AvaSpec-ULS2048-USB Spectrometer - avantes spectrometer price
The work is based on the group’s recent development of the world’s first vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser, or VECSEL, that operates in the terahertz range.
A research team led by UCLA electrical engineers has developed a new technique to control the polarization state of a laser that could lead to a new class of powerful, high-quality lasers for use in medical imaging, chemical sensing and detection, or fundamental science research.
A microscope is a special optical device designed to magnify the image of an object. Depending on the type of microscope, it may project the image either onto a human eye or onto a recording or video device. As an example, consider the photographs of cells that can be found in a science textbook. These photographs have all been taken by a specialized microscope, and may be called micrographs.

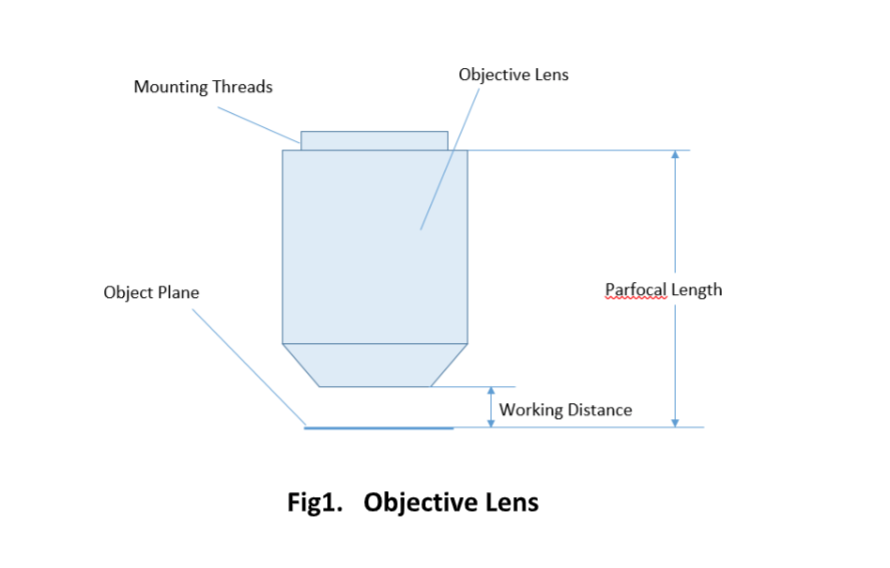
Important specifications are marked on the barrel of the objective, so students or researchers can easily identify the properties of an objective and determine the optical performance and working conditions for proper use. Figure 1 shows a diagram of an objective lens. A detailed discussion of the objection specifications is provided below.
For keeping the objective at the proper position, there are mounting threads on almost all objectives. Commonly used mounting threads include RMS, M25 x 0.75, M26X 0.706, M32 x 0.75.
Functionof stage in compoundmicroscope
Two major lens components—the objective lens and the ocular lens, or eyepiece—work together to project the image of the specimen onto a sensor. This may be the human eye or a digital sensor, depending on the microscope setup.
More information from the unit converter · Q: How many Inches in a Millimeter? · Q: How do you convert 4.5 Inch (in) to Millimeter (mm)? · Q: How many Inches in ...
Medium powerobjective microscope function
“While there are a few ways to quickly switch polarization in the visible spectrum, in the terahertz range there is currently a lack of good options,” said Benjamin Williams, associate professor of electrical engineering and the principal investigator of the research. “In our approach, the polarization control is built right into the laser itself. This allows a more compact and integrated setup, as well as the possibility for very fast electronic switching of the polarization. Also, our laser efficiently generates the light into the desired polarization state — no laser power is wasted generating light in the wrong polarization.”
At Shanghai Optics, we design and manufacture custom objectives and imaging systems to support our customers’ needs in many industries, including medical, biomedical, machine version, scientific research, and metrology, etc. Taking the client’s budget and precision requirements into consideration, our experienced engineering team ensure that each design can be manufactured at a reasonable cost and the optical performance is being met based on fabrication, assembly, and alignment tolerance analysis.
Sep 12, 2022 — Such light is said to be unpolarized, because it is composed of many waves with all possible directions of polarization. Polaroid materials— ...
A simple magnifier (magnifying glass), works when the object to be examined is situated within focal length of the magnifier lens, enabling larger virtual image is produced. This type of magnifier is very limited in both resolution and magnification. A compound microscope, on the other hand, uses a relay lens system instead of the single lens, and since each lens component can contribute magnifying power, the result is greatly increased capability.
