laser cut paper without burning - laser burn paper

Diffraction limitresolution
Dr. Jennifer Waters (Director of the Nikon Imaging Center, Harvard Medical School) provides additional insight on the topic of Numerical Aperture (NA). Numerical Aperture is critical because it limits both the resolution and the brightness of an image obtained from a microscope. She begins with the Rayleigh Criteria, showing how NA impacts resolution and then shows the physical properties that impact NA. This leads into an informative discussion about the benefits of higher NA.
Another insight is that diffraction in the sample tells us something about the size of the objects in the field of view and interference between the diffracted beams is what gives rise to the image of the sample. Dr. Thorn conveys this insight in the form of a famous quote from Abbe: “The microscope image is the interference effect of a diffraction phenomenon”.
20151113 — Eyepieces work in combination with microscope objectives to further magnify the intermediate image so that specimen details can be observed.
Diffraction limit of lightformula
Allied Vision's Alvium 1800 series is a cross-over machine vision camera that combines the high performance and durability of machine vision cameras with the compact hardware and cost efficiency of embedded devices. These cameras, now available with Sony IMX CMOS sensors with up to 20 megapixel resolution, offer high frame rates, high sensitivity, and excellent image quality. With industrial-grade hardware, a USB3 vision-compatible interface with screw-locked connectors, built-in image correction functions and high-precision triggering, they meet all the requirements of industrial image processing.
Kit includes two replacement 7mm, two 10mm, and two 13mm lens springs. This spring set comes stock with purchase of the Sienci LaserBeam Laser System.
The Point Spread Function (PSF) of microscope is the basis for many practical and theoretical concepts in light microscopy, both basic and advanced. In the video, Dr. Jennifer Waters defines the PSF of a microscope and then shows how it relates to the resolution of a microscope. She further explains that the PSF is a result of diffraction and interference: this concept is concretized in the video with the help of animations and examples. This video is also very helpful in integrating in the viewer’s mind the concept of the PSF with the well-known Rayleigh Criterion. Dr. Waters also helps viewers connect the PSF to real-world insights: for example, (citing Vogel et al, Science, 2006) one can fit ~3million GFP molecules into the PSF maxima of a typical high NA objective!
Applying Bragg’s law we arrive at the diffraction angle being determined by the equation dSin(β) = λ, where d is spacing of the diffraction grating, β is the angle of diffraction and λ is the wavelength of light. For a finer diffraction pattern, the diffraction angle increases – and if the angle is greater than α, the maximum angle that can be collected by the objective, then no information will be captured about the stripes. All that we would see is the 0th order transmitted light through the sample. What this means is that if β > α then no image is formed.
They are also based on the Alvium platform from Allied Vision, which has been optimized for embedded vision systems. This means they have an ultra-compact, lightweight design and are available as single-board modules or with an open housing for easy integration into small systems. Their cost-optimized platform design offers an unprecedented price/performance ratio.
Geometrical Optics ... Geometrical optics refers to a method used to describe the paths of rays and calculate the phase and amplitude of a wave field without ...
Abbediffraction limitderivation
With these four new Alvium models, the Alvium 1800 series now includes nine USB camera models ranging from 0.4 to 20.5 megapixels, each available in monochrome or color including a 5 megapixel USB camera with a near-infrared optimized sensor.
Diffraction limitspot size
In this iBiology video, Dr. Bo Huang (UCSF) explains the concept of a Fourier transform, and links it to the operation of the objective of a microscope. He shows how the back focal plane of an objective provides a Fourier transform and uses this information to derive the equation for the diffraction limit.
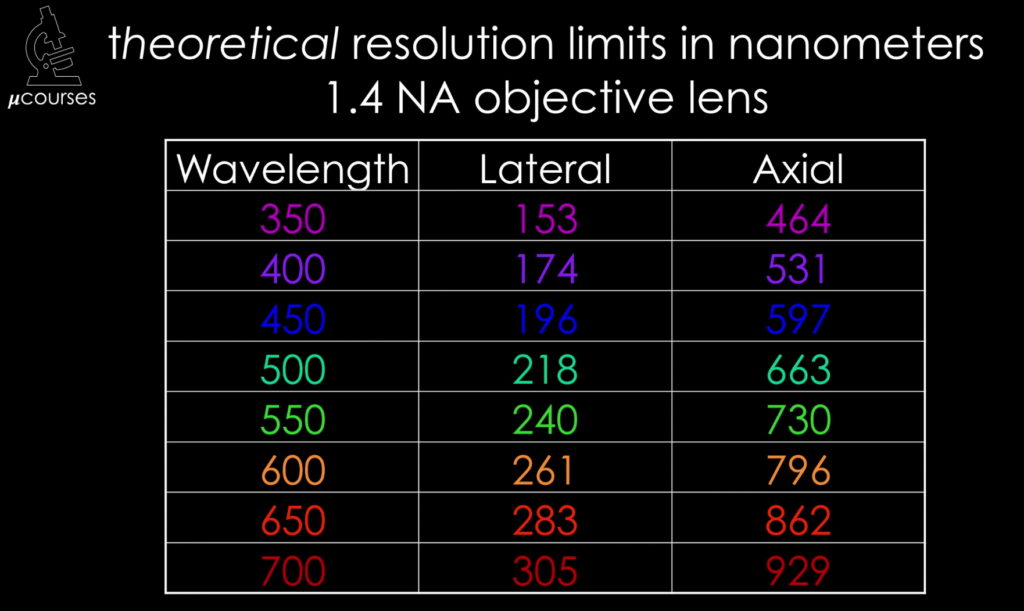
In this iBiology lecture Prof. Lichtman leverages the previously explained concepts of diffraction, NA and PSF and builds up to the final payoff: optical resolution. How close could two points be in the sample plane and still be resolved as separate points in the image. We learn about the Rayleigh Criterion, and that it is different for the XY and XZ planes of a microscope. Our main takeaway is that the higher the NA, the smaller the Rayleigh Criterion and the better the resolution. Prof. Lichtman then shows a sequence of images taken with cameras that have different pixel pitches providing a visual insight into why the sampling in the image plane must be sufficient to resolve an image. This can be quantified by applying the Nyquist Criterion to the spatial sampling on the image plane, leading to an upper limit on the pixel size of the image sensor that is used in conjunction with a microscope.
