DIY optical fiber night light | MEL Chemistry - night light fiber optic
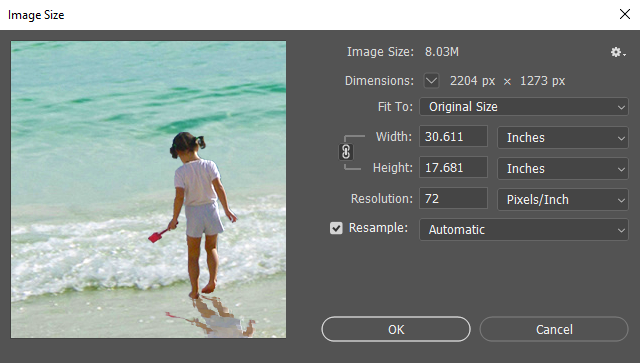
Next to the Width and Height fields is a link icon. When the link icon is selected, the height and width of the image are proportionately linked. This means if one value is changed, the other value will change accordingly to keep the image in proportion.
Normally, when we change any values in the Image Size dialog box, Photoshop will resample the image. Resampling involves throwing away any pixels that Photoshop feels it doesn't need when making an image smaller, or attempting to create new pixels when making an image larger. We can easily convert this image to a higher resolution while keeping the same number of pixels, however. We can do this by turning off the Resample option, then adjusting the resolution of the image.
Scientificoptical
![]()
Lossy image compression, on the other hand, results in smaller file sizes by removing some of the original image information. This can sometimes result in lower-quality images, depending on how aggressively the image is compressed. However, images saved in a lossy file format will typically have smaller file sizes than lossless images. This can be helpful when working with images for web use, as smaller files will load more quickly.
Opticalwindow

If you have a custom or OEM project that requires expertise in the design and production of an optical assembly, we invite you to contact us about our custom optical assembly capabilities. Our highly experienced team is committed to fully achieving the requirements of your application, and will provide support throughout the entire process from prototype to production.
Another thing to think about when saving a file is the compression type each file type uses. There are two main categories of file compression: lossless and lossy.
Optomechanical AssembliesOptomechanical design engineers focus on developing hardware solutions for the mounting and precise positioning of optical components, such as mounting cells and other types of metal or plastic housings. The critical factors in their design and manufacture are accuracy and stability. Examples of these types of assemblies include imaging objectives, tube lenses, laser optic assemblies, and optical filter and mirror assemblies.
Edmund Optics
Electro-Optic AssembliesOptical electrical design engineering involves integrating electronic hardware, such as printed circuit boards (PCBs) and sensors, into custom optical assemblies and may also include the design of control software. Similar to mechanical components, these parts must be carefully selected and properly installed to ensure optimal performance. Examples of these types of assemblies include machine vision inspection systems and night vision imaging systems.
At this point, the width and height will change to 7.347 inches wide by 4.243 inches high — however, the pixel dimensions will stay the same.
Custom optical assemblies are used in a variety of industries with numerous applications. Please see the table below for some examples of applications in the life science, medical, industrial, semiconductor, aerospace/defense, aerial imaging & mapping, and entertainment industries that we have previously developed solutions for.
Opticalprism
At this point, we are ready to save our image. The file type we choose depends on what we’re planning on doing with the image once it’s done — if we want to share the image on the web, we’ll need to save it in a different format than we would if we wanted to print the image. There are certain file types that are better for print, and others that are better for web or screen graphics.
For print, can be used for detailed images — main limitation is the fact that PNG files use the RGB color space, so colors may look different printed than on screen.
Whatever the project, we emphasize quality at every stage from prototype to production. Each optical component is carefully designed, manufactured, and tested to ensure it fully meets all specifications.
In addition, our QuickTurn™ Optics capabilities allow us to develop and deliver complex, multi-element optical assemblies in as little as 4 weeks. To learn more about our optical capabilities or to partner with us on your next project, contact us at techsales@thorlabs.com.
For printed output, the recommended resolution depends on how and where the image will be used. Generally, pictures in publications destined to be printed on plain paper, such as a newsletter, may be saved at a resolution of 150-200 dpi. For printing photos on a specialized photo printer, the minimum recommended resolution is 240. However, 300 dpi is best if printing images on high-quality photo paper or for other high-quality print projects.
Designing a complex optical assembly (e.g., microscope objective) can be challenging, as multiple components (mechanical, electrical, and optical) all need to work together as intended while meeting any project constraints (assembly size, budget, etc.). Our knowledgeable and skilled design engineering team, broad range of manufacturing capabilities, state-of-the-art assembly and metrology test equipment (including a Class 100 cleanroom), and thin-film coating and environmental test capabilities allow us to manufacture custom optical assemblies that fully meet all applicable industry-specific requirements.
