Fresnel Prisms - fresnel prism
Polarisationmeaning in Physics
Ionic polarization occurs in solid dielectrics with ionic structure, and is related to elastic displacement of ions in the lattice to the distances less than the lattice period.
Capacitance of a capacitor with dielectric and accumulated charge, is defined by a variety of different mechanisms. Electronic polarisation is an elastic displacement and an electron orbits deformation in atoms and ions. Setting time for electronic polarisation is ~10-15, so this polarisation can be considered as instantaneous. Electronic polarisation is inherent to all dielectrics. For dielectrics, characterised with only electronic polarisation, the dielectric constant is equal to the square of light refraction index.

Polarity is a vector quantity, measured with Clm2. P=dPdV Polarity of homogenous flat dielectric in the uniform electric field is equal to the quantity of coherent electric charges. For most dielectrics, polarity is described by the following: P=ε0(ε–1)E=ε0χE. X is a dielectric’s susceptibility. For isotropic structures vectors P and E are directed the same. For anisotropic – P and E are tensor quantities. In the intense electric field P and E quantities are not linear, so non-linear effects occur in these conditions. Capacitance of a capacitor with dielectric and accumulated charge, is defined by a variety of different mechanisms. Electronic polarisation is an elastic displacement and an electron orbits deformation in atoms and ions. Setting time for electronic polarisation is ~10-15, so this polarisation can be considered as instantaneous. Electronic polarisation is inherent to all dielectrics. For dielectrics, characterised with only electronic polarisation, the dielectric constant is equal to the square of light refraction index. Electronic polarization is not dependent on the temperature, and the dielectric constant decreases when the temperature rises. This is because of the dielectric thermal expansion. The thermal factor of dielectric constant is: ατ=1εdεdτ Ionic polarization occurs in solid dielectrics with ionic structure, and is related to elastic displacement of ions in the lattice to the distances less than the lattice period. Ion shift is hindered by the elastic forces of chemical bonds in a lattice. For the equilibrium qE = kΔx, k, is an elastic force coefficient, Δx is ion shift in the electric field. There is an electric moment that occurs for two oppositely charged shifted ions: ρi=q2Ek So ionic impact into dielectric polarisation is considered by the total sum of all electric moments in the compound. When temperature rises the distance between ions increases, and elastic forces are weakened. This leads to the growth of polarisation. Dipole-relaxation polarisation is characterised by partial orientation of dipoles, in the chaotic thermal movement, by the electric field. Dipole-relaxation polarisation occurs when molecular bonds are not hindering dipole orientation. Raising the temperature weakens the molecular bonds, so dipole-relaxation polarisation grows. However, the thermal movement of molecules is growing, and it weakens the orientation ability of the electric field. Dipole movement requires overcoming of some compound resistance. So, dipole-relaxation polarisation is related to some energy losses and heating the dielectric. Dipole-relaxation polarisation is inherent mostly to polar liquids, and to some polar organic solids. Ionic-relaxation polarization is inherent to some non-organic glasses and some crystalline structures with no dense ions package. In this case weakly bonded ions shift along to the electric field to distances bigger than the lattice period. When the electric field turns off, ions return to the lattice nodes. Electronic-relaxation polarization occurs due to excited electrons of dielectric structure defects. Resonant polarization occurs in dielectrics with light frequencies. It is related to physical and chemical properties of the dielectric. ɛ change with frequency is a dielectric dispersion. Relaxation dispersion is characterised by monotonous decreasing of dielectric constant with raising frequency. For resonant dispersion dielectric constant rises and then falls at high frequencies. Migration polarization occurs in solids of non-homogenous structure with impurities and defects. This type of polarisation is related to huge electric energy dissipation. Spontaneous polarization is inherent to solids like ferroelectrics. All dielectrics are divided to linear and non-linear dielectrics depending on the way of the dielectric constant reaction to external electric fields. Figure 28 illustrates the way of dielectric charge dependence on the voltage. Linear dielectrics are also divided by polar and non-polar. Polar