C retainer ring (for shafts) | Ochiai | MISUMI MEXICO - retainer c
A UV water filter is a purifier that kills harmful microorganisms in water with the use of germicidal ultraviolet (UV) light. UV water treatment is possible because UV light damages the nucleic acids in the DNA of microorganisms, thereby severely hampering their ability to reproduce or multiply.
Uv filter what does it doreddit
UV filtervs NDfilter
This results in a beam of "coherent light" that has a fully uniform wavelength and phase, and easily interferes with another beam of coherent light. When the intensity of coherent light rises above a certain level, it penetrates the half mirror to reach the outside. This is known as a laser beam. A variety of materials are used for lasers. When a ruby is used, yellowish-green and blue light rise to the fifth floor (excited state) and then emit red light with a wavelength of 694 nanometers when returning from the fourth floor to the first floor (ground state), thereby producing a red laser beam. Semiconductor lasers use a diode combining p-type and n-type silicon.
There are numerous benefits to the use of UV water purification. This is why this disinfecting method is still in existence even after over a century. So what are the advantages of UV water purification?
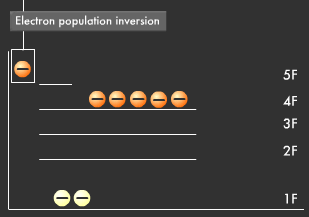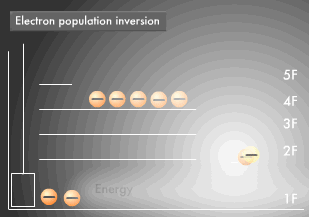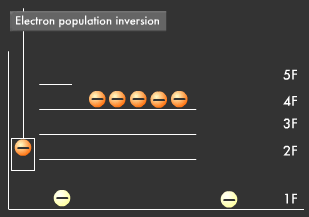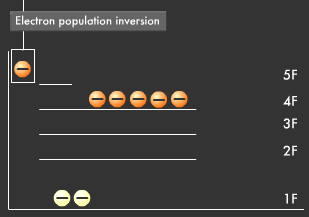
What do you suppose would happen if we continuously applied energy to the elevator? Electrons would ride the elevator one after the other directly to the fifth floor (excited state) and then go down to the fourth floor (metastable state) where they would accumulate. This results in the phenomenon called population inversion, in which more electrons end up on the fourth floor (metastable state) than on the first floor (ground state).
DoI need aUV filterfor my lens
The atoms and molecules in substances emit light (electromagnetic waves) when one of their electrons falls back down to the outermost orbit after receiving external energy and jumping to a higher orbit (energy level). This is called "spontaneous emission." Related terms include excited, which means jumping to a higher energy level and ground, which refers to the original energy state.
Do UVfilters affect image quality
With the many advantages of a UV water filter it is an excellent decision to install a whole house UV water filter or a High Output UV System for commercial use to ensure that whatever water you use is free of germs, bacteria and viruses.
Purification using a UV water treatment system is one of the most effective techniques for removing bacteria from water. Not only does it attack harmful bacteria but also other dangerous pathogens in water that can cause diseases such as typhoid, cholera, gastroenteritis, hepatitis, flu, etc. UV systems can destroy 99.99% of harmful microorganisms, including bacterial, viruses, fungi, and protozoans such as Escherichia coli, Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Salmonella etc. UV treatment also quickly eliminates viruses and other microorganisms that are highly resistant to chlorine, e.g., the hepatitis virus.
One cannot be too careful when it comes to the aspect of safety. After all, we are exploring the potentials of UV water purification to ensure we have safe drinking water in the first place. So is UV water purification safe? Yes, UV water treatment is safe! A significant reason why it is safe is that it eliminates the use of harmful chemicals. Besides, UV light water filters do not alter the composition of water, meaning, in essence, that water remains water.
UV water treatment is much safer than the use of chlorine or chloramine treatment. One of the reasons is because UV light treats water for protozoa, while chlorine and chloramine disinfection is unable to do that. Also, the use of chlorine treatment requires the use of retention tanks and the precise use of injection pumps and solutions. UV water filters are now employed by many wastewater treatment plants to eliminate some harmful chemical by-products generated from chlorine or chloramine treatment.
Whatis aUV filterfor water
Let's compare this distribution process to an elevator in a five-story building. Think of the first floor as ground state and the fifth floor as excited state. When energy is applied, the elevator goes straight to the fifth floor, where its passenger (electron) gets off. However, the fifth floor is too small and unstable for many to stay for long periods of time, so most electrons go down to the fourth floor. The fourth floor is the "metastable state." Electrons can stay longer on the forth floor than on the fifth floor, but most return to the first floor (ground state), emitting energy. As you can see in the diagram below, we end up with a distribution in which most electrons are on the first floor (ground state) while only a few are on the fourth floor (metastable state).
Uv filter what does it dofor lenses
The laser principle we have discussed thus far applies to what is called a three-level laser. The disadvantage of such lasers is that the material they use limits the wavelength of light they can produce. There are lasers such as the free electron laser, one example of lasers that can produce laser beams in a specific wavelength. Free electron lasers make use of the phenomenon in which electrons traveling straight near the speed of light will release light if their course takes a sudden turn.