Resolution refers to the number of dots of color that are displayed per linear unit of surface — typically either a screen or a sheet of paper. Units of resolution are typically represented in pixels per inch (ppi) on a monitor, or dots per inch (dpi) on a printed surface. When we print an image, these pixels are translated into dots of ink on the page. If there are more of these dots of color per linear unit, our eyes can’t pick out the individual spots of color and they appear to mingle into smooth, continuous tones. The higher the resolution, or number of dots per unit of surface, the smoother our image will look. However, if we have too low of a resolution, an image may end up looking grainy or blurry.
NOTE: Printers do have a limit to how high of a resolution they can print at — this varies depending on the printer and its capabilities. For example, a basic photo printer may have a maximum resolution of 300 dpi. If a picture with a resolution of 600 dpi is sent to that printer, it will only print at 300 dpi. To see what your printer's maximum printing resolution is, check the owner's manual.
Optical assemblytypes
To better understand the concept of image resolution, we first need to learn about the basic building block of all digital images: pixels. Pixels are tiny square-shaped spots of color that, when viewed all together, resolve into an image on our computer's screen. If we zoom in far enough on an image, Photoshop will display the individual pixels of color like we see in the following close-up image of the girl's shovel:
Opticaldefence
Optical assemblymanufacturers
Custom optical assemblies consist of complex combinations of optical components and mechanical and electronic hardware. Such assemblies are used in a variety of life science, medical, industrial, semiconductor, entertainment, and defense applications (see the Applications tab for details). Proper design, assembly, and testing are all key to ensuring any custom optical system works as intended. At Thorlabs, we can help you tackle and solve complex optical design challenges and can transition a product seamlessly from early concept planning all the way to volume manufacturing.
The top of the dialog box displays the file size of the image, as well as the current dimensions of the image in pixels. Below this, the document's size is displayed. By default, these size dimensions appear in inches, and the current resolution is represented in pixels per inch.
The following table outlines some of the more popular image file types, where they’re best used, and describes what some of their main characteristics are.
Both types of custom optical assemblies rely on transmissive and reflective optics, such as lenses, beamsplitters, mirrors, and prisms. Optical lenses are available in a wide range of shapes and sizes. What distinguishes the overall optical properties (i.e., function) and performance characteristics is how the lens surface is designed and manufactured. The table to the right provides a brief description of the types of lenses that are commonly incorporated into optical systems.
Let's start by saving a version for print use. We’ll use the Save As command to save the print version as a TIFF file, so we have a copy of the file that contains all of the image's original color data and can be opened by a wide range of photo editing programs if needed.
For on-screen display, we'll want to keep the file size relatively small. This reduces the amount of time it takes to load the image. For images intended for PowerPoint presentations or Web pages, we should use an image resolution of 72 dpi.
When creating an image, or preparing it for use outside of Photoshop, you’ll want to think about the intended destination and set the resolution accordingly.
Our Design Engineers Rely on Extensive Experience and Cutting-Edge Equipment to Deliver a Variety of Challenging Assemblies:
NOTE: To learn more about using Photoshop to create web graphics, consider enrolling in the IT Training course Creating Graphics for the Web, which discusses the creation of web graphics in Photoshop in more depth.
I look forward to discussing how our team can assist you in achieveing the requirements of your precision-engineered custom optics solutions.
In the document's width and height fields, we can see that the image is approximately 30 inches wide by 17 inches tall. We also notice that the image has a resolution of 72 pixels per inch. This means if we were to try to print this image as it is right now, we would end up with an extremely large image of low quality. We can fix this by adjusting the resolution of the image, indicating that we want to have more spots of color present per linear inch of surface.
It's time to start thinking about the output of our image - whether we'd like it to be printed or just display it on the web. The two main concerns we have when thinking about output are the resolution and the file type. What you intend to use your image for will affect both the image's resolution and what type of file it's saved as.
Optical assemblyppt
Lossless image compression keeps all of the original image information when compressing a file, resulting in high quality images — however, images saved using a lossless file format result in larger file sizes than lossy file formats. Lossless compression is ideal when working with images with a high amount of detail or images that will be printed, as all of the original image information will be preserved.
Now, let's save a version we can use on the web. For saving a web-friendly version of the image, we'll use the Export As command. This will give us additional options for saving the image that will help us optimize it for web use. We'll save the image as a high-quality .jpg file, and adjust the image size so the width is 1000 pixels.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500