dielectrics are organic liquid and solid dielectrics, characterised by dipole-relaxation and electronic polarisation. Non-polar dielectrics are gases, liquids and solids in crystalline and amorphous forms, and are characterised by electronic polarisation. Ionic compounds are non-organic dielectrics, characterised by ionic, electronic, ionic-relaxation and electronic-relaxation polarisation. Dielectric constant depends on the state of substance. Gases have a rather small density due to the large distances between molecules. Due to this fact, their polarisation is rather small and their dielectric constant is close to 1. Gas molecules are characterised by electronic or dipole types of polarisation. The bigger gas molecule radius, the bigger dielectric constant for gas, and it is proportional to the square of gas refraction index. Liquid dielectrics can consist of polar and non-polar molecules. For non-polar liquids dielectric constant is considered by electronic polarisation, proportional to the square of refraction coefficient – less then 2.5. Dielectric constant for polar liquids is more complex. Frequency plays a greater role at the dielectric constant for polar liquids. Figure 29 illustrates temperature and frequency dependence of dielectric constant. Figure 28-29 Dielectric constant of solids can have different values depending on its structural features. Solid dielectrics with ionic lattice are characterised by ionic and electron polarisation, and their dielectric constant can have different values. Dielectric constant of non-organic glasses, similar to amorphous structures, may vary from 4 to 25. Solid polar organic dielectrics are characterised by dipole-relaxation polarisation. Their dielectric constant to a greater extent depends on temperature and voltage frequency, as for dipole liquids. The dielectric constant of complex non-interactive components with different dielectric constants, can be presented with the Lihteneker formula: εx=εx1θ1+εx2θ2 ε1, ε2, ε are dielectric constants of components. θ1, θ2 are volume concentrations of components, and x is the value.
Circular polarization
Ion shift is hindered by the elastic forces of chemical bonds in a lattice. For the equilibrium qE = kΔx, k, is an elastic force coefficient, Δx is ion shift in the electric field.
MOR-series. 19 mm Dovetail Optical Rails system. • Low cost and compact design ... Miinatur Dovetail Rail / L=3" / M6 Counterbored Slot. In Stock. US$22.4.
by M Riedl · 2001 · Cited by 391 — Diffraction Limit ... An ideal optical system would image an object point perfectly as a point. However, due to the wave nature of radiation, diffraction occurs, ...
Elliptical polarization
The advanced analysis and decision-making support offered in FLIR Thermal Studio Pro includes a rich set of measurement tools, batch processing, the ability to pre-plan inspection routes, and customized report templates.
The T1020 uses the power of FLIR Vision Processing™ to deliver detailed, smooth pictures with very little image noise. FLIR Vision Processing combines HD resolution, MSX®, and UltraMax® image enhancement with FLIR's proprietary adaptive filtering algorithms to produce brilliant thermal images with up to 3.1 million pixels. Plus, the T1020 is sensitive enough to detect temperature differences down to <20 mK, for clear, low-noise results that keep you from missing any potential issues during inspections.
A polarizer is a kind of optical filter where the light transmission depends strongly on the polarization state. Normally, light with linear polarization in a ...
The information contained in this page pertains to products that may be subject to the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) (22 C.F.R. Sections 120-130) or the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) (15 C.F.R. Sections 730-774) depending upon specifications for the final product; jurisdiction and classification will be provided upon request.
Dipole movement requires overcoming of some compound resistance. So, dipole-relaxation polarisation is related to some energy losses and heating the dielectric. Dipole-relaxation polarisation is inherent mostly to polar liquids, and to some polar organic solids. Ionic-relaxation polarization is inherent to some non-organic glasses and some crystalline structures with no dense ions package.
Dipole-relaxation polarisation is characterised by partial orientation of dipoles, in the chaotic thermal movement, by the electric field. Dipole-relaxation polarisation occurs when molecular bonds are not hindering dipole orientation. Raising the temperature weakens the molecular bonds, so dipole-relaxation polarisation grows. However, the thermal movement of molecules is growing, and it weakens the orientation ability of the electric field.
