Fiber connector options of fiber cables - fiber fc connector

A 36° beam angle is slightly narrower, making it ideal for more focused lighting applications. This angle is frequently used in gallery lighting, where focused illumination is needed to highlight specific areas or objects. Due to its narrower spread, a 36° angle delivers more concentrated light, enhancing details and textures. It’s often used in retail displays and accent lighting where creating visual interest is key.
Radiopaque contrast agents are often used in radiography and fluoroscopy to help delineate borders between tissues with similar radiodensity. Most contrast ...
The above mentioned factors plays a vital role in determining the degree of charge separation within a bond, contributing to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Choosing the right beam angle is key to achieving the best lighting results. Beam angles determine how light spreads across a space, impacting the room’s ambiance and functionality. This guide will break down what beam angles mean, how to calculate them, and provide practical tips for selecting the best one for your needs, whether you’re a homeowner, interior designer, or lighting professional.
Selecting the wrong beam angle can lead to issues such as over-lighting, creating harsh shadows, or insufficient coverage. Here are some common mistakes and tips for avoiding them:
In chemistry, polar substances have an uneven distribution of charge, leading to a dipole moment, while nonpolar substances exhibit an even distribution of charge.
Polarizing power of anion
In contrast, nonpolar molecules like carbon dioxide boast a symmetrical arrangement of atoms, resulting in the absence of a net dipole moment. The role of molecular geometry becomes crucial in determining the overall polarity of the molecule.
Molecular polarity refers to the overall distribution of charge within a molecule, arising from the combination of individual bond polarities and the molecular geometry. A molecule is considered polar if it contains at least one polar bond, and its overall structure leads to an uneven distribution of electron density.
A 120° beam angle offers wide coverage, making it ideal for ambient lighting in large spaces. This wide angle floods a room with light, ensuring even illumination across the area. It’s perfect for general lighting in expansive spaces like living rooms, large offices, and outdoor areas. Because of the broad spread, a 120° beam angle is commonly used in fixtures meant for ambient or overhead lighting.
A 40° beam angle offers a medium spread that balances light intensity and coverage. This angle is well-suited for general lighting in mid-sized spaces, as it delivers an even spread of light without overwhelming intensity. Common applications for a 40° beam angle include accent lighting, such as spotlighting artwork or illuminating specific areas in a room. This angle is also versatile enough to work in both residential and commercial settings, providing a focused yet balanced light spread.
Chemical property of polarity refers to the uneven distribution of charge within a molecule, influencing its interactions with other molecules and affecting properties such as solubility and boiling points.
Define polarization in chemistryclass 12
Knight Optical offers a range of custom Fresnel lenses made from PMMA Acrylic or glass. Available as a plastic or large Fresnel lens.
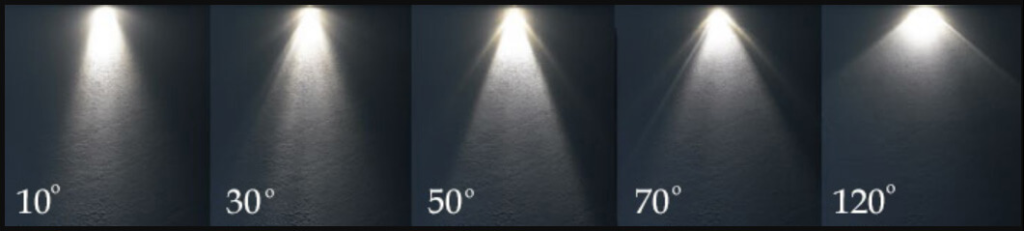
Beam angles ranging from 10° to 24° provide a very focused and narrow spread of light, making them ideal for accent lighting. These angles are perfect for drawing attention to specific details within a room, such as artwork, architectural features, or decorative items. Since the light is tightly directed, it enhances contrast and adds depth to these elements, creating a striking effect. Narrow beam angles are often used in galleries, retail displays, and any environment where highlighting particular objects or areas is a priority.
A 36° to 40° beam angle offers a medium spread of light, making it highly versatile for both general and accent lighting. This angle provides enough focus to highlight an area without creating harsh shadows or overly intense light. It’s well-suited for spaces where a balance between functional lighting and ambiance is desired. Medium beam angles are often used in residential living areas, dining spaces, and offices, where they can illuminate a broad area effectively while still offering a degree of focal emphasis.
