Adaptive Immunity and the Immunoglobulin Superfamily - immunoglobulin wiki
IR Magic Black Solas3™ is a Covert IR Material that is only Reflective when viewed with night vision equipment. This matt black Military grade IR material, ...
When designing a lens that transmits light, it is necessary to consider the material’s refractive index. Even a small change in the refractive index can affect the candela distribution of the transmitted light. This can be seen in the example below, where light travels through two identically shaped plano convex lenses with different refractive indices.
When reviewing a glass property sheet and designing a part, it’s important to know if the industry specifications you’re trying to meet are for external transmission or internal transmittance. For instance, many of the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) specifications for airport and aerospace applications have requirements that are provided in external transmission. SAE Aerospace Standard AS 25050 requires specific external transmission ratios for the different colored ware. Depending on the transmission level, various grades (A-D) are assigned to the ware.
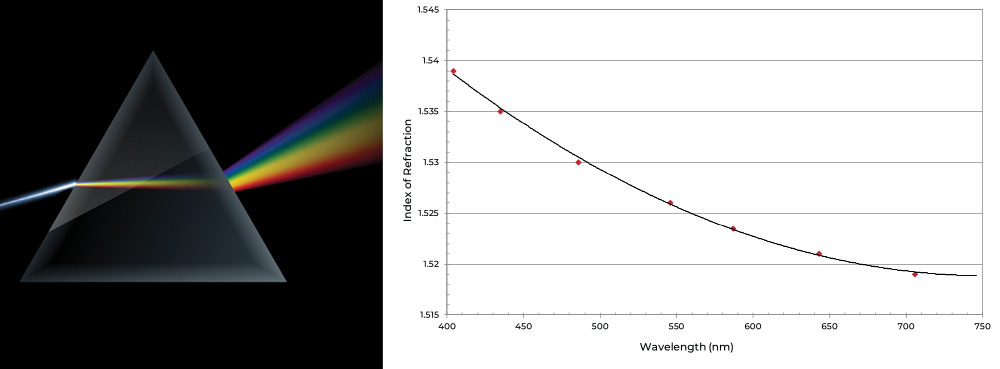
For example, if you are designing optical prisms or other features of a lens, it is critical to choose the correct index of refraction. As previously mentioned, the index of refraction changes with wavelength, so it may be necessary to address any index changes and design optical features that work across the spectrum with LEDs that range from blue to green to red.
Strong and dependable, Steelman hex key wrenches are designed to provide maximum torque without rounding out fasteners. With both standard chamfered and ...
It’s important to note that all of the optical properties previously outlined are wavelength dependent. For example, the refractive index of a glass increases as the wavelength of incident light gets shorter. The dispersion of the refractive index is often shown using the example of white light splitting while traveling through a prism. According to Snell’s law, since nblue > nred, light with blue wavelengths refract or change directions more while red wavelengths refract less as they enter, travel though, and leave surfaces of different matter.
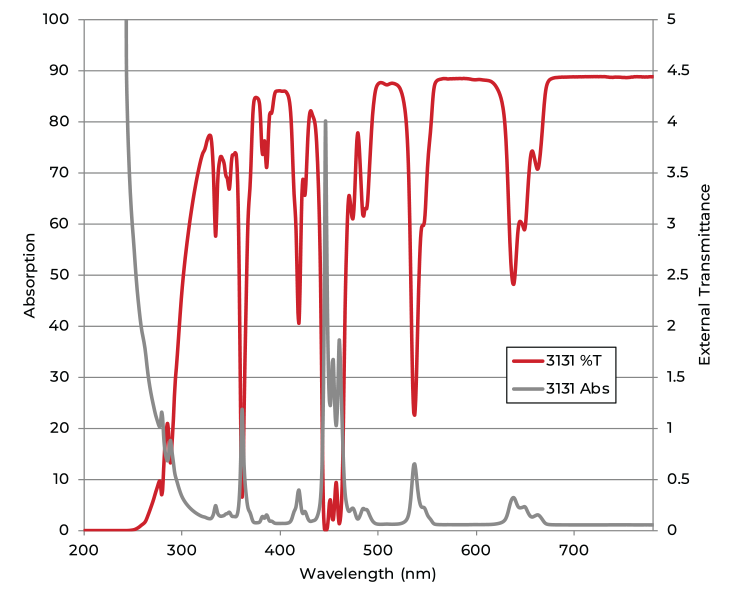
External transmittance includes both the absorption loss of the material and the loss of light due to reflection at the two glass surfaces, while the internal transmittance only includes absorption losses of the material.
