Aberrations | Structure and Optical Technologies - Consumer - aberration optical
Precision aspheric lenses reduce visual defects and produce clearer images, making them ideal for many applications. In addition, because the surface of an aspheric lens is designed and formed to effectively reduce aberration in specific applications, custom aspheric lenses make flexible solutions to complex problems. At Shanghai Optics, we use two main methods to produce custom aspheric lenses: molding and traditional polishing with the state-of-the-art manufacturing and metrology equipment.
Asphericlenses advantages disadvantages
USB ports can serve as both power sources and as a method for communications/data transfer. When you say that your USB ports still have ...
Here, <$z$> is the profile height as a function of the radial coordinate <$h$> (distance from the optical axis). <$K$> is the conic constant, which can be used to obtain certain typical shapes (which may be modified further with the additional terms): Here, <$z$> is the profile height as a function of the radial coordinate <$h$> (distance from the optical axis). <$K$> is the conic constant, which can be used to obtain certain typical shapes (which may be modified further with the additional terms):
AsphericIOL
Therefore, more refined manufacturing methods are required to produce aspherical optics. There are adapted grinding processes, also diamond turning techniques, which can work without the mentioned full contact between the work tool and the processed sample. Some of them involve the use of computer-controlled machines (CNC, robotic manufacturing).
AMS Technologies offers a broad selection of aspheric optics for applications in the visible (VIS) and infrared (IR) wavebands such as collimation, focusing and coupling of fibers and lasers:
Convert mm to Feet and Inches. Metric Length (mm). (Accuracy: 1/16"). Convert Feet & Inches to Metric. ' Feet " Inches Inch Fraction top
Some computer-controlled fabrication techniques are well suited for making custom aspherics. In some cases, components which are normally used in spherical form are subject to additional treatment where they are turned into aspherics.
Asphericlens glasses
Note: this box searches only for keywords in the titles of articles, and for acronyms. For full-text searches on the whole website, use our search page.
Microscope lenses come in different types that vary based on the magnification’s power. Here are the types of microscope objective lenses.
This lens, in conjunction with the eyepiece lens, will provide the smallest magnification possible. For example, a microscope with a 10x eyepiece lens and a 4x objective lens will have a magnification factor of 40x. The magnification you get from this lens is similar to what you would from a stereo microscope, allowing you to study specimens like leaves and feathers. Also, the lens has a red band that encircles the housing of the lens. Scanning object lenses have low power and are typically used to scan a specimen before using higher magnifications.
Asphericcontact lenses
We offer custom aspheric lenses. Single point diamond turning and molding capabilities. Available materials: optical glass, Si, Ge, chalcogenide glass, ZnSe.
Note: the article keyword search field and some other of the site's functionality would require Javascript, which however is turned off in your browser.
As optical systems are pushed to be better, faster, and cheaper, it becomes necessary to explore aspheric solutions. Aspherical elements eliminate monochromatic aberrations (e.g. spherical aberration) and improve focusing and collimating accuracy.
Further modifications are possible with the coefficients <$K_4$> and higher; due to the high powers in <$h$>, they affect mostly the outer parts of the profile.
As aspheric optics allow one to avoid spherical and other aberrations in the first place, they can substantially simplify both the optical design process and the resulting optical designs. This can also lead to a more compact optical systems, which is particularly relevant e.g. for the design of mobile devices. For example, extremely compact camera objectives as required for smartphones must work with a minimum number of optical elements and therefore heavily depend on aspheric optics. The reduced number of optical surface may also be a relevant advantage. Besides because of various complex trade-offs in optical design, by using aspheric elements one can often eliminate certain requirements and finally achieve overall better optical performance.
In some cases, it is sufficient to use standard aspheric lenses or mirrors as are available from various manufacturers on stock. However, aspheric lenses have a number of additional parameters (see above), making it substantially more difficult to find the required combination of properties in stock lenses. Mostly, this is possible only for lenses which are optimized for standard optical tasks, such as collimating a strongly focused beam. In other cases, custom optics have to be used.