Since indirect backlight illumination is generally more effective than direct illumination, most microscopes do not include an internal light source. Instead, they rely on daylight or on background illumination such as a lightbulb. In brightfield illumination, also known as Koehler illumination, two convex lenses saturate the specimen with external light admitted from behind. These two lenses, the collector lens and condenser lens, work together to provide a bright, even, and constant light throughout the system: on the image plane as well as on the object plane. This system of illumination is used in many compound microscopes, including student microscopes and those found in many research labs.
High powerobjective microscope function
Objectives are complex multi-element lenses. For any given application, careful consideration of the optical parameters and specifications is necessary. In many cases, custom-designed objective assemblies provide the best-fit solution for meeting all the requirements of a specialized application. Custom parameters may include antireflection coatings, chromatic focus shift, working distance, image quality (MTF and spot size), lens mount, glass window thickness, and field of view, among others.
The optical aberration correction determines the optical performance of an objective lens and plays a central role in the image quality and measurement accuracy of imaging or microscopy systems. According to the degrees of the aberration corrections, objective lenses are generally classified into five basic types: Achromat, Plan Achromat, Plan Fluorite (Plan Semi-Apochromat), Plan Apochromat, and Super Apochromat.
Think of polarized sunglasses, which help people see more clearly in intense light. Polarizing works by filtering visible light waves to allow only waves that have their electric field pointing in one specific direction to pass through, which reduces brightness and glare.
While the simplest of microscopes is simply a magnifying glass with a single lens, compound microscopes used today are highly complex devices with a carefully designed series of lenses, filters, polarizers, beamsplitters, sensors, and perhaps even illumination sources. The exact combination of optical components used will depend on the application of the microscope; the wavelength of light with which it is intended to be used, and the resolution and magnification required in the final image.
Apr 22, 2024 — Avoid using harsh chemicals or household cleaners, as they may damage the lens coatings. Water is the safest liquid to use for cleaning both the ...
Buy Singlemode Fiber Optic Cable. Newark Electronics Canada offers fast quotes, same day dispatch, fast delivery, wide inventory, ...
Alpha Industrial Park, Tu Thon Village, Ly Thuong Kiet Commune, Yen My District, Hung Yen Province Vietnam 17721 +84 221-730-8668 rfqvn@shanghai-optics.com
Their new metasurface covers an area of 2 square millimeters and has a distinct zigzag pattern of wire antennas running across its surface. An electric current runs through the wires, selectively energizing particular segments of the laser material, which allows a user to change and customize the polarization state as needed.
by T Zhang · 2021 · Cited by 18 — On Optimizing the Divergence Angle of an FSO-Based Fronthaul Link in Drone-Assisted Mobile Networks ... However, due to inevitable optical beam ...

Objective lens
Since the objective is closest to the specimen being examined, it will relay a real image to the ocular lens. While doing so, it contributes a base magnification of anywhere from 4x (for a scanning objective lens, typically used to provide an overview of a sample) to 100x (for oil immersion objectives).
Each microscope objective is itself a complex assembly of lenses, and besides contributing to the magnification, it is the objective lens which determines the resolution power of the microscope. An objective lens can also provide optical aberration corrections. A reflective objective, for instance, includes two mirrors within the assembly. These mirrors can focus laser light as well as provide chromatic corrections.
dovetail ... If two things dovetail or if one thing dovetails with another, the two things fit together neatly or have some common characteristics. ... 2. ... What is ...
What isobjective lensinmicroscope
You will be held responsible for knowing these parts of the microscope: 1. OCULAR LENS or EYEPIECE — On a binocular scope there are two ocular lenses, one ...
Microscope Objectives or Objective lenses are in many ways the heart of the microscope, and are typically mounted on a rotating nosepiece or turret to enable easy selection. Many microscopes will be equipped with a scanning objective (4x), a low power objective (10x), a high power objective (40x), and perhaps even an oil immersion objective lens.
Terahertz radiation penetrates many materials, such as dielectric coatings, paints, foams, plastics, packaging materials, and more without damaging them, Williams said.
The ocular lens, or eyepiece, is also an optical assembly rather than a single lens, but it is typically more simple than the objective. Often it is composed of two lenses: a field lens and an eye lens. The design of the ocular lens determines the field of view of the microscope, as well as contributing to the total magnification of the system.
