He-Ne Lasers - ne laser
\[ \sin \theta _ { 1 } = \frac { n \sin \alpha } { \sqrt { 2 ( 1 + \cos \alpha ) } } = n \sin \frac { 1 } { 2 } \alpha. \label{eq:1.6.4} \]
Uses ofprism inoptometry
Selection of Hex Keys / Allen Wrenches. Various Types & Sizes. Available in Standard or Metric. Begin filtering to find your part.
Thorlabs offers a diverse range of polarizers, including wire grid, film, calcite, alpha-BBO, rutile, and beamsplitting polarizers. Collectively, our line of wire grid polarizers offers coverage from the visible range to the beginning of the Far-IR range. Our nanoparticle linear film polarizers provide extinction ratios as high as 100 000:1. Alternatively, our other film polarizers offer an affordable solution for polarizing light from the visible to the Near-IR. Next, our beamsplitting polarizers allow for use of the reflected beam, as well as the more completely polarized transmitted beam. Finally, our alpha-BBO (UV), calcite (visible to Near-IR), rutile (Near-IR to Mid-IR), and yttrium orthovanadate (YVO4) (Near-IR to Mid-IR) polarizers each offer an exceptional extinction ratio of 100 000:1 within their respective wavelength ranges.
Types ofprism in optics
Again, the rate of change of deviation with angle of incidence is least near minimum deviation, and consequently we may see another halo, of radius about 46°. For both haloes, the violet is deviated more than the red, and therefore both haloes are tinged violet on the outside and red on the inside.
Properties ofprism in optics
The angle of minimum deviation \(D_{\text{min}}\) is \(2\theta_1 − \alpha\), where \(\theta_1\) is given by Equation \(\ref{eq:1.6.4}\), and this leads to the following relation between the refractive index and the angle of minimum deviation:
When hexagonal ice crystals are present in the atmosphere, sunlight is scattered in all directions, according to the angles of incidence on the various ice crystals (which may or may not be oriented randomly). However, the rate of change of the deviation with angle of incidence is least near minimum deviation; consequently much more light is deviated by 21°.8 than through other angles. Consequently we see a halo of radius about 22° around the Sun.
What isprism inPhysics
The IR illuminator lights the scene with infrared light and the camera sees in low-light conditions. The small size allows easy hiding in clocks, smoke ...
\[ \frac{\sin\theta_1}{\sin\phi_1} =n \quad \text{and} \quad \frac{\sin\theta_2}{\sin(\alpha - \phi_1)}=n, \label{eq:1.6.2a,b} \]
Of particular interest are prisms with \(\alpha\) = 60° and \(\alpha\) = 90°. I have drawn, in Figure I.12 the deviation versus angle of incidence for 60- and 90-degree prisms, using (for reasons I shall explain) \(n = 1.31\), which is approximately the refractive index of ice. For the 60° ice prism, the angle of minimum deviation is 21°.8, and for the 90° ice prism it is 45°.7.
I have drawn just one ray of a single color. For white light, the colors will be dispersed, the violet light being deviated by the prism more than the red light. We’ll choose a wavelength such that the refractive index of the prism is \(n\). The deviation D of the light from its original direction is \(\theta_1 − \phi_1 + \theta_2 − \phi_2\). I want to imagine, now, if we keep the incident ray fixed and rotate the prism, how does the deviation vary with angle of incidence \(\theta_1\)? By geometry, \(\phi_2 = \alpha − \phi_1\), so that the deviation is
C-mount 1.1" Lenses. Teledyne FLIR offers a selection of lenses for your convenience so you can start imaging right away. Selecting a lens can be challenging ...
Jun 4, 2024 — How to calculate a laser beam expander's magnification. The effect of the expander on beam size and divergence. How to calculate the size of the ...
How to useprism in optics
Glassprism in optics
The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Legal. Accessibility Statement For more information contact us at info@libretexts.org.
Since the wire grid is prone to damage, the protective glass cover serves to reduce this risk. In addition, the glass surfaces may be cleaned, which extends the typical working lifetime when compared to unprotected wire grid polarizers.
... vaginal and urinary tracts essential for a healthy urogenital system. They also help to prevent and manage common urogenital conditions such as vagina yeast ...
To explore the available types, wavelength ranges, extinction ratios, transmission, and available sizes for each polarizer category, click More [+] in the appropriate row below.
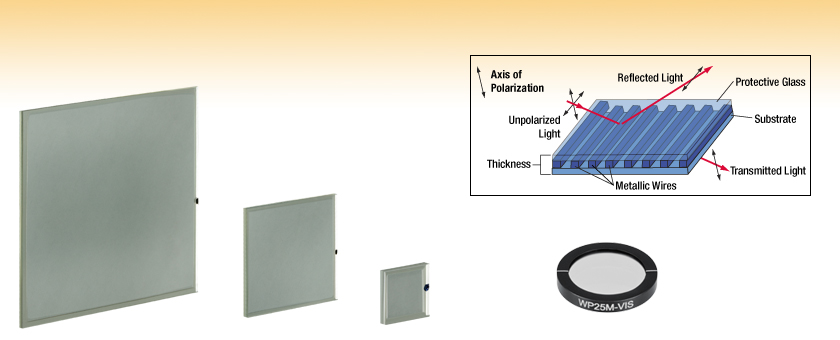
These polarizers consist of an array of parallel metallic wires sandwiched between an Eagle XG®* (-VIS) glass substrate. Featuring high transmission and operating temperatures up to 200 °C (unmounted), wire grid polarizers are an alternative to both traditional film-based polarizers and holographic wire grid polarizers. Additionally, our -VIS wire grid polarizers have an antireflection coating deposited on the back of substrate as well as on both sides of the cover glass.
Opticalprismglasses
Wire grid polarizers transmit radiation with an electric field vector perpendicular to the wire and reflect radiation with the electric field vector parallel to the wire. The direction of polarized transmitted light is marked by a small dot on the square polarizers and by a line on the round polarizers (see diagrams to the upper right). Due to surface reflections, the reflected beam contains both polarizations. Please note that the mark on these wire grid polarizers indicates the axis of polarization and not the orientation of the wires (see the diagrams to the upper right).
Laser light is a form of non-ionizing radiation. Laser equipment produces and amplifies light that has unique properties that cannot be produced any other way.
Uses ofprism in optics
Seen sideways on, a hexagonal crystal is rectangular, and consequently refraction is as if through a 90° prism (Figure I.14):
Equations \(\ref{eq:1.6.1}\) and \(\ref{eq:1.6.3}\) enable us to calculate the deviation as a function of the angle of incidence \(\theta_1\). The deviation is least when the light traverses the prism symmetrically, with \(\theta_1 = \theta_2\), the light inside the prism then being parallel to the base. Putting \(\theta_1 = \theta_2\) in equation shows that minimum deviation occurs for an angle of incidence given by
If you're a landlord, you've probably wondered, Why is it so hard to find good cleaners near me? With the new AllBetter app, it's a lot easier.
I use a version of number 1 because I ware glasses and #1 works with glasses. I set it up for maximum magnification and never change it. Once in a while I use ...
May 26, 2004 — Hmmm... can't say I'd noticed. As far as I (a British English speaker) am concerned its 'lens' in the singular and 'lenses' in the plural. What ...
These Heathrow Scientific Plastic Disposable Forceps feature a corrugated handle and serrated tips. Disposable forceps come in a pack of six. Key Features.
This page titled 1.6: Refraction by a Prism is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jeremy Tatum via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500