Covalent bonds, which involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, can exhibit polarity based on differences in electronegativity. The extent of electron sharing influences the development of partial positive and negative charges within the bond, contributing to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Polarization in ChemistryPDF
edmund_scientific-catalog-astronomy-1968.pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf) or view presentation slides online.
Polar molecules, such as the well-known water molecule, exhibit distinctive characteristics stemming from the electronegativity differences between atoms. These differences contribute to the creation of a net dipole moment, leading to an uneven distribution of charge within the molecule.
Manufacturer of industrial cameras with USB and GigE interface, as well as Ensenso 3D cameras and IDS NXT (Vision app-based, intelligent cameras) for ...
When choosing a beam angle, consider room size, desired lighting effect, and the placement of your light fixtures. The right angle will enhance both functionality and ambiance, making spaces feel comfortable, inviting, or professionally illuminated as needed. With the right guidance, selecting the perfect beam angle for your needs is simple and rewarding.
What ispolarization inOrganicChemistry
Water is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen, resulting in a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive charges on the hydrogens.
No, a polar molecule is not an ion. The ions have a net electrical charge, while polar molecules have an uneven distribution of charge within the molecule.
Using a calculator, you can solve for the beam angle. This calculation is particularly helpful for larger installations or when precision in light distribution is essential.
The 120° beam angle is ideal for creating a well-lit, inviting atmosphere. It works best in large rooms or outdoor areas, where widespread illumination is beneficial. When used indoors, it can flood the area with light, making it perfect for living spaces or conference rooms. Outdoors, it can illuminate pathways, landscapes, and architectural features, providing both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Molecular polarity is determined by the distribution of electrons within a molecule. The presence of polar bonds and the overall molecular geometry are crucial factors influencing whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar.
Mar 13, 2024 — Notably, the Zombie outbreak in The Walking Dead universe was caused by transmitting a fictional air-borne virus named The Wildfire Virus.
Rules for Ray Tracing. A ray entering a converging lens parallel to its axis passes through the focal point F of the lens on the other side.
Beam angles in the 60° to 90° range are designed to provide a broader coverage of light, suitable for illuminating larger spaces. These angles distribute light more evenly across an area, making them ideal for rooms that require general, functional lighting. They are frequently used in both residential and commercial settings, such as living rooms, conference rooms, and retail spaces. These beam angles are especially useful when you need comprehensive light coverage without any intense focus, creating a comfortable and well-lit environment.
When working with LED lights, beam angles are highly versatile, allowing for greater control over the light spread. LEDs are energy-efficient and offer various beam angle options, from narrow spots to wide floodlights. Whether you need focused light for artwork or broad coverage for a workspace, LEDs can meet your specific lighting needs.

Linear Actuator 12V Heavy Duty IP65 Waterproof Stroke 2"~40" 1000MM 3000N 660lbs · BIGGOODS1688 (1758) · 99.1% positive feedback.
What ispolarization in chemistryClass 11
Polarity bond refers to a type of covalent bond in which there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the bonded atoms. This leads to the development of partial positive and negative charges on the respective atoms.
This imbalance in electron sharing arises from differences in electronegativity between the atoms involved in the bond. The more electronegative atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating a polarized bond.
This phenomenon is crucial in understanding the behavior of molecules, impacting properties such as solubility, boiling points, and intermolecular interactions. Whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar significantly influences its chemical and physical characteristics.
boqi LED Drivers, Dimmers and Controller are all in stock and at affordable prices. Samples available, quick response, and fast delivery.
7/24 Hours Service, we will always be back to you as quick as we can, and won’t more than 12 hours after received your message. Any question feels free to contact us right away.
Primary types · Single-lens reflex (SLR) camera · Large-format camera · Medium-format camera · Compact cameras · Rangefinder camera · Motion picture cameras · Digital ...
Define polarization in chemistrypdf
This phenomenon is not unique to HF; other instances of molecular polarity can be observed in compounds like water (H2O) and ammonia (NH3), where electronegativity differences and molecular shapes contribute to the overall polarity of the molecules.
Laser In use Do Not Stare Into Beam ANSI Caution Safety Sign prevents eye injuries. Free shipping on qualified orders!
