How to Change Magnification on Stereo Microscopes - microscope eyepiece magnification
Compressed Airfor optics
In contrast, spectacles with prisms of equal power for both eyes, called yoked prisms (also: conjugate prisms, ambient lenses or performance glasses) shift the visual field of both eyes to the same extent.[5]
Each OZPEN is equipped with a flexible coaxial tube, spray pen applicator, and foot switch. The basic system provides precision cleaning capability right out of the box and includes all components for precision cleaning apart from the process gases.
The OZPEN replaces or augments conventional solvent-aided wiping cleaning techniques which can spread, smear, shed, or redeposit trace residues and particles over critical surfaces.
Reflective prisms are used to reflect light, in order to flip, invert, rotate, deviate or displace the light beam. They are typically used to erect the image in binoculars or single-lens reflex cameras – without the prisms the image would be upside down for the user.
Various thin-film optical layers can be deposited on the hypotenuse of one right-angled prism, and cemented to another prism to form a beam-splitter cube. Overall optical performance of such a cube is determined by the thin layer.
Best way to cleanoptics
Depolarization would not be observed for an ideal monochromatic plane wave, as actually both devices turn reduced temporal coherence or spatial coherence, respectively, of the beam into decoherence of its polarization components.
Reflective prisms use total internal reflection to achieve near-perfect reflection of light that strikes the facets at a sufficiently oblique angle. Prisms are usually made of optical glass which, combined with anti-reflective coating of input and output facets, leads to significantly lower light loss than metallic mirrors.
Another class is formed by polarizing prisms which use birefringence to split a beam of light into components of varying polarization. In the visible and UV regions, they have very low losses and their extinction ratio typically exceeds 10 5 : 1 {\displaystyle 10^{5}:1} , which is superior to other types of polarizers. They may or may not employ total internal reflection;
By shifting corrective lenses off axis, images seen through them can be displaced in the same way that a prism displaces images. Eye care professionals use prisms, as well as lenses off axis, to treat various orthoptics problems:
Bestcleaning system for critical optics
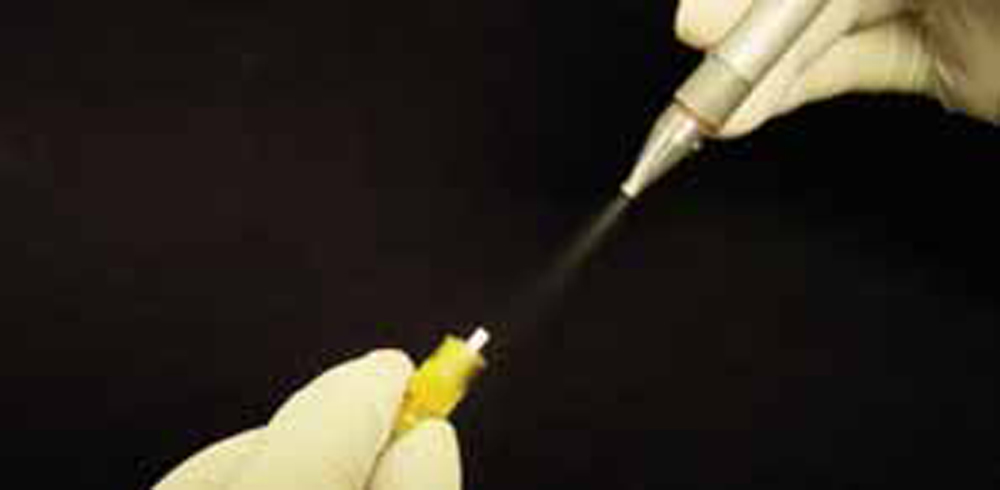
How to clean dichroic mirror
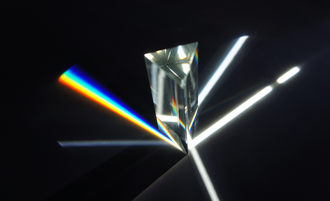
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite.
Spectral dispersion is the best known property of optical prisms, although not the most frequent purpose of using optical prisms in practice.
Thin film organic contamination may also be removed by CO2 composite snow cleaning. To remove organic species they must be soluble in liquid CO2. Typical light oils are good candidates for CO2 cleaning.
In comparison with a usual glass substrate, the glass cube provides protection of the thin-film layer from both sides and better mechanical stability. The cube can also eliminate etalon effects, back-side reflection and slight beam deflection.
Prism spectacles with a single prism perform a relative displacement of the two eyes, thereby correcting eso-, exo, hyper- or hypotropia.
Prisms made of isotropic materials like glass will also alter polarization of light, as partial reflection under oblique angles does not maintain the amplitude ratio (nor phase) of the s- and p-polarized components of the light, leading to general elliptical polarization. This is generally an unwanted effect of dispersive prisms. In some cases this can be avoided by choosing prism geometry which light enters and exits under perpendicular angle, by compensation through non-planar light trajectory, or by use of p-polarized light.
The composite spray cleaning technique is a patented process where one can deliver controlled shear stress on surface contaminants using the chemically active, dry CO2 spray for efficient and effective removal of inorganic and organic surface contamination from critical substrate surfaces.
The main method for removal of particulate and other loosely bound contaminants is momentum transfer. In this process, an incoming CO2 particle strikes a particle on the surface. The resulting force overcomes the force holding the particle to the surface, and the CO2 gas spray/propellant plume then carries the particle away. This unique dry process can remove very small particles (< 100 nm in size) without the need for using other wet cleaning techniques.
The OZPEN is a versatile small surface area precision cleaning system for critical fibre optics and other small components. The OZPEN generates and propels an adjustable spray of clean dry air or nitrogen containing small CO2 'dry ice' particles to efficiently remove foreign matter from a surface.
The solid CO2 spray within the plume is at a temperature of around -78 °C. The cooling properties of CO2 can be used to remove contaminant with high water content, first by freezing, then by fracturing it from the underlying substrate.
The cleaning unit delivers a precisely controlled accelerated stream of solid carbon dioxide particles at high velocity. This snow is created from the conversion of liquid CO2 to solid CO2 particles and CO2 gas at the spray nozzle. The nozzle, propellant pressure, and temperature can be adjusted for an optimal cleaning process.
Dispersive prisms are used to break up light into its constituent spectral colors because the refractive index depends on wavelength; the white light entering the prism is a mixture of different wavelengths, each of which gets bent slightly differently. Blue light is slowed more than red light and will therefore be bent more than red light.
These are typically made of a birefringent crystalline material like calcite, but other materials like quartz and α-BBO may be necessary for UV applications, and others (MgF2, YVO4 and TiO2) will extend transmission farther into the infrared spectral range.
A dispersive prism can be used to break white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) to form a spectrum as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflect light, or to split light into components with different polarizations.
Total internal reflection alters only the mutual phase between s- and p-polarized light. Under well chosen angle of incidence, this phase is close to π / 4 {\displaystyle \pi /4} .




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500