FS-70 - fs70

FOV meaningin gaming
The brain has 100 billion nerve cells (neurons). Each nerve cell connects with many others to form communication networks. Groups of nerve cells have special jobs. Some are involved in thinking, learning and remembering. Others help us see, hear and smell.
In 1906, German physician Dr. Alois Alzheimer first described "a peculiar disease" — one of profound memory loss and microscopic brain changes — a disease we now know as Alzheimer's. Today, Alzheimer's is at the forefront of biomedical research. Researchers are working to uncover as many aspects of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias as possible. Some of the most remarkable progress has shed light on how Alzheimer's affects the brain. The hope is this better understanding will lead to new treatments. Many potential approaches are currently under investigation worldwide. Sign up for our weekly E-News to receive updates about Alzheimer’s and dementia care and research. Learn more: Research and Progress
Fov meaningmedical
It's the destruction and death of nerve cells that causes memory failure, personality changes, problems carrying out daily activities and other symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Learn More: Take the Brain Tour

Many people have trouble with memory — this does NOT mean they have Alzheimer's. There are many different causes of memory loss. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of dementia, it is best to visit a doctor so the cause can be determined.
People with memory loss or other possible signs of Alzheimer’s may find it hard to recognize they have a problem. Signs of dementia may be more obvious to family members or friends. Anyone experiencing dementia-like symptoms should see a doctor as soon as possible. If you need assistance finding a doctor with experience evaluating memory problems, your local Alzheimer's Association can help. Earlier diagnosis and intervention methods are improving dramatically, and treatment options and sources of support can improve quality of life. Two helpful support resources you can tap into are ALZConnected, our message boards and online social networking community, and Alzheimer's Navigator, a web tool that creates customized action plans, based on answers you provide through short, online surveys.
FOV meaningFortnite
The most common early symptom of Alzheimer's is difficulty remembering newly learned information. Just like the rest of our bodies, our brains change as we age. Most of us eventually notice some slowed thinking and occasional problems with remembering certain things. However, serious memory loss, confusion and other major changes in the way our minds work may be a sign that brain cells are failing. Alzheimer's changes typically begin in the part of the brain that affects learning. As Alzheimer's advances through the brain it leads to increasingly severe symptoms, including disorientation, mood and behavior changes; deepening confusion about events, time and place; unfounded suspicions about family, friends and professional caregivers; more serious memory loss and behavior changes; and difficulty speaking, swallowing and walking.
Alzheimer's has no cure, but two treatments — donanemab (Kisunla™) and lecanemab (Leqembi®) — demonstrate that removing beta-amyloid, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease, from the brain reduces cognitive and functional decline in people living with early Alzheimer’s. Other treatments can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms and improve quality of life for those with Alzheimer's and their caregivers. Today, there is a worldwide effort underway to find better ways to treat the disease, delay its onset and prevent it from developing.
By pressing submit, your feedback will be used internally to improve Sierra-Olympia products and services. Privacy Policy
Alzheimer's is a type of dementia that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. Symptoms eventually grow severe enough to interfere with daily tasks. Subscribe to E-News to learn how you can help those affected by Alzheimer's. Understanding Alzheimer's and dementia Plaques and tangles Symptoms Research Changes in the brain
FOVcamera
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with Alzheimer's or another dementia, you are not alone. The Alzheimer's Association is the trusted resource for reliable information, education, referral and support to millions of people affected by the disease. Call our 24/7 Helpline: 800.272.3900 Locate your local Alzheimer's Association Go to Alzheimer's Navigator to create customized action plans and connect with local support services
To do their work, brain cells operate like tiny factories. They receive supplies, generate energy, construct equipment and get rid of waste. Cells also process and store information and communicate with other cells. Keeping everything running requires coordination as well as large amounts of fuel and oxygen.
If we were to look at the Vayu HD with a 50 millimeters lens and a 25 millimeter lens, the 25mm lens has one half the focal length of the 50mm, and therefore again, it will roughly double the field of view if I install the 25mm lens instead of the 50 millimeters lens.
FOV meaningSlang
Field of view describes the entire extent of the whole image that is being detected by an infrared thermal imaging system. It can be stated in terms of the angle, the extent of the angle, starting from your imager out into the scene. Or it can be described as the linear extent of the scene at some distance from the imager. Instantaneous field of view, or IFOV, as we call it, is the angle subtended by just a single pixel in your detector array out into the scene. This can be calculated as the pixel size divided by the focal length.
Field of view depends on the application. If we decrease the focal length, we will increase the overall field of view, but we will also increase that number I talked about earlier, the instantaneous field of view, the IFOV. That has the effect of lowering the spatial resolution down at the level of the individual pixel. That may be okay for some applications, situational awareness applications that just rely mostly on a big picture view of a scene, for example. On the other hand, there can be applications where you want a large field of view, but you also want to maintain spatial resolution. In that case, the way you would increase field of view would be to increase the detector array size. That would provide a larger field of view while maintaining the same spatial resolution as before. These are the kinds of considerations that we can help you work out in deciding how to use an infrared imaging system in which system to choose.
