Anti-Reflective Coatings - ar coatings
The laser power reached 2.42W with a slope efficiency of 45.9% and a polarization purity of 95.5% at 6.2W pump power when applying a 1.8m long gain fiber. To ...
When the object is crossing the focal plane, the image transoms from a very small to a very large abruptly. But you are not able to notice this abruptness since it is very hard to recognize the image approaching the focal plane from the both sides.
Converging mirrorexamples
Most of the light rays are close to parallel to one another (with a maximum angle of about 0.5 degrees). We call such parallel light rays collimated.
Looking for mirror 6 inch round rentals in Surrey BC? Browse our extensive online rental catalog or call us now about our mirror 6 inch round.
A DCS creates a grayscale photo when you decide to take the picture and press the button. The DCS is exposed to light, which opens up the light cavities in a ...
Convexmirror
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Converging mirroruses
In contrast, spectacles with prisms of equal power for both eyes, called yoked prisms (also: conjugate prisms, ambient lenses or performance glasses) shift the visual field of both eyes to the same extent.[5]
Prisms made of isotropic materials like glass will also alter polarization of light, as partial reflection under oblique angles does not maintain the amplitude ratio (nor phase) of the s- and p-polarized components of the light, leading to general elliptical polarization. This is generally an unwanted effect of dispersive prisms. In some cases this can be avoided by choosing prism geometry which light enters and exits under perpendicular angle, by compensation through non-planar light trajectory, or by use of p-polarized light.
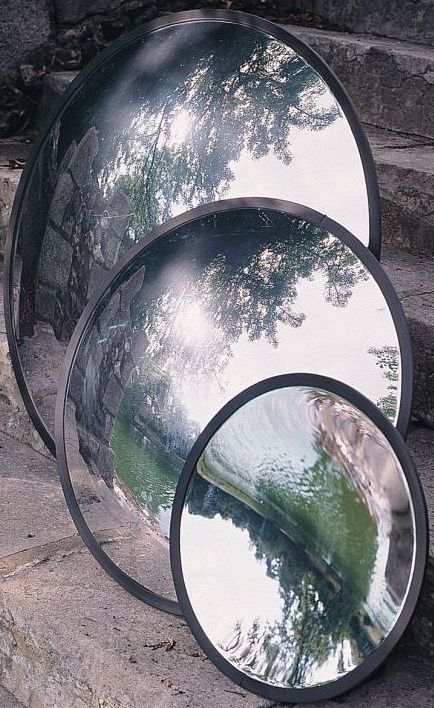

Converging mirroris concave or convex
In comparison with a usual glass substrate, the glass cube provides protection of the thin-film layer from both sides and better mechanical stability. The cube can also eliminate etalon effects, back-side reflection and slight beam deflection.
Depolarization would not be observed for an ideal monochromatic plane wave, as actually both devices turn reduced temporal coherence or spatial coherence, respectively, of the beam into decoherence of its polarization components.
The concave mirror does not necessary leads to an inverted image. It depends how far you are from the mirror. When you are placed between the focal plane and mirror's surface (see Fig. 1) you see a non-inverted image. When you are exactly at the focal plane you see nothing (Fig. 2). And when you are located behind the focal plane, that is usual case, you see an inversion (Fig. 3, 4). Changing mirrors shape can be considered in this context as an equivalent moving of the object relative to the focal plane.
Converging mirroris also known as
A dispersive prism can be used to break white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) to form a spectrum as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflect light, or to split light into components with different polarizations.
Buy Kodak #102 Yellow-Green Wratten 2 Filter (75 x 75mm) featuring Converts Barrier-Layer Response, Designed for Use with Densitometers, Gelatin Filter for ...
Aperture setting · Lens focal length · Sensor size · Distance from camera to subject and distance of subject to background, (assuming your focus point it on your ...
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite.
Converging mirrorand divergingmirror
Total internal reflection alters only the mutual phase between s- and p-polarized light. Under well chosen angle of incidence, this phase is close to π / 4 {\displaystyle \pi /4} .
I was talking with a friend recently about concave mirrors, which frequently invert the reflected image - I think we were playing with a spoon. I raised the question, if you had a mirror whose shape could be easily controlled so you could move it from convex through being flat to being concave, at what point does the image flip from being the right way up to being inverted - is there some sort of discontinuity? If not how would this transition occur?
Converging mirrorfocal length
Industrial Laser Supply represents Epilog Laser, Kern, Electrox, Tykma, and BOFA in Connecticut.
Spectral dispersion is the best known property of optical prisms, although not the most frequent purpose of using optical prisms in practice.
Divergingmirror
Dispersive prisms are used to break up light into its constituent spectral colors because the refractive index depends on wavelength; the white light entering the prism is a mixture of different wavelengths, each of which gets bent slightly differently. Blue light is slowed more than red light and will therefore be bent more than red light.
Prism spectacles with a single prism perform a relative displacement of the two eyes, thereby correcting eso-, exo, hyper- or hypotropia.
Notice that changing the curvature of the mirror is characterized by some critical radius when one observe this effect and this is not the case when the mirror is flat. When the mirror becomes flat the image changes smoothly changing just a zoom.
Reflective prisms are used to reflect light, in order to flip, invert, rotate, deviate or displace the light beam. They are typically used to erect the image in binoculars or single-lens reflex cameras – without the prisms the image would be upside down for the user.
By shifting corrective lenses off axis, images seen through them can be displaced in the same way that a prism displaces images. Eye care professionals use prisms, as well as lenses off axis, to treat various orthoptics problems:
Senior Electrical Engineer. Dayton, Dayton, OH, US ; Assembler. Tulsa, OK, US ; Assembler. Tulsa, OK, US ; Assembler. Tulsa, OK, US ; Assembler. Tulsa, OK, US.
Our protected aluminum front surface mirrors offer high UV reflectivity. The mirror coating consists only of Al+SiO2 to ensure low absorption in the ...
Various thin-film optical layers can be deposited on the hypotenuse of one right-angled prism, and cemented to another prism to form a beam-splitter cube. Overall optical performance of such a cube is determined by the thin layer.
These are typically made of a birefringent crystalline material like calcite, but other materials like quartz and α-BBO may be necessary for UV applications, and others (MgF2, YVO4 and TiO2) will extend transmission farther into the infrared spectral range.
Basic Tube Lens Module with Achromat Tube Lens · 80 mm (C60-TUBE-80) · 100 mm (C60-TUBE-100) · 160 mm (C60-TUBE-160) · 200 mm (C60-TUBE-200) · 250 mm (C60-TUBE- ...
Another class is formed by polarizing prisms which use birefringence to split a beam of light into components of varying polarization. In the visible and UV regions, they have very low losses and their extinction ratio typically exceeds 10 5 : 1 {\displaystyle 10^{5}:1} , which is superior to other types of polarizers. They may or may not employ total internal reflection;
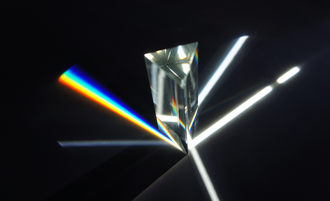
Reflective prisms use total internal reflection to achieve near-perfect reflection of light that strikes the facets at a sufficiently oblique angle. Prisms are usually made of optical glass which, combined with anti-reflective coating of input and output facets, leads to significantly lower light loss than metallic mirrors.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500