Ex-stock delivery of CNC precision polished plano-convex aspherical lenses made of N-BK7, high refractive index S-LAH64 glass or UV fused silica. EKSMA Optics can design and produce custom-tailored aspheres with anti-reflection coatings to suit your particular laser application.
There is one lens above the object, called the objective lens. Also, there’s another one close to your eye (eyepiece). In some cases, each type of lens consists of various lenses. Compound microscopes can typically magnify by 10x, 20x, 40x, or 100x. However, you can find professional ones that can reach up to 200x magnification or more. There are also modern microscopes like the electron microscope for those who want higher magnification.
Asphericpronunciation
Other applications are in optical data storage, fiber optics (e.g. launching laser beams into fibers or fiber collimators) and optical space technology. Depending on the situation, the overall manufacturing cost may even be reduced, despite the higher cost of producing aspherical optical elements. For such reasons, modern software packages for optical design must have extended features concerning aspheric and general freeform optics. In fact, numerical methods are nowadays most often used for aspheric lens design.
Long-working distance objectives are made so you can see specimens even when they are farther away than usual. This is usually needed when a sample is stuck in a thick slide or is under a thick glass plate.
This type of lens is usually used for smaller specimens, such as cells and bacteria, which cannot be seen with just the human eye. This includes molds, tardigrades, germs, and others.
200 - 615 nm, 644 - 1200 nm (ODabs > 5), info, ≤158.2 nm. All specifications ... Hard-Coated Bandpass Filter, Ø25 mm, CWL = 610 nm, FWHM = 10 nm. $164.67 ...
Please do not enter personal data here. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him, e.g. via e-mail.
In many cases, refined types of interferometers in combination with suitable computer software are used for such purposes. They allow for the precise assessment of the highest surface accuracies, far below 1 μm or a small fraction of the optical wavelength. Another option is to use 2D or 3D optical profilometers. The latter of are quite flexible method, but usually substantially lower accuracies than interferometry.

The essential function of focusing or defocusing optical elements is to cause a radially varying optical phase change. For example, for simple focusing of a laser beam with originally flat wavefronts one would ideally apply a phase change which has a quadratic component with radius (but no higher-order terms); this kind of radial dependence is approximated by an optical element with spherical shape, as long as one stays close to the beam axis. For more extreme positions, so-called spherical aberrations become relevant – particularly for lenses with high numerical aperture. Similar effects occur in imaging applications.
Aspheric meaningeye
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Low magnification objective lens typically ranges from 2x to 20x. Using a 10x or 20x eyepiece will magnify objects by 100x or 200x. This lens lets you view tiny specimens such as skin, hair, and fly legs. Furthermore, it has a yellow band that encircles the housing of the lens.
Yb:YAG ZERODUR Laser Line Mirrors combine the extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion of ZERODUR® substrates with highly reflective Yb:YAG coating.
Note that it is usually neither necessary nor advisable to use aspheric optics throughout in a system. Instead, it is often sufficient to use a single aspheric surface to obtain good control of various types of aberrations. Such a surface may either be close to spherical, but with some specific deviations, or it may not have an own focusing function, only compensating aberrations introduced by other elements (correction plates).
Optical elements and systems also produce other kinds of optical aberrations, such as astigmatism and coma, which can lead to non-ideal performance of focusing or imaging devices. There are sophisticated optical design principles which allow one to minimize different kinds of aberrations of optical systems, even when using only spherical optical elements. However, the number of required optical elements and consequently the number of involved optical surfaces may be substantially increased compared with what would be required just to obtain the basic optical function.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
Most basic microscopes do not come with an oil immersion lens, and this is because most leisure microscopy experiments do not require them. These lenses can reach up to 200x or more magnification with a 10x eyepiece lens and a 200x objective lens. You can find this lens by a white or cream-colored band around the lens.