Linepair resolution
The resolving power of a lens is measured in line pair per millimeter or lp/mm. It is a measurement of spatial resolution used to calculate how small a detail in an image can be resolved by a lens. The unit expresses the number of line pairs you can fit within one millimeter.
For instance, if you are using See3CAM_CU135 – a 13 MP high-resolution USB camera from e-con Systems™ – to read barcodes, you need to make sure that the lens you pick can meet the maximum desired resolution.
When a beam of light hits a glass surface, part of the beam is reflected and part is transmitted. The index of refraction of the glass determines not only how much light is reflected and transmitted, but also its refracted angle in the glass. The angle of transmission can be calculated using Snell’s law:
Prismatic Laser is a Psychic-type attack. Advertisement. Learnability. The only Pokémon capable ...
A line pair is a pair of black and white lines next to each other with the same width and orientation. The ability to differentiate two bars as separate entities in a specific resolution would be based on the contrast level. It means that calculating resolution in terms of lp/mm is extremely useful when comparing lenses. This can act as one of the criteria while choosing the best-fit lens for a given sensor and application.
The reflection, absorption, and transmission of a glass also vary with wavelength. The color of a glass is determined by the wavelengths that the glass absorbs and transmits. For example, a glass that absorbs green, yellow, and red wavelengths and transmits blue wavelengths will appear blue to the eye. Chromaticity is something we know a lot about and will discuss in greater detail in a future blog article.
For instance, if you want to calculate the resolving power of See3CAM_CU135 – 4K USB camera – with the default product lens, you should capture the image of the resolution chart with the desired aspect ratio at the prescribed working distance.
Rare earth glass filters are often used to calibrate the absorption and transmittance of spectrophotometers. These glasses absorb light at very specific wavelengths, which enable the calibration of well characterized absorption peaks across the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared spectrums.
To give you an example, if the aspect ratio considered for See3CAM_CU135 – 13MP USB camera – is 4:3, the image of the resolution chart has to be captured at that aspect ratio to finally arrive at the resolving power. Below is a sample image of the resolution chart taken at an aspect ratio of 4:3.
This is the second article in a three-part series that reviews the thermal, optical, and mechanical properties of glass. We will define common glass properties and explain their application and importance in component design.
When light travels through a glass, the intensity of the light is typically reduced. This absorption happens when the energy of a photon of light matches the energy needed to excite an electron within the glass to its higher energy state, and the photon is absorbed by the glass.
Line pairs per mmcalculator
The resolving power of a lens can be calculated manually as well as in automated manner. The manual method is called the human eye perception method, and the automated technique is called the IMA Test method. We will look at both these in detail in this section.
May 3, 2023 — Types of Polarization: There are three main types of polarization namely, linear polarization, circular polarization, and elliptical ...
Using the above data, you can validate how much lp/mm a particular lens would resolve at a specific working distance. Based on this, you can select the right lens for your application. It is pertinent to note that a change in FoV will affect the magnification factor, which will end up affecting the practical image space resolution.
lp/mm calculator
Any light that is not absorbed by a glass or reflected at its surface will be transmitted through the glass. It is often very important to know exactly how much light will pass through a glass at specified wavelengths. Often, glasses are discussed in terms of their transmittance or transmission. The same information is provided by both of these terms but transmission is reported with ranges from 0 % to 100 % and transmittance from 0 to 1.
As shown in the chart, you can count the number until the line pair degrades. It is where you can’t distinguish the black and white lines (due to merge, grey colors will appear). Typically, the values of this line will be mentioned in the resolution chart (100 x per picture height).
To calculate the resolving power or object space resolution value using the human eye perception method, you need to first find the LW/PH (line width per picture height) value. To do this, you must observe the line pair highlighted in red (horizontal or vertical) in the resolution chart given in the previous section (Figure 1).