Field of view human eye
Take our free, online education courses: Understanding Alzheimer's and Dementia and Know the 10 Signs: Early Detection Matters
Scientists do not know exactly what role plaques and tangles play in Alzheimer's disease. Most experts believe they somehow play a critical role in blocking communication among nerve cells and disrupting processes that cells need to survive.
Field of view definition microscope
Alzheimer's is the most common cause of dementia, a general term for memory loss and other cognitive abilities serious enough to interfere with daily life. Alzheimer's disease accounts for 60-80% of dementia cases.
Field of viewmeaning
Though autopsy studies show that most people develop some plaques and tangles as they age, those with Alzheimer’s tend to develop far more and in a predictable pattern, beginning in the areas important for memory before spreading to other regions.
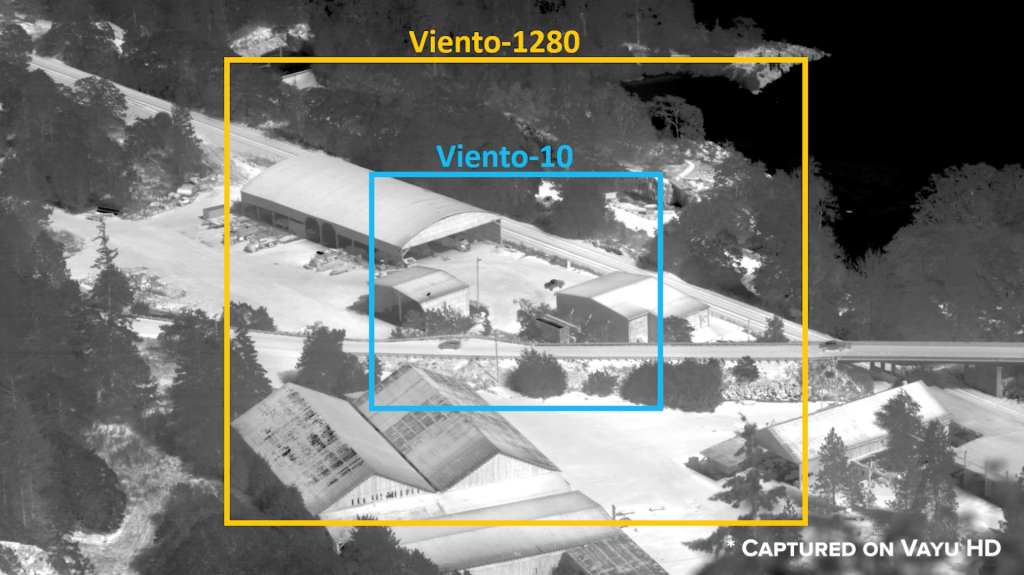
There are two knobs that we have that we can turn to adjust this. One is the size of the detector array in the system, and the other is the focal length of the lens that we put on the system. Let’s talk about detector array size first. Let’s assume that we have the same focal length lens on this on these two cameras to take that out of consideration. This is the Viento-10, which has a 640 pixel array of ten micron pixels. This is the Viento 1280 (figure 1), which has the same ten micron pixels, but it has twice as many pixels in width, 1280 pixels in width. So its detector array is twice as large as the Viento-10 with a detector array twice as large as the Viento- 10 (figure 1). The Viento 1280 has roughly twice the field of view as the Viento-10 (figure 2). Notice so far I’m just talking in terms of the detector array with 640. In the case of the Viento-10, 1280 pixels in the case of the Viento 1280 detector arrays usually have a different height than they do width. That means they also have a vertical field of view that can be calculated. But for simplicity of this discussion, I’m just going to talk about the horizontal field of view.
Alzheimer's is not a normal part of aging. The greatest known risk factor is increasing age, and the majority of people with Alzheimer's are 65 and older. Alzheimer’s disease is considered to be younger-onset Alzheimer’s if it affects a person under 65. Younger-onset can also be referred to as early-onset Alzheimer’s. People with younger-onset Alzheimer’s can be in the early, middle or late stage of the disease.
Welcome back to Ask an Expert. I’m Stan Voynick, Chief Technology Officer at Sierra-Olympia Technologies. Today, we’ll be discussing field of view and instantaneous field of view, how they work together to form the thermal images in airborne systems, security and surveillance, optical gas imaging, and other thermal imaging applications. Three of the most important factors we consider when we’re designing a thermal imaging system are field of view, aperture and spectral response. I’ll be going over some questions about Field of View and closely related cousin instantaneous field of view.
© 2024 Alzheimer's Association®. | All rights reserved. | Alzheimer's Association is a not-for-profit 501(c)(3) organization.
Scientists believe Alzheimer's disease prevents parts of a cell's factory from running well. They are not sure where the trouble starts. But just like a real factory, backups and breakdowns in one system cause problems in other areas. As damage spreads, cells lose their ability to do their jobs and, eventually die, causing irreversible changes in the brain.
Learn more: Younger/Early-Onset Alzheimer's, Risk Factors Alzheimer's worsens over time. Alzheimer's is a progressive disease, where dementia symptoms gradually worsen over a number of years. In its early stages, memory loss is mild, but with late-stage Alzheimer's, individuals lose the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to their environment. On average, a person with Alzheimer's lives 4 to 8 years after diagnosis but can live as long as 20 years, depending on other factors.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500