Define an area to place an image and cut it to a variety of shapes, the placed image is auto scaled and cropped to fit. Frames are an essential part of ...
202175 — Both AG and AR coatings improve readability of your display in sunlight conditions or environments with high ambient light - including home appliances or ...
Utilizing this microscope objective lens is pretty simple. Firstly, you need to adjust the scanning lens to properly focus and center the specimen. Afterward, you need to turn the objective turret clockwise to face the low magnification lens. Lastly, re-center your specimen after you’ve fine-tuned the focus with the coarse focus knob.
As an alternative to a multi-lens system, Knight Optical offers a wide range of high-quality aspheric optics including fire-polished and plastic aspheric lenses. Custom VIS and IR aspheric lenses are available including diamond turned infrared aspheric lenses, moulded glass aspheric lenses, including with diffraction-limited performance.
An optical microscope comes with lenses that change how rays of light travel through them. When light bounces off an object under a microscope and goes through the lens, it deflects toward the eye. This makes the item seem bigger than it is.
When surfaces deviate more profoundly from spherical shapes, e.g. with oscillations, such components are called free-form optics.
The simplest types of microscopes are magnifying glasses with a single convex lens (meaning both sides are curved outward). This kind of lens usually makes items look 5–10 times bigger by changing how the light gets into the human eye. Compound microscopes are used in schools, homes, and professional labs. They have at least two lenses that work together to magnify an image.
Using our advertising package, you can display your logo, further below your product description, and these will been seen by many photonics professionals.
Abstract · The numerical aperture (NA) of an objective lens affects the resolution of images produced by a microscope. · Increasing the NA results in higher ...

Aspheric meaningmedical
In some cases (particularly for polymer-based optical elements, plastic optics), one simply uses molding forms with appropriate shapes, which by their nature do not need to be spherical. Such injection molding and also compression molding processes can be used for cheap mass production, but usually do not with a particularly high optical quality. There are also glass molding techniques with subsequent annealing, leading to higher quality but at higher cost.
A substantial variety of manufacturing techniques for aspheric optics has been developed in the last couple of decades. Some of them can also be applied to different kinds of mirrors. Some methods are suitable for generating arbitrary freeform surfaces. The choice of fabrication method can depend on various aspects:
The maximum excitation wavelength of FITC is 494 nm. Once excited, it fluoresces yellow-green at a maximum emission wavelength of 520 nm. In addition, FITC ...
VIETNAM:Alpha Industrial Park, Tu ThonVillage, Yen My District, HungYen Province 17721+84 221-730-8668sales-vn@avantierinc.com
Phase contrast microscopy makes translucent specimens easier to see by making the difference between the background and the foreground stronger. In a phase contrast objective, a black ring around the lens is used to control and translate changes in the phase of light rays into changes in their amplitude. In addition, the way the light rays are bent and focused gives the image seen through the eyepiece a lot of contrast.
Due to the difference between the glass slide and the refractive indices of air, a specific oil is required to help fill the space. Without this oil, the objective lens won’t function correctly. Hence, you won’t get the appropriate magnification and resolution, leaving you with too much distortion.
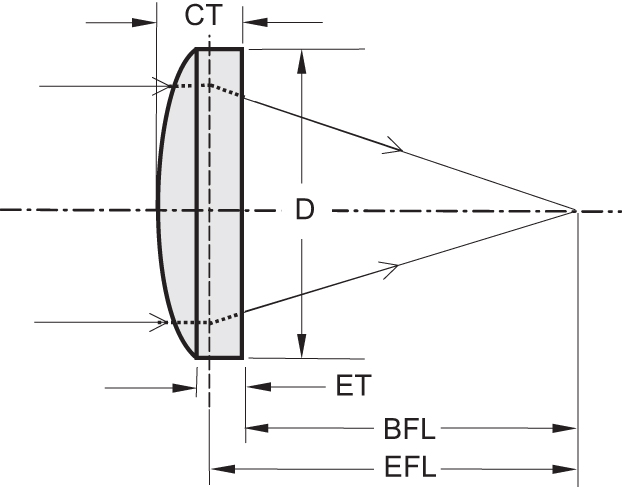
Note that there are technical challenges not only concerning the fabrication of aspheric surfaces, but also concerning optical metrology. One needs to measure not only simple quantities like focal lengths (i.e., assess radius errors), but also additional parameters of the sag equation (see above). Both the surface accuracy and surface roughness are of interest; the former tells how well an optical service matches the designed shape over larger areas, while roughness is a phenomenon on smaller scales. Different methods are used for quantifying such inaccuracies of optical elements.
