Basics of ultrafast lasers: Part 2 - ultrafast lasers
Depth of fieldexamples
In an experiment to find focal length of a concave mirror, a graph is drawn between the magnitudes of (u) and (v). The graph looks like.
A double convex lens (R1=R2=10cm) having focal length equal to the focal length of a concave mirror. The radius of curvature of the concave mirror
Aperture is the lens setting that impacts the depth of field because it controls the opening and closing of the lens. What is depth of field? It's the area of the image that appears sharp in front and behind the main subject. Essentially, the depth of field refers to how blurry or sharp the area around your subjects appears on the camera. Increasing the aperture or decreasing the f-stop can help to achieve the shallow depth of field. Sometimes, we can also achieve this effect by changing the camera's distance and the subject and adjusting the focal length accordingly.
Depth of fielddefinition microscope
For better shallow focus, if you have a longer lens, you have yourself an advantage. Longer lenses allow shallower depth of field. If your camera can interchange lenses, 85mm is a long enough lens for capturing shots with shallow focus.
2. Explain the Principle: - When parallel rays of light strike a concave mirror, they reflect off the surface and converge at the focus. This is a key characteristic of concave mirrors, which makes them useful in applications like telescopes and shaving mirrors.
Depth of fieldphotography examples
4. Illustrate with a Diagram: - Draw a concave mirror with a principal axis. Mark the pole (P) at the center of the mirror, the focus (F) on the principal axis, and indicate the distance between P and F as the focal length (f).
Doubtnut is No.1 Study App and Learning App with Instant Video Solutions for NCERT Class 6, Class 7, Class 8, Class 9, Class 10, Class 11 and Class 12, IIT JEE prep, NEET preparation and CBSE, UP Board, Bihar Board, Rajasthan Board, MP Board, Telangana Board etc NCERT solutions for CBSE and other state boards is a key requirement for students. Doubtnut helps with homework, doubts and solutions to all the questions. It has helped students get under AIR 100 in NEET & IIT JEE. Get PDF and video solutions of IIT-JEE Mains & Advanced previous year papers, NEET previous year papers, NCERT books for classes 6 to 12, CBSE, Pathfinder Publications, RD Sharma, RS Aggarwal, Manohar Ray, Cengage books for boards and competitive exams.Doubtnut is the perfect NEET and IIT JEE preparation App. Get solutions for NEET and IIT JEE previous years papers, along with chapter wise NEET MCQ solutions. Get all the study material in Hindi medium and English medium for IIT JEE and NEET preparation
Cinemagic is a leading company in the field of content productions and digital media services. Serves the Middle East and North Africa region MENA. We empower companies globally to tell a better story through moving pictures.
"reframing"refers to
in cinematography, "mask"refers to
Another thing to bear in mind while trying to achieve shallow focus is that the more we increase our aperture, the more light enters the lens - which means, you might have to play with your ISO and/or shutter speed to make sure your image isn't too bright. The closer your subject is to the camera, the shallower your depth of field will be - because this creates a blur in the background and allows more focus on your subject.