Jul 16, 2012 — f/1.2 is f/1.2, f/3.5 is f/3.5, etc. Much like focal length, aperture is a physical measurement, it is a ratio (1:2.8 for example) relative to ...
If you want to learn how to design glass lenses and components that are optimized for both your performance requirements and operating environment, download our free eBook.
As a New Product Development Engineer, Mike develops a strong understanding of customer needs and works with the Kopp Glass commercial and technical teams to provide innovative solutions in the forms of molded glass. Mike is a Pittsburgh native and graduate of The Pennsylvania State University where he earned a B.S. in Engineering Science and Mechanics and a B.S. in German. He has four years’ experience in thin film organic electronics and five years’ experience in automotive glass product development. He enjoys exploring Pittsburgh and the surrounding areas while jogging, hiking, biking, and skiing with his friends and his wife, Mallory, and their dog, Rocky.
Let’s say you have to decode an object like a small barcode and that too at a longer distance. You would have to differentiate the bars by allowing a certain amount of space between them. This minimum distance depends on the resolution of the camera. However, when you use a sensor with the desired resolution, it is also important to choose a lens that can help capture the level of detail expected from that resolution. This is where knowing the resolving capacity of the lens becomes important.
Image Space Resolution is the resolution in the image plane in consideration of the sensor pixel size. Generally, two pixels or one line pair is the highest frequency which can be resolved by a sensor – using the Nyquist frequency. Therefore, image space resolution is theoretically calculated as:
To understand how the theoretical and practical methods of calculating resolving power differ, we will look at how these are done for e-con Systems’ See3CAM_CU135 in the next section.
Vinoth Rajagopalan is an embedded vision expert with 15+ years of experience in product engineering management, R&D, and technical consultations. He has been responsible for many success stories in e-con Systems – from pre-sales and product conceptualization to launch and support. Having started his career as a software engineer, he currently leads a world-class team to handle major product development initiatives
lp/mm to pixel size
Line pairs per mmconverter
For most glasses with a refractive index of 1.5, reflection losses at the surface result in an approximate 4% decrease in light intensity.
Calculating the resolving power value of a camera lens practically involves taking into consideration the real aspect ratio of the camera.
The absorbance of a glass, shown in the figure above as a function of wavelength, is often used to describe the decrease in intensity of light as it travels through the glass. It is defined as
Photo shared by SÉRIE DOM on June 23, 2021 tagging @flaviotolezani,. Família ❤️ #Dom no @primevideobr @conspiracaofilmes 📽️ .
Get the best deal for infrared goggles from the largest online selection at eBay.ca. | Browse our daily deals for even more savings!
The reporting of transmittance values of a material can vary depending on the application or common industry nomenclature. While most industrial glasses report optical properties as external transmittance, values for filter glasses are typically given as internal transmittance. This is because filter glasses may be treated with anti-reflective coatings to prevent intensity losses at the glass surface. For example, a glass filter which has an external transmission of 92% at 589.2 nm might have a much higher internal transmittance of 0.98, as is the case with our 3131 filter.
You’re probably familiar with the concept of “traveling at the speed of light”, but did you know that the speed of light can change? Light’s speed is reduced when it travels through a medium due to the interaction of photons with electrons. Typically, higher electron densities in a material result in lower velocities. This is why light travels fast in glass, faster in water, and fastest in a vacuum. The refractive index (n) of a material is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that of light in the material.
Line pairs per mmand pixel size
If you are looking for help in selecting a camera solution with the best-fit lens for your application – no matter the industry, please write to us at camerasolutions@e-consystems.com. You can also visit our Camera Selector to get a full view of e-con Systems’ camera portfolio.
Given below is the comparison of image space resolution and object space resolution values obtained using the theoretical and practical methods.
The luminous intensity distribution on the right is from a glass lens with a typical refractive index of 1.5.Displayed on the left, a lens with a refractive index of 1.6.It could be made from a higher index of refraction glass or plastic, such as polycarbonate. For an application that requires light illumination across a larger surface area, it may be better to choose a glass with a smaller refractive index. Or for instance, you want to obtain more intensity closer to the center of the candela distribution; you would choose a material with a higher refractive index. Understanding this optical property will provide you with one more tool to help you select the right material and achieve your desired performance results.
