anatomy of a camera - dslr anatomy

Aperture diaphragmmicroscope
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this.
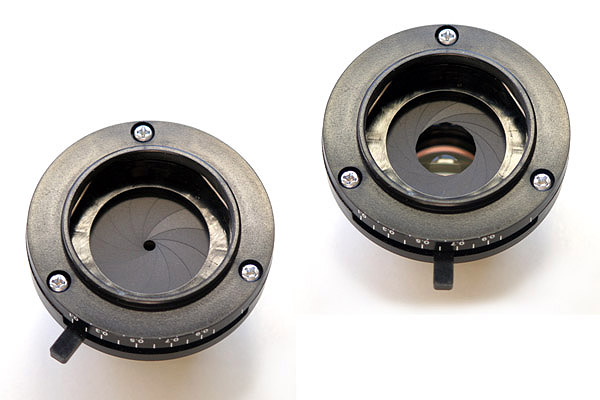

Aperture diaphragmradiology
The lens mount is an interface that allows a lens to be attached to an interchangeable lens camera. As of 2018, Canon has produced 8 mainstream lens mounts.However, a lens mount does not exist simply as a means of attaching a lens to the camera. It also facilitates communication between the camera and the lens, enabling both to perform a wide range of functions.Canon’s first mount was a standard-thread-type screw mount that supported the mechanisms found in rangefinder cameras. Subsequent mounts evolved with the times in order to meet users’ expectations, delivering such advancements as automatic aperture, auto-exposure and autofocus mechanisms.The newest mount, the RF mount, promises even better image quality and usability thanks to its large mount diameter, short back focus distance and enhanced lens-camera communication system. It is indeed a mount designed for the future.It can be said that the lens mount is the key to the future evolution of both lenses and cameras.
Many modern course microscopes are equipped with a condenser and an associated condenser diaphragm. The purpose of the condenser is to concentrate the light onto the specimen, its diaphragm regulates resolution, contrast and depth of field. There is a trade-off to consider:
Aperture diaphragmfunction
It is up to the microscopist to find the optimum setting of the aperture diaphragm, but for optimum resolution the setting of the diaphragm should be more or equal to the numerical aperture of the objective (this value is printed on the objective). Visit the Microscopy Shop! >>> USA Shop | Germany Shop | UK Shop | Canada Shop <<< As an Amazon Affiliate, I earn a commission but it does not cost you more. Many beginning microscope users prefer to generally close the aperture diaphragm all the way. The image possesses more contrast and subjectively appears more crisp. The image looks less “washed-out” The increased depth of field also makes it easier to find the plane of focus.
Aperture diaphragmdiagram
A spigot mount supporting TTL metering at maximum aperture and featured a predecessor of the automatic exposure (AE) mechanism.
This site uses cookies. By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. For more information
In this post, the function of the condenser aperture diaphragm is explained. The purpose of the condenser is to concentrate the light onto the specimen, its diaphragm regulates resolution, contrast and depth of field.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500