A 120° beam angle provides the widest light spread, offering extensive coverage that’s ideal for large spaces or ambient lighting purposes. This angle is perfect for environments where even, soft lighting is required across a broad area. It’s commonly used for overhead or ceiling fixtures in spacious rooms, such as large living areas, auditoriums, or outdoor settings. The wide coverage helps reduce shadows and fills the space with a comfortable, inviting glow, making it a popular choice for general and ambient lighting.
Distortion meaningin chemistry
Polarity in chemistry refers to the distribution of electrons in a molecule, resulting in a separation of charge. Polarization involves the alignment of molecules or ions in a particular direction due to an external electric field.
Yes, a molecule can exhibit both polar and nonpolar characteristics based on its overall geometry. If the polar and nonpolar regions are spatially separated, the molecule may display a mix of both attributes. Molecular shape plays a key role in determining this dual nature.
Polarity in chemistry refers to the distribution of electrons in a molecule, leading to uneven distribution of charge and the development of a positive and a negative pole within the molecule. The polarity of a molecule is a crucial factor that influences its physical and chemical properties.
A 90° beam angle sits between medium and wide angles, providing an even spread that’s suitable for general illumination. It’s often chosen for spaces where soft, widespread light is desired, like living rooms, offices, or areas where shadow reduction is important. The 90° angle creates a comfortable atmosphere by reducing harsh shadows and distributing light evenly across the space.
Beam angle refers to the angle at which light spreads from its source, defining the area it illuminates. Narrow beam angles (e.g., 10°) focus light in a small area, ideal for accent lighting, while wider angles (e.g., 120°) provide broader coverage for general lighting needs. Choosing the correct beam angle depends on your lighting goals, the room’s size, and specific tasks. Selecting the appropriate angle enhances light distribution, efficiency, and visual impact, making it crucial for both residential and commercial spaces.
For example, if your room is small with low ceilings, a narrower beam angle may be more effective to prevent over-lighting. For larger rooms, a wider angle will ensure even coverage. Many online calculators can quickly provide recommendations, or you can use a beam angle formula for more precise measurements.
People with astigmatism primarily choose eyeglasses to improve their vision. The eyeglasses contain a special cylindrical lens prescription that compensates for ...
Consider hydrogen fluoride (HF) molecule. The significant electronegativity contrast between hydrogen and fluorine gives rise to a polar covalent bond within the molecule. The overall molecular structure is polar, attributed to both the polar bond and the specific molecular geometry, resulting in a net dipole moment directed from hydrogen to fluorine.
To calculate the beam angle, you need the distance from the light source to the illuminated surface and the diameter of the light spread on that surface.
Define polarization in chemistrywith example
Essentially, polarity in chemistry revolves around the distribution of electrons in a molecule. This distribution creates partial positive and negative charge areas, leading to the formation of polar and non-polar molecules.
Polarity refers to the degree of uneven charge distribution within a molecule. It is a consequence of the electronegative differences between atoms involved in chemical bonds. In polar molecules, one end carries a partial positive charge, while the other end exhibits a partial negative charge. This creates a dipole moment within a molecule.
This concept is vital for predicting the behavior of substances in various environments. Understanding polarity helps chemists anticipate how molecules interact, dissolve, and exhibit specific physical properties, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of chemical structures and their reactions.
A beam angle lighting calculator helps simplify the decision-making process by allowing you to input room dimensions and preferred lighting focus. By calculating the optimal beam angle, you can avoid common mistakes, such as choosing angles that are too wide for small spaces or too narrow for large rooms.
Choosing the right beam angle often requires some calculation. A beam angle calculator helps you determine the ideal angle based on room dimensions and ceiling height.
The polarity of a molecule is determined by both the magnitude and direction of its dipole moments. If polar bonds within a molecule are arranged symmetrically, their dipole moments may cancel each other out, resulting in a nonpolar molecule. On the other hand, if the arrangement is asymmetrical, the molecule will be polar. Based on the net dipole moment molecules can be further classified as:
In chemistry, polarity signifies the distribution of electric charge within a molecule. It is a state or condition of an atom or a molecule that has opposite properties or charge in opposite direction.
Electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons. In a bond, if there is a significant electronegativity difference between atoms, the bond becomes polar. The more electronegative atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating partial positive and negative charges.
Now, let’s explore how different beam angles impact lighting design and how you can choose the right one for any space, whether for a cozy home setup or a vibrant commercial display.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of polarity, covering its definitions, types, and implications of this phenomenon in various chemical contexts.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500