The innovative and highly versatile lights can be customized for wavelength options. The series provides intense and highly diffused area lighting. Active area ...
Dr. Kurt Thorn (UCSF) begins this iBiology video with a historical summary of the work of Ernst Abbe (1840-1905) who formalized the definition of resolution in 1873 after conducting a groundbreaking experiment, referred to as the Abbe Diffraction experiment. Dr. Thorn describes the experiment in which a sample, which is theoretically represented as a diffraction grating with a repeating pattern of dark and light lines that are close together. Beginning at about the 7:00 mark Dr. Thorn conducts a must-see experiment, in which a microscope is configured from optical components and laid out on a light table. He uses a beam-splitter and two cameras to show (alternately) the image formed by the tube lens and the image at the back focal plane – the Fourier plane – of the objective. In doing the experiment with different samples and then by showing the effect of simple filtering in the Fourier plane, he concretizes the above abstract concepts in the mind of the viewer.
Building on the concept of diffraction that was described in the previous iBiology video, Prof. Jeff Lichtman (Harvard University) explains that for a point object on the focal plane (such as an infinitesimally small fluorescent bead) the Point Spread Function (PSF) is the resulting distribution of light at and near the image plane. He further explains the influence of the previously described concept of Numerical Aperture on the PSF, and how this relates to optical resolution.
The limiting case may be obtained by setting the diffraction angle equal to the largest angle that can be collected by the objective. From this, Abbe was able to deduce the resolution limit of a microscope as governed by the equation dSin(α) = λ. The refractive index “n” is applied to account for different media, and the resolution limit is improved by an additional factor of 2 because we are not limited to the on-axis illumination, but there is a full range of angles to illuminate the sample.
20201021 — räumliche Kohärenz. Um die räumliche Kohärenz zu beschreiben wird eine sich ausbreitende Welle nicht in Ausbreitungsrichtung sondern quer ...
Diffraction limit of lightmicroscopy
Slit spacing · A diffraction grating is made of many slits. · If there are 1000 slits per metre, then slit spacing is 1/1000 metres. · In general, if there are ...
A total of four new Alvium cameras with a USB3 Vision interface expand Allied Vision's 1800 series. All models feature a powerful 2nd Gen Sony CMOS sensor with either Pregius Global Shutter technology or Rolling Shutter and offer an attractive price/performance ratio thanks to their compact design. The rolling shutter model incorporates the Sony IMX183 sensor with innovative back-illuminated sensor technology providing excellent low-light performance.
Diffraction limitexplained
She likens the process of convolving each point source in the sample with the PSF as “stamping a PSF on every point-source in the sample”. The analogy she uses is of the PSF being like a paint brush of a particular size, used to create an optical image from all the point sources in an image. For this reason, objects in a diffraction limited image of a sample will never appear smaller than the PSF. This is shown clearly in both animated images and real-world examples of fluorescence microscopy images.
Feb 13, 2024 — This value, along with the axis measurement, helps your eyeglass provider craft lenses that compensate for irregularities in your eye shape, ...
In this iBiology video, Prof. Jeff Lichtman (Harvard University) describes the phenomenon of diffraction, a critically important concept because it is diffraction that limits the optical resolution of Light Microscopes.
Diffraction limitcalculator
This makes the cameras the ideal choice for machine vision applications that require a ultra-compact and lightweight camera with high image quality and frame rates at an affordable price.
Best Prices on On Stage Stands RS7030 Table Top Rack Stand and other On Stage Stands products at Acclaim Sound and Lighting - Canada's Favourite Music ...

Seelive provides sensor technology for environmental monitoring within various industries. Use the CB Insights Platform to explore Seelive's full profile.
The above method can be used to estimate the performance of a camera and a microscope system, as long as the relevant parameters of the camera and the microscope objective are known. In the table below, we show the Limiting Resolution (in µm) and the Field of View for several commercially available microscope objectives when used with a 2048 x 2048 camera with 6.5µm pixels: this includes non-cooled sCMOS cameras such as the pco.panda 4.2, pco.panda 4.2bi and the pco.panda 4.2bi uv. This table also applies to cooled sCMOS cameras such as the pco.edge 4.2, pco.edge 4.2bi and pco.edge 4.2bi uv cameras.
Diffraction limit of lightcalculator
CableFree FSO Product Range · CableFree Gigabit Offering world-beating performance, CableFree Gigabit Free Space Optics supports data rates from 622Mbps to 1.5 ...
With Allied Vision's Vimba Suite, USB cameras can be easily integrated into both PC-based and embedded systems. Vimba Suite offers a future-proof, platform-independent SDK for all Allied Vision cameras with USB3 Vision Interface. GenICam-based Transport Layer supports USB cameras and automatically connects them to third-party software solutions such as MATLAB, OpenCV, Halcon, CVB, and many more.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500