All Details About Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) - plastic fiber optic cable
Lasers and laser systems are divided into four major classifications according to their potential to cause biological damage to the eye or skin. The purpose of these classifications is to warn users of the hazards associated with the laser relative to the Accessible Emission Limits (AEL). These limits are based on laser output energy or power, radiation wavelengths, exposure duration, and cross-sectional area of the laser beam at the point of interest.
Saturdays, Sundays and Federal holidays please leave a message. A customer representative will contact you within 24 hours of the next business day.
Class 2m laserpointer
Class I: cannot emit laser radiation at known hazard levels (typically continuous wave: CW 0.4 µW at visible wavelengths). Users of Class I laser products are generally exempt from radiation hazard controls during operation and maintenance (but not necessarily during service).
Representation of a right-circularly polarized electromagnetic wave. Yellow arrows are the electric field, green arrows are the magnetic field.
Class4laser
Class I.A.: A special designation that is based upon a 1000-second exposure and applies only to lasers that are “not intended for viewing” such as a supermarket laser scanner. The upper power limit of Class I.A. is 4.0 mW. The emission from a Class I.A. laser is defined such that the emission does not exceed the Class I limit for an emission duration of 1000 seconds.
This page was originally published on Friday, July 7, 2017. This page was last updated on Wednesday, October 9, 2024 at 12:07 AM EDT.
Class3Blaser
Class II: Low-power visible lasers that emit above Class I levels but at a radiant power not above 1 mW. The concept is that the human aversion reaction to bright light will protect a person. Only limited controls are specified.
Class2laserpointer
Class 2: Low power lasers (CW: up to 1mW) in visible wavelength range (400-700nm). The aversion response will protect the eye from damage due to direct exposure. There is no hazard from exposure to diffuse radiation.
Laserclasses
Since lasers are not classified on beam access during service, most Class I industrial lasers will consist of a higher class (high power) laser enclosed in a properly interlocked and labeled protective enclosure. In some cases, the enclosure may be a room (walk-in protective housing) which requires a means to prevent operation when operators are inside the room.
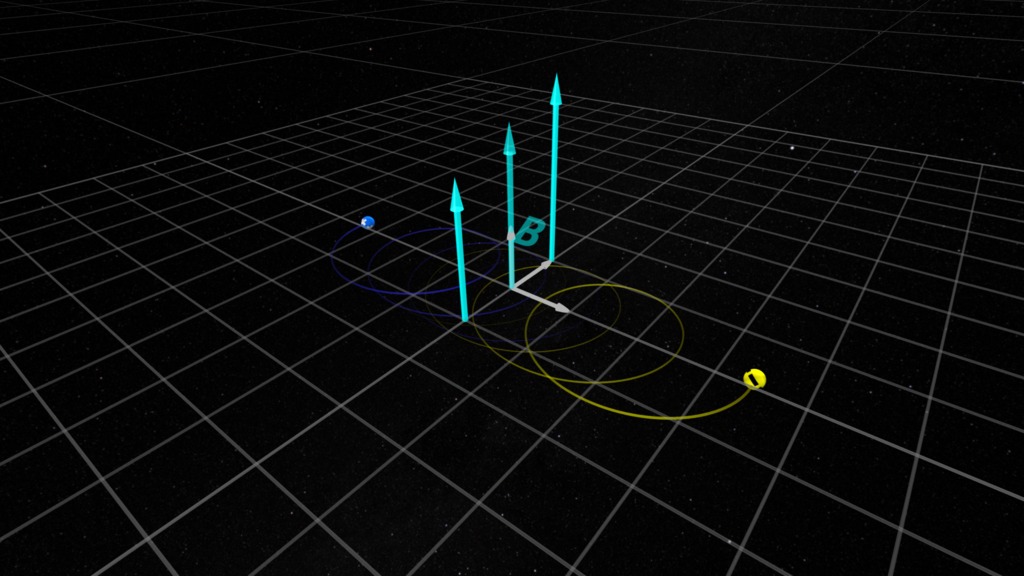
Representation of a left-circularly polarized electromagnetic wave. Yellow arrows are the electric field, green arrows are the magnetic field.
Class 4: High power lasers (CW: above 500mW). Direct and diffusely scattered radiation from Class 4 lasers is hazardous to the eye. Direct exposure of Class 4 lasers are also a potential skin hazard and fire hazard.
