Baldur's Gate 3: How To Loot Topaz's Nest - bg3 magnifying glass

A compound microscope is a high-magnification microscope that uses two lenses to compound or multiply the level of magnification. The first lens is the objective lens and the second lens is known as the eyepiece lens.
The amount of light falling on the object is regulated through the diaphragm that is seen below the stage. The disc and iris are the two diaphragm types.
The rack and pinion have a small screw used to stop the downward sliding of the body tube and avoid any damage to the objective lens.
f-stop app
These are compound lens that generates a real inverted image of what is inside the body tube. Objective lenses are seen over the nose piece and have a few types:
Focal length
The A-mode (Aperture Priority mode) is a mode that allows you to set the f-number the way you want. In this mode, the camera automatically sets the shutter speed and ISO sensitivity to shoot a well-exposed photograph. This mode is suitable when you want to defocus the foreground and background, with the focus only on the main subject, or when you want to render the entire landscape clearly by focusing on the wide range from the foreground to the background.
My relatives every time say that I am killing my time here at web, however I know I am getting experience every day by reading such nice articles
As the f-number gets larger, the opening to let the light into the camera gets smaller. As a result, the shutter speed will slow down, which may cause the image to blur because of camera shake. If this occurs, try shooting with a smaller f-number again.
f-stop是什么
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the issues. It was truly informative. Your site is very helpful. Thank you for sharing!
Shutter speed
An intriguing discussion is definitely worth comment. I do believe that you should publish more about this subject, it may not be a taboo matter but usually folks don’t speak about such subjects. To the next! Cheers!!
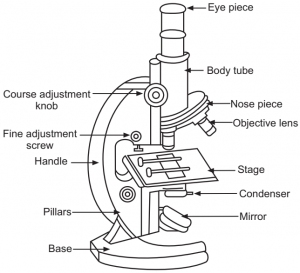
From the above Compound Microscope diagram, as you can observe, there are different types of parts like Eye Piece, Mirror, Base, Course Adjustment Knob, Nose Piece, Stage, Pillars, Base, Fine Adjustment Screw, Body Tube, Handle, Base, Pillars, Objective Lens, and many more. Moreover, all the parts are differentiated into two types, Optical Parts, and Non-Optical Parts.
Generally, the smaller the f-number is, the more light comes into the camera, and the more defocus effect you can enjoy. Each lens has a minimum f-number, and this is called the maximum aperture of the lens. To check the maximum aperture of a lens, refer to the lens specifications or the value printed on the lens, as shown in the picture below. A lens with a small f-number is generally called a fast lens.
The compound microscope was invented back in the year the 1590s along with the simple microscope by inventors, Hans Janssen, and Zacharias Janssen.
Numerical aperture
The ocular lens also called the eyepiece helps in viewing the image of microscopic objects. There are four types of magnification ensured by the ocular lens:
The upper end of the body tube with a fixed tube is called the drawtube which is primarily meant to hold the ocular lens.
The aperture is a part that adjusts the amount of light coming from the lens. As shown in the pictures below, it is located inside the lens, and it adjusts the amount of incoming light by changing the size of the opening.
Here, the eyepiece or ocular lens facilitates the image viewing. The light then is allowed to pass through the thin transparent object. A magnified image or the real image of the object is generated by the objective lens. The ocular lens now magnifies this real image further to be viewed as the virtual image.
F-stops
The ability of a compound microscope to successfully differentiate two lines or points in an object is stated as the Resolving Power.
Field of view
It looks like JavaScript is disabled in your browser. To get the full experience on Sony.co.uk, please change your settings to allow JavaScript.
The compound microscope works simply and it just needs the light to pass through a transparent object. The result of this entire exercise is the formation of the image, in the objective lens, and not just that image formed under this lens is a real image. Here, the ocular lens is applied to magnify the real image that is formed on the first lens. The image formed thus becomes a virtual one.
The aperture also affects the range of in-focus area, or the amount of defocus in a photograph. The following shows the comparison between the amount of defocus and the aperture. You can see the foreground and background are defocused more as the f-number gets smaller.
A reflector is a mirror attached above the base. One side of the mirror has a plane mirror while the other has a concave mirror. When the light is strong, the plane mirror side is used and when it is weaker, the concave mirror side is put into action. The light on the object is directed with the aid of the reflector through the diaphragm and condenser.
As you know, there are many types of microscopes available, like the Compound Microscope. However, the main difference is that this microscope can magnify the complex system in an object. Moreover, there are two types of lenses involved in the Compound Microscope, each having its function as shown in the Compound Microscope diagram above.
Aperture
A compound microscope is a high-magnification microscope that uses two lenses to compound or multiply the level of magnification. The first lens is the objective lens and the second lens is known as the eyepiece lens.
The first lens is the magnifier that is positioned closer to the subject while the second one is the ocular lens that helps in viewing the 2D image of the subject more clearly.

The Compound Microscope is a special kind of microscope that features two sets of high-resolution lenses, that are capable of providing a 2-dimensional image of the sample. And because of the presence of two lenses in this microscope, it is referred to as a compound microscope. Moreover, based on the purpose of these microscopes, they are differentiated into multiple types, such as Metallurgical Microscopes, Fluorescence microscopes, Phase Contract Microscopes, and Polarizing microscopes.
There are two pairs of adjusting screws used for a coarse adjustment or for fine adjustment. In the case of fine adjustment, the body tube or the stage moves in short distances while in coarse adjustment, the body tube and stage move up. Through fine adjustment, a sharp image is generated.
If the observation has to be done in a sitting posture, then the microscope has to be tilted using the inclination joint.
Microscope Devices are very crucial for various types of studies and research related to plants, microorganisms, fungi, and many more. So, every student will come across this topic, and they should know what is microscope before moving on to this, they often struggle in this chapter, as it involves various complex sub-topics and questions. Therefore, to help you understand the topic more easily, we have provided a complete guide to Compound microscopes, here in the below article.
In the above article, we have given a complete description, and diagram of the Compound Microscope, its Function, Parts of the Compounds Microscope, as well as its various advantages and disadvantages. If you want to learn all the complex topics in Physics like what is microscope, simple microscope diagrams, and compound microscopes more easily, then the online interactive classes offered by Tutoroot might be beneficial for you. As it offers various amazing benefits like expert staff, cost-effective prices, doubt-clearing sessions, the best educational guides, and a lot more.
The arm is also called the limb and is a metallic handle that acts as a connection between the arm to the inclined joint. The stage and the body tube is supported by the arm.
The main function of this body tube is to hold the objective and ocular lenses at two ends. The end that has an ocular lens is called the head whereas the end with the objective lens is the nose piece. This is the pathway for the flowing of the light rays through the body tube.
A compound microscope is known to be a standard microscope that is used for general use and purposes. In a compound microscope, the lens is arranged in such a way that it magnifies the objects from the complex system. It is also called a bright-field microscope since the light flows directly from the source to the eye, through the two lenses.
The amount of light coming into the camera affected by the size of the aperture is quantified as f-numbers. F-numbers have fixed standard values, such as F2, F2.8, F4, F5.6, and F8. As the f-number gets larger, the aperture is closed and less light passes through the lens. As the f-number gets smaller, the aperture is opened and more light passes through the lens. For example, if the aperture is changed from F8 to F5.6, the amount of light is doubled. As a result, even if the shutter speed is doubled, it can let the same amount of light into the camera, as long as other conditions are the same.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500