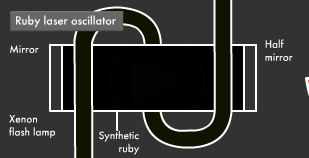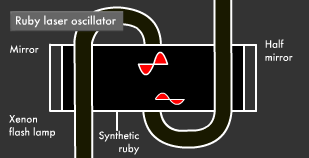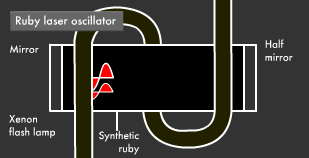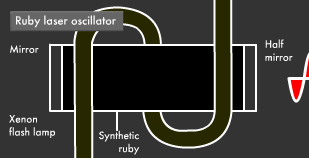
Laser beams are another form of widely used artificial light. Let's understand the mechanism of the laser beam, one of the most crucial inventions of the 20th century.
What does UV filter doin water purifier
However, UV light is not so effective at removing particles from water or eliminating some contaminants in water, such as heavy metals (e.g., lead, mercury, and iron), chlorine, and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). UV disinfection also does not remove bad taste and odor from water.
However, it is essential to note that UV sterilizers use UV-C light to bring about disinfection. The catch here is that this UVC light is as harmful to humans as it is to microorganisms. You’re, however, not at risk of any harm whatsoever provided you don’t expose yourself to the UV bulb by touching or looking at it while it is on.
IsUV filternecessary for water
Although the germicidal property of the sun was known as far back as 1877, the concept was not fully understood. From then on, research into the disinfection principles began. In 1903, Niels Finsen was awarded the Nobel Prize for his use of UV light to combat tuberculosis. However, it was not until the 1950s that significant research into the use of UV light for water disinfection began. By the 1960s, the principle was already widely used in commercial applications and gradually introduced into the residential market.
At an intensity of 254nm, UV light emits enough radiation to damage bacterial DNA and the DNA in other microorganisms. This germicidal wavelength of radiation falls within the UV-C radiation wavelength. A UV water treatment system usually consists of a UV light source (at about 254nm output) mounted in front of a flow chamber where the water will pass. A glass quartz sleeve which allows the UV wavelength to pass through unhindered usually holds the UV lamp. The glass quartz is necessary to protect the UV lamp from water.
However, since the fourth floor (metastable state) is not completely stable, one electron in the population inversion goes down to the first floor (ground state), releasing energy in the process and causing others to surge back to the first floor. This kind of energy release is called "stimulated emission," and this phenomenon is the means through which laser beams are produced.
Fast forward to today, there is full acceptance of UV disinfection as an efficient and effective chemical free treatment for the elimination of microbiological contaminants from water, and point-of-entry UV is becoming a standard mainstream feature in homes. The UV water filter system combines UV treatment with other forms of filtration, such as sediment and carbon block filters and is used as pre and post treatment on reverse osmosis systems.
The laser beam was discovered in 1960. The term laser is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation." Lasers are a form of artificial light with uniform direction, phase and wavelength, and they are produced by precisely controlling the excited and ground states of electrons. Unlike other forms of light that do not have uniform wavelength and phase, lasers can create intense light spots from faint light sources and are thus one of the most important forms of artificial light. Lasers are currently used in all manner of applications, from the more obvious CD-ROM drives, fiber optics and other industrial products, to others such as the medical field and entertainment.
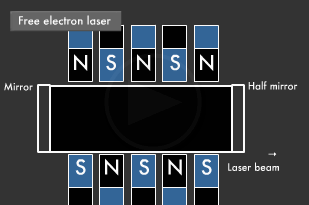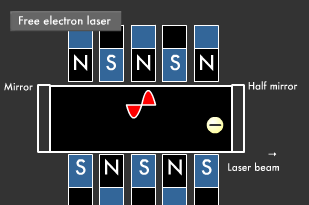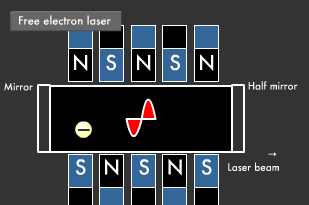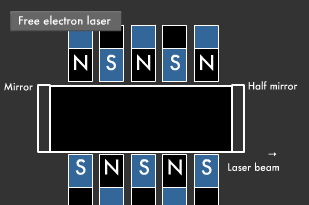
The light obtained through stimulated emission travels in all four directions. Its wavelength is uniform, but its phase is not. Guiding this light into a tube with mirrors at either end (one of which is a translucent half mirror), where it reflects back and forth a number of times, causes only light with uniform phase and direction to intensify and remain.
If you place magnets with their north and south poles facing each other, and then fire in an electron at high speed as shown in the diagram below, the electron emits light while winding at the mercy of the magnetic field. Amplifying the movement of electrons between the mirrors produces a laser beam. A laser beam's wavelength can be varied by changing the energy of the electrons fired in, thus enabling every kind of laser beam, from microwave to ultraviolet lasers.
As the water passes through the flow chamber, it becomes exposed to the germicidal UV light source. At this stage, the harmful microorganisms present in the water become inactivated. The UV water purifier can be used both on a large scale and small scale and water from most sources. For example, you can use a UV light for well water, spring water, lake water, surface water and wafer from a municipal water supply.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500