Prime vs Zoom Lenses: What's the difference? - what is fixed lens
Track your Illumination Technologies, Inc order status with tracking number, get real time notifications when your parcel delivery status updated.
In a compliant installation, system access is limited to authorized individuals. Wyatt software leverages the Microsoft Windows security system to provide user authentication:
The green experiment is the result of a default method for separating a sample containing three nanoparticle sizes. The dashed green line shows the cross-flow gradient used, and the solid green line is the measured concentration signal.
Tyler 1 Light 5.38 inch Spot Light. More Options. WAC Lighting. Tyler 1 ... Tyler Natural Brass 5.8 watt LED Spot and Flood Lighting, WAC Landscape. WAC ...