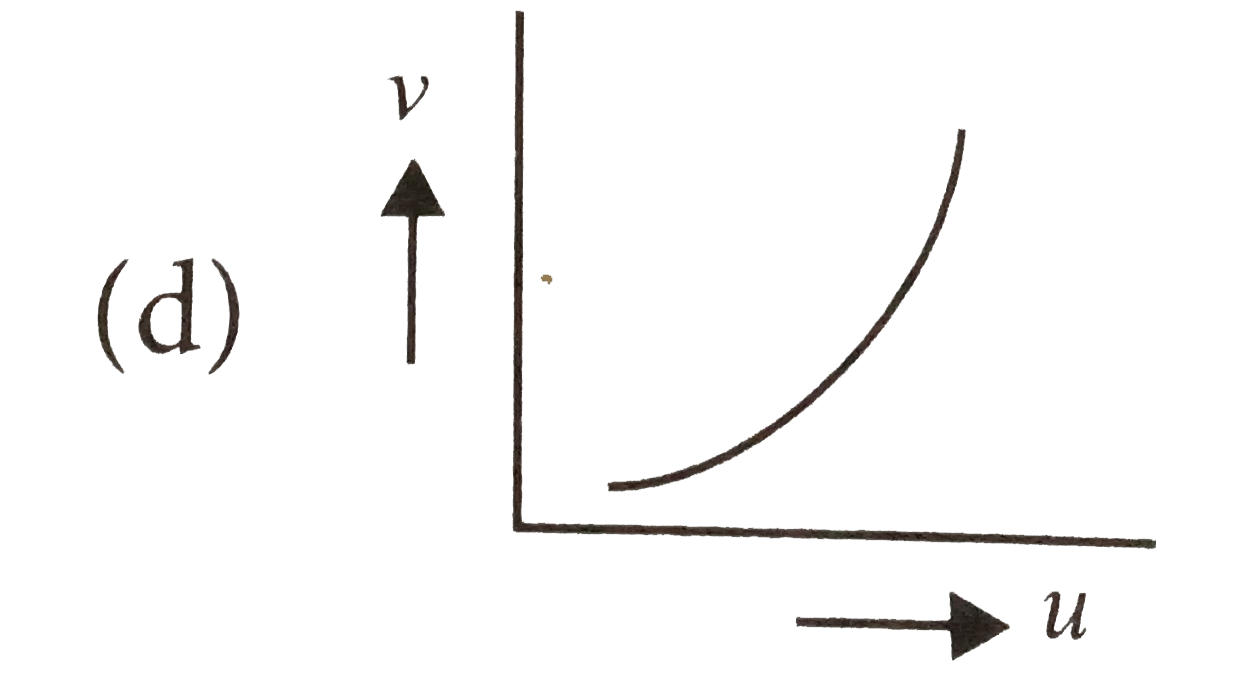
Diagram:F|||Pââââââââââ¢âââââââPrâcipalAξs|||//////- In the diagram, 'P' represents the pole of the mirror, 'F' represents the focus, and the distance 'PF' is the focal length.
We want viewers to be attracted to the object or subject as opposed to anywhere else on the scene. This is very prominent for an interview, so it's important to understand how to frame an interview. - StudioBinder
Depth of field refers toquizlet
If you have your interest in photography or cinematography, you might be aware of the different tips and tricks out there that you can use to make your images or videos more powerful. Cinematic effects in a video add so much more value and meaning to a shot. This blog post covers a shot technique known as the 'Shallow Focus' or 'Shallow Depth of Field'.
depth of field refers tothe distance between the camera and the subject in focus. true or false
If the camera is closer to the subject in question, parts of the image will be blurred, resulting in a smaller depth of field, or narrower area of focus. Similarly, a longer focal length, can also create background blur. - StudioBinder
I use shallow depth of field to isolate my subject from the background and the foreground. It helps me drive the viewers' eyes to my subjects and gives me better control that absolutely helps my storytelling. Plus I also use it for beauty product shots because I can achieve the cinematic sweet bokeh look that is creamy and eye-candy-ish for the viewer. - Jasem Al Muhanna, Director, Cinemagic.
Shallowdepth of field
Film-makers tend to use this shot to make something stand out. Usually, this shot is seen when a director of the film emphasizes a particular aesthetic or character in the setting. When the aesthetics of a specific subject are the most primary focus of the shot, we get to experience the shallow depth of field shot's uses.
3. Define Focal Length: - The focal length (denoted as 'f') is the distance between the pole (the center of the mirror's surface) and the focus. It is a measure of how strongly the mirror converges or diverges light.
Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of , suitable ray diagram.
It's a beautiful technique that helps explain to the audience an essential part of the shot. When you highlight one point in the image and softly blur the rest of the composition, we can add weight to the shot.
The Shallow focus is one of the most commonly used techniques in filming. This happens when there is a narrow or thin depth of field. It can sound a little confusing, but if you're well aware of aperture's functions and depth of field, it'll be relatively simpler to understand and finally master.
1. Define Focus: - The focus of a concave mirror is defined as the point on the principal axis where all parallel rays of light converge after reflecting off the mirror. It is denoted by the letter 'F'.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500