Accessible Emission Limits (AEL) – the maximum accessible level of laser radiation permitted within a particular laser class. Aversion Response – Blinking of the eye, or movement of the head to avoid exposure to a bright light. Continuous Wave (CW) – Continuous emission of radiation as opposed to short bursts. Controlled Area – An area where the occupancy and activity of those within is subject to control and supervision for the purpose of protection from radiation hazards. Diffuse Reflection – Change of the spatial distribution of a laser beam when it is reflected in multiple directions by a rough or matte surface. Intrabeam Viewing – Exposing the eye to all or part of a laser beam. Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) – The level of laser radiation to which a person may be exposed without hazardous effect or adverse biological changes in the eye or skin. Nominal Hazard Zone (NHZ) – The space within which the level of the direct, reflected, or scattered radiation during normal operation exceeds the applicable MPE. Specular Reflection – A mirror-like reflection of a laser beam.
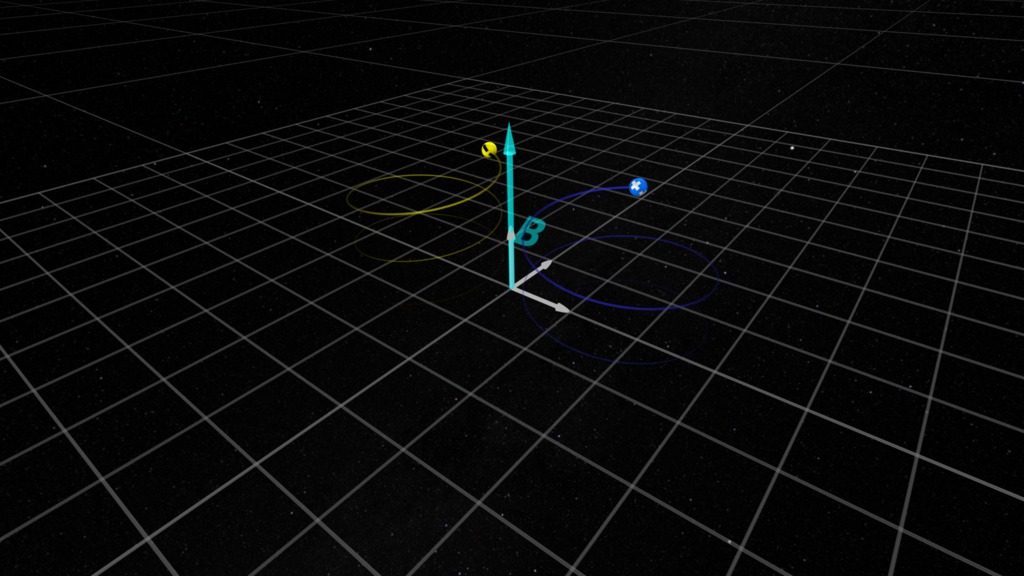
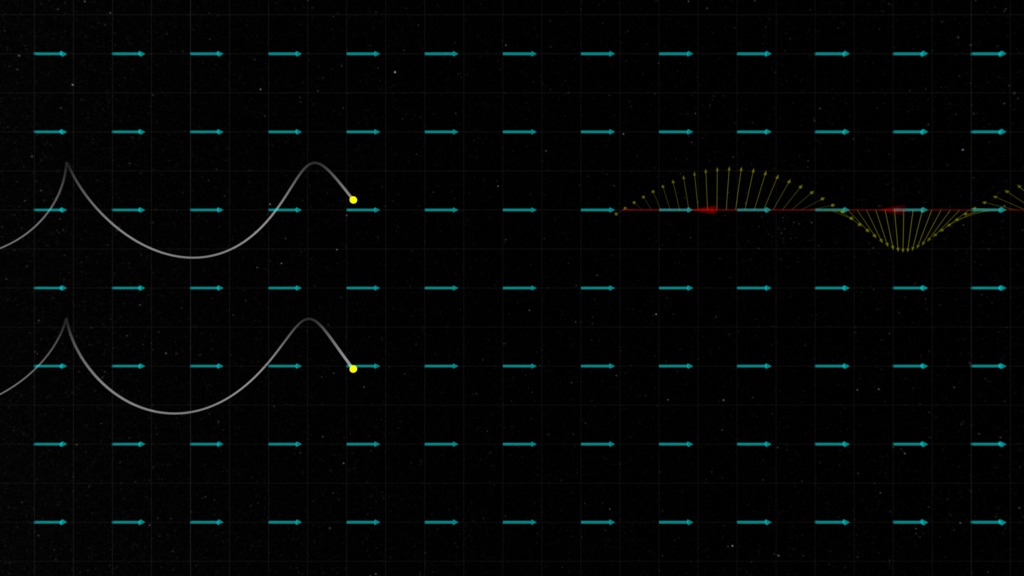
A huge amount of our remote sensing capability depends on the light, AKA electromagnetic radiation, which we receive from distant objects. In addition to the light's wavelength and frequency (which tell us the speed of the radiation - which can be slower than 'c' in some environments), the polarization of the waves can reveal more insights on the source of the light, and the region through which it has passed.The wave polarization is determined by the direction of the electric vector (represented by yellow arrows in these visualizations). We classify electromagnetic wave polarization as linearly polarized or circularly polarized, depending on whether the electric vector maintains a fixed direction in space (linear polarization) or rotates around the direction vector (red arrows) in the case of circular polarization. Circular polarization can be classified as left-circularly polarized or right-circularly polarized. There is also elliptical polarization which can be constructed as a combination of linear, left- and right-polarized waves.For these visualizations, we define left- and right-circular polarization based on the 'Right-hand rule' (Wikipedia), determined by the motion of the electric vector at a fixed position along the wave (see Wikipedia: Circular Polarization). There is some ambiguity in these conventions, so use caution when applying.
Representation of a left-circularly polarized electromagnetic wave. Yellow arrows are the electric field, green arrows are the magnetic field.