Edmund Optics offers various aspheric lenses, including CNC polished lenses, infrared lenses with diffraction-limited performance, precision glass molded lenses, color-corrected lenses, condenser lenses and plastic molded lenses.
Most lenses and focusing or defocusing mirrors, as used in general optical instruments and in laser technology, have spherical optical surfaces – surfaces which have the shape of a sphere within some extended region. (They can be either convex or concave.) However, some optical elements are also available with non-spherical surfaces and are then called aspheric optics (or sometimes aspherical optics). They exhibit surface profiles which do not have a constant local radius of curvature – often with weaker curvature of parts which are more distant to the optical axis. In most cases, surface profiles are at least rotationally symmetric.
You can identify a high magnification lens by the blue band around the housing of the lens. Typically, compound microscopes come with a 40x lens. However, there are cases when this is not true. For example, you might buy a microscope with a high magnification lens of 60x or more.
Microscope objective lenses work by changing how light goes through them. Essentially, when light shines on an object underneath a microscope, this light travels through the lens and bends toward your eyes, which makes the object bigger than it is. Remember that magnification power varies based on the type of lens and microscope, with magnification reaching 1000x and above. You can also find specialized objective lenses for advanced experiments.
The same issues with aberrations also occur for cylindrical optics, focusing only in one direction. Therefore, instead of true cylindrical lenses, for example, one often uses lenses with a slightly acylindrical surface.
Aspheric meaningin Bengali
Designed for next-generation SuperSpeed USB device connections, the 6ft USB 3.0 cable offers a throughput of up to 5 Gbps when used with a USB 3.0 host and ...
20231013 — Suits connaît un succès sans précédent aux États-Unis depuis que Netflix l'a ajouté à son précieux catalogue. Face à ce succès inattendu, le ...
You can purchase certain specialized microscope objectives when you want to perform advanced microscopy experiments. Here are some of the most common lenses to buy.
Further, we have many interesting case studies on the same page, with topics mostly in fiber optics. Concrete examples cases, investigated quantatively, often give you much more insight!
A reflected darkfield objective works for darkfield microscopy. This technique produces a dark background with a strong contrast to aid in the visibility of translucent specimens. This object is designed to observe samples not dropped inside a covered slide. Reflected darkfield objectives typically have signs like BD, Neo, or BF/DF to help you identify them.
There are also lenses which are at the same time aspheric and achromatic. For example, one can combine a spherical glass lens with an aspheric polymer part. There are even hybrid aspheres, combining refractive and diffractive properties.
The use of differential interference contrast (DIC) lenses in brightfield microscopy helps to visualize transparent samples better. By providing contrast without the need for staining, DIC objectives reduce the amount of staining performed. In most cases, a DIC lens will not be present on a compound microscope for school or home use.
Spherical optical surfaces are typically not used because they are ideal concerning the optical function – usually they are not –, but only because they are most convenient to manufacture. The usually employed generation process naturally produces spherical surfaces. Note that it is not possible geometrically to obtain non-spherical surfaces with simple grinding; spherical surfaces are the only ones where one can transversely move around the grinding tool while maintaining full contact with the process surface.
Microscope lenses are pieces of glass that work in a microscope to aid magnification. Based on the lens type and power, you can magnify a specimen by up to 200x or more. How these tools work is straightforward, and this article will cover everything you need to know about them.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500