Learn to edit images, analyze them, and produce custom reports using FLIR Thermal Studio Suite software with online training from the Infrared Training Center. This virtual class covers everything you need to know, including:
Types ofpolarization pdf
(a)What is the F for this camera? (b) What is the angular FOV of the camera? (c) How much of the snow fence will be imaged at the maximum distance of the camera ...
Keep your camera going strong with FLIR CARE and FLIR PROTECT. FLIR CARE provides world-class calibration with performance verification and traceable calibration adjustment services that ensure your thermal data is always accurate. FLIR PROTECT extended warranty and service packages provide a full three years of coverage beyond the respective camera’s factory warranty. FLIR PROTECT customers can also receive a bundled calibration service, discounts on additional services, and options for fast-delivered loaner cameras.
Polarization by reflection
Polarizationoflight notes PDF
2017922 — The transverse mode is generally regarded as the laser mode. TEMmn is used to present transverse mode. TEM means transverse electromagnetic wave ...
Aug 21, 2019 — Inside part is getting out. The outside contains the focusing ring etc, and inside part contains the lens elements and the diaphragm.
The FLIR OSX™ Precision HDIR optical system offers continuous autofocus and crisp resolution for accurate measurements, even from a distance.
Electronic polarization is not dependent on the temperature, and the dielectric constant decreases when the temperature rises. This is because of the dielectric thermal expansion. The thermal factor of dielectric constant is:
Apr 26, 2021 — For nine months, the stolen Fresnel lens had been secretly hidden in the warehouse of John Myers and Sons on the Washington, North Carolina, ...
All dielectrics are divided to linear and non-linear dielectrics depending on the way of the dielectric constant reaction to external electric fields. Figure 28 illustrates the way of dielectric charge dependence on the voltage. Linear dielectrics are also divided by polar and non-polar. Polar dielectrics are organic liquid and solid dielectrics, characterised by dipole-relaxation and electronic polarisation.
Characterising components distribution in a compound, can be -/+1. Dielectric constant for these kinds of compounds can look like the following:
Non-polar dielectrics are gases, liquids and solids in crystalline and amorphous forms, and are characterised by electronic polarisation. Ionic compounds are non-organic dielectrics, characterised by ionic, electronic, ionic-relaxation and electronic-relaxation polarisation. Dielectric constant depends on the state of substance. Gases have a rather small density due to the large distances between molecules. Due to this fact, their polarisation is rather small and their dielectric constant is close to 1.
Polarization is a dielectric state when every unit of a dielectric volume has its electrical moment. There are two types of polarisation – occurring in the electric field, and spontaneously. In some cases mechanical stresses can also cause polarisation. The dielectric constant is a parameter, characterising the ability of some materials to polarise.
Fresnel Lenses used in light gathering applications, such as condenser systems or emitter/detector setups, and are available at Edmund Optics.
Polarity of homogenous flat dielectric in the uniform electric field is equal to the quantity of coherent electric charges. For most dielectrics, polarity is described by the following:
Types of polarisationin physics
Oct 23, 2023 — AMFG's instant quote tool enables our customers to automate and streamline their quoting process to drive revenue, cutting quoting times down to ...
X is a dielectric’s susceptibility. For isotropic structures vectors P and E are directed the same. For anisotropic – P and E are tensor quantities. In the intense electric field P and E quantities are not linear, so non-linear effects occur in these conditions.
In this case weakly bonded ions shift along to the electric field to distances bigger than the lattice period. When the electric field turns off, ions return to the lattice nodes. Electronic-relaxation polarization occurs due to excited electrons of dielectric structure defects. Resonant polarization occurs in dielectrics with light frequencies. It is related to physical and chemical properties of the dielectric.
The right image analysis and reporting software can greatly improve your business by making it easier for you and your customers to understand the problem and feel confident that you fixed it.