NOTE: There are different logotype labeling requirements for Class IIIA lasers with a beam irradiance that does not exceed 2.5 mW/cm2 (Caution logotype) and those where the beam irradiance does exceed 2.5 mW/cm2 (Danger logotype).
Class3Rlaser
Class IIIB: Moderate power lasers (CW: 5-500 mW, pulsed: 10 J/cm2 or the diffuse reflection limit, whichever is lower). In general Class IIIB lasers will not be a fire hazard, nor are they generally capable of producing a hazardous diffuse reflection. Specific controls are recommended.
Class 1M: Class 1M lasers are not capable of producing hazardous exposure under normal operating conditions, but may be hazardous if viewed with the aid of optical instruments.
Representation of a right-circularly polarized electromagnetic wave. Yellow arrows are the electric field, green arrows are the magnetic field.
Class1Mlaser
Class IIIA: Intermediate power lasers (CW: 1-5 mW). Only hazardous for intra-beam viewing. Some limited controls are usually recommended.
Class1laser
Class 2M: Low power lasers (CW: up to 1mW) in visible wavelength range (400-700nm). Class 2M lasers are not hazardous under normal operating conditions because of the aversion reaction. Class 2M lasers may be hazardous if viewed with the aid of optical instruments.
Representations of electromagnetic waves of different polarizations: Right circular polarization (upper/right); Linear polarization (middle); and Left circular polarization (lower/left). Yellow arrows are the electric field, green arrows are the magnetic field.
Class 1: Class 1 lasers are safe under all operating conditions. There is no risk to eyes or skin. Class 1 lasers may consist of a higher power laser housed within an enclosure.
Class 3R: Moderate power lasers (CW: up to 5mW) for visible wavelengths (400 to 700nm). Up to a factor of five over maximum allowable exposure of Class 2 lasers for other wavelengths. Class 3R lasers are considered low-risk but potentially hazardous.
Class 3B: Moderate power lasers (CW: up to 500mW, Pulsed up to 30mJ) in wavelength range of 300nm to far infrared. Direct eye exposure to Class 3B lasers is hazardous; however, diffusely scattered radiation is generally safe. Direct exposure to skin is a potential hazard.
Representations of electromagnetic waves of different polarizations: Right circular polarization (upper/right); Linear polarization (middle); and Left circular polarization (lower/left). Yellow arrows are the electric field, green arrows are the magnetic field.
Class IV: High power lasers (CW: 500 mW, pulsed: 10 J/cm2 or the diffuse reflection limit) are hazardous to view under any condition (directly or diffusely scattered) and are a potential fire hazard and a skin hazard. Significant controls are required of Class IV laser facilities.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500