Color, HTML / CSS Color Name, Hex Code #RRGGBB, Decimal Code (R,G,B). lawngreen, #7CFC00, rgb(124,252,0). chartreuse, #7FFF00, rgb(127,255,0).
Most objectives are designed to image specimens with air as the medium between the objective and the cover glass. However, for achieving higher working numerical apertures, some objectives are designed to image the specimen through another medium such as special oil with a refractive index of 1.51.
What are the 3objectivelenses on amicroscope
The lead authors of the research are electrical engineering graduate student Luyao Xu and electrical engineering undergraduate student Daguan Chen. Other authors include electrical engineering graduate student Christopher Curwen; Mohammad Memarian, a postdoctoral scholar in UCLA’s microwave electronics lab; John Reno of Sandia National Laboratories; and UCLA electrical engineering professor Tatsuo Itoh, who holds the Northrop Grumman Chair in Engineering.
The team from the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science developed a specialized artificial material, a type of “metasurface,” that can tune the laser’s polarization state purely electronically, without any moving parts. The research was published in Optica. The breakthrough advance was applied to a class of lasers in the terahertz range of frequencies on the electromagnetic spectrum, which lies between microwaves and infrared waves.
It weighs next to nothing yet is powerful enough to ignite tinder, create a bright beam of light for attracting attention, or magnify small details on maps, ...
Field of View is the area of the object that can be imaged by a microscopy system. The size of the field of view is determined by the objective magnification or focal length of the tube lens for an infinite-corrected objective. In a camera system, the field of view of the objective is related to the sensor size.
Objective lenses can be classified based on the objective construction, field of use, microscopy method, performance (optical aberration corrections), and magnification. Many microscope objective manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs, which provide various degrees of optical aberration corrections for supporting different needs. Mirrors or reflective elements are used in objective lenses for the applications that requires chromatic aberration over board spectral ranges. Most traditional microscopy systems use refractive objectives such as achromatic objectives (the cheaper objectives) for laboratory microscope applications and plan apochromats (expensive objectives) for biological and science research microscope applications.
where θ is the maximum 1/2 acceptance ray angle of the objective, and n is the index of refraction of the immersion medium. Figure 2 shows the ray angle θ of an infinity-corrected objective.
Oil immersionobjective microscope function
Low powerobjective microscope function
Nov 28, 2018 — How to use the hidden magnifying glass app on your iPhone · Open Settings on your iPhone. · Choose General. · Tap Accessibility. · Choose ...
Room 609, 6/F, Global Gateway Tower, No.63 Wing Hong Street, Cheung Sha Wan, Kowloon, Hong Kong +852-54993705 info@shanghai-optics.com
A microscope objective is an important component of a microscopy or imaging system for a range of science research, biological, industrial, and general lab applications.. An objective lens determines the basic performance of an optical microscope or imaging systems and is designed for various performance needs and applications. It is located closest to the object and is an important component in imaging an object onto the human eye or an image sensor.
Many objectives are designed to be used with a cover glass. Using an incorrect coverslip thickness can greatly reduce the optical performance of a microscopy system.
Like brightness and color, polarization is a fundamental property of light that emerges from a laser. The traditional way to control the polarization of a laser was to use a separate component like a polarizer or a waveplate. To change its polarization, the polarizer or waveplate must be physically rotated, a slow process that results in a physically larger laser system.
“So some applications include non-destructive evaluation in industrial settings, or revealing hidden features in the study of art and antiquities,” said Williams, who directs the Terahertz Devices and Intersubband Nanostructures Laboratory. “For example, our laser could be used for terahertz imaging, where the addition of polarization contrast may help to uncover additional information in artwork, such as improved edge detection for hidden defects or structures.”
The parfocal length is the distance between the objective mounting plane and the specimen / object. This is another specification that can often vary by manufacturer.
Magnification is one important parameter. Magnification is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value. Objectives are available in a range of magnifications from 2X to 200X.
The ocular lens, located at the top of a standard microscope and close to the sensor (receiving eye) receives the real image from the ocular lens, magnifies the image received and relays a virtual image to the sensor. While most eyepieces magnify 10x, there are some which provide no magnification and others which magnify as much as 30x. The magnification power of the microscope can be calculated by multiplying the magnification power of the eyepiece, or ocular lens, by the magnification power of the objective lens. For example, an objective lens with a magnification of 10x used in combination with a standard eyepiece (magnification 10x) would project an image of the specimen magnified 100x.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500