We often hear from engineers who are evaluating the impact of a design change from one lens material to another. For example, they may be switching from an existing polycarbonate lens design to glass due to concerns about durability in harsh environments. They ask “Can I use my existing lens design with the new glass material? Will the resulting light output have the same chromaticity, distribution, and intensity?” The answers to these questions are rooted in understanding the optical properties of materials.
As a New Product Development Engineer, Mike develops a strong understanding of customer needs and works with the Kopp Glass commercial and technical teams to provide innovative solutions in the forms of molded glass. Mike is a Pittsburgh native and graduate of The Pennsylvania State University where he earned a B.S. in Engineering Science and Mechanics and a B.S. in German. He has four years’ experience in thin film organic electronics and five years’ experience in automotive glass product development. He enjoys exploring Pittsburgh and the surrounding areas while jogging, hiking, biking, and skiing with his friends and his wife, Mallory, and their dog, Rocky.
As LED adoption increases and replaces conventional light sources, it is important to consider how their light output differs. The image below shows how the spectral power varies between a blue, green, and red LED compared to an incandescent (CIE Illuminant A) source. Colored LEDs have narrow wavelength bands of emitted light which must be considered when designing for specific application wavelengths.
Larger indices of refraction in glass result in greater differences between the angle of incidence and transmission of light. The reflection of light at the surface occurs due to an instantaneous change in refractive index between glass and its surrounding medium. For normal incidence (Θi = 0°), the amount of light reflected is found by
KDJXZ Adjustable Glasses,Prima Focus Glasses Adjustable Focus Glasses Clear Vision Suitable for Women Men HD Upgraded Deep Focus Adjustable. Brand: KDJXZ.
In some applications it is beneficial to reduce light output in equal parts across all wavelengths. Neutral density filters, for example, absorb all wavelengths nearly equally and are often used in photography to reduce the intensity of light without affecting the color. They’re also used to attenuate lasers and other light sources where the power can’t be adjusted or reduced.
In today’s blog, let’s look at how to determine the resolving power of a lens, which is one of the most critical parameters to consider while choosing a lens for your application.
Line pairs per mmradiology
As mentioned above, Object Space Resolution denotes the resolving power of a lens. It defines the size elements of the object that can be resolved. It is calculated as:
here A, B, and C are constants specific to the glass composition. This relationship works well for visible wavelengths, but often does not accurately describe ultraviolet or infrared behavior.
Dec 11, 2023 — Infrared lenses are specialized optical components designed to operate in the infrared spectrum, a range of electromagnetic radiation beyond the ...
In the IMA test method – which is the automated method – the LW/PH value is calculated by considering the MTF30 value. This is an objective measurement of sharpness, which is better than the subjective analysis. The data in the IMA chart is in the units LW/PH, and it can be converted to lp/mm as shown in the above calculation.
lp/mm to resolution
Image space resolution is inversely proportional to the sensor’s pixel size. This means the smaller the pixel size, higher will be the image space resolution value.
The reason why this is called the human eye perception method is that the number of lines counted may differ depending on the ability of the observer to distinguish between two consecutive lines.
Resolving power is calculated as object space resolution. And object space resolution is derived from what is called the image space resolution. We will now look at both the terms and learn now they are calculated.
Buy Keikan Panny My Melody Mini Wallet CMNS1-MMDirect From JAPAN ☆ online today! Description Genuine Products Warranty We are a Japanese company.
To help you design better-performing glasses lenses, we created a comprehensive eBook that includes more than 40 pages of information on the thermal, optical, and mechanical properties of glass.
So far in this series we’ve discussed thermal and optical properties of glass and their impact to product design. These are just two elements of successful design. Our final article in this series will explore the mechanical properties of glass, which are especially relevant when products are used in harsh environments or are subject to corrosive chemicals.
In a camera system, the image sensor receives incident light (photons) – either focused through a lens or any other optics. Hence, lens selection plays a major role in determining image quality, FoV (Field of View), DoF (Depth of Field), etc.
The optical properties of a material determine how it will interact with light. Today, most engineers use advanced software tools to simulate the properties of a material and their impact on optical performance. Still, familiarity with a few fundamental optical properties will help engineers pick the right material for their application. In this article, we review refractive index, transmission, absorption, and wavelength dependency and discuss how these properties impact product design.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500