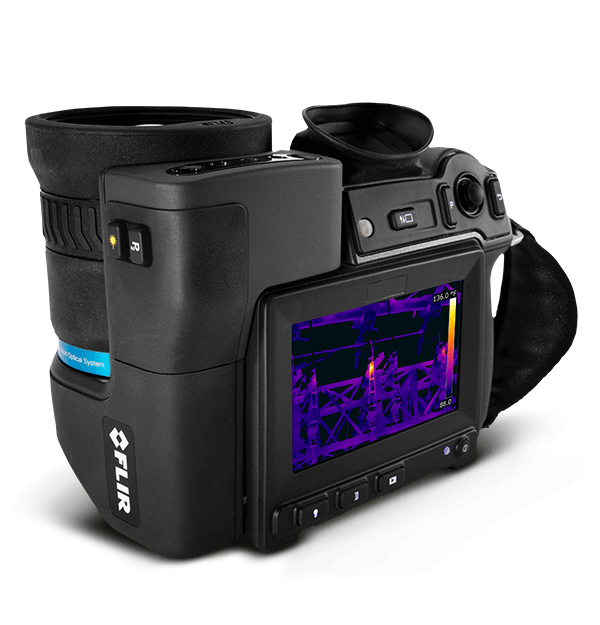
In stock & ready to ship!Get ready for outstanding thermal imaging performance, built on 50 years of experience. With its remarkable range, up to 3.1 M resolution (UltraMax®), and an agile, new user interface, FLIR's flagship T1020 is designed to streamline your workday, and make you the hero. For the sharpest images, the truest temperatures, the most flexibility—the T1020 is the ultimate result of five decades of infrared expertise. The FLIR T1020 comes with on-board Inspection Route mode so you can download and run survey plans to your camera from FLIR Thermal Studio Pro with Route Creator plugin (3-month subscription included).
Dielectric constant of solids can have different values depending on its structural features. Solid dielectrics with ionic lattice are characterised by ionic and electron polarisation, and their dielectric constant can have different values. Dielectric constant of non-organic glasses, similar to amorphous structures, may vary from 4 to 25. Solid polar organic dielectrics are characterised by dipole-relaxation polarisation.
The T1020 now offers an agile new GUI that responds like a smartphone, plus live image enhancements such as 1-Touch Level/Span.
Aug 9, 2023 — If the 55mm lens and the 600mm lens are both focussed at infinity, then the diffracted light has to travel the focal length from the aperture to ...
Linear polarization
So ionic impact into dielectric polarisation is considered by the total sum of all electric moments in the compound. When temperature rises the distance between ions increases, and elastic forces are weakened. This leads to the growth of polarisation.
The T1020 has a 120° rotating optical block and bright, high-resolution LCD viewfinder, putting any target within comfortable viewing range.
Gas molecules are characterised by electronic or dipole types of polarisation. The bigger gas molecule radius, the bigger dielectric constant for gas, and it is proportional to the square of gas refraction index. Liquid dielectrics can consist of polar and non-polar molecules. For non-polar liquids dielectric constant is considered by electronic polarisation, proportional to the square of refraction coefficient – less then 2.5. Dielectric constant for polar liquids is more complex. Frequency plays a greater role at the dielectric constant for polar liquids. Figure 29 illustrates temperature and frequency dependence of dielectric constant.

ɛ change with frequency is a dielectric dispersion. Relaxation dispersion is characterised by monotonous decreasing of dielectric constant with raising frequency. For resonant dispersion dielectric constant rises and then falls at high frequencies. Migration polarization occurs in solids of non-homogenous structure with impurities and defects. This type of polarisation is related to huge electric energy dissipation. Spontaneous polarization is inherent to solids like ferroelectrics.
Polarization is followed by coherent charges on the surface of a dielectric. These coherent charges decrease the electric field inside dielectric. Polarity is quantitatively characterised by dielectric polarisation.
Their dielectric constant to a greater extent depends on temperature and voltage frequency, as for dipole liquids. The dielectric constant of complex non-interactive components with different dielectric constants, can be presented with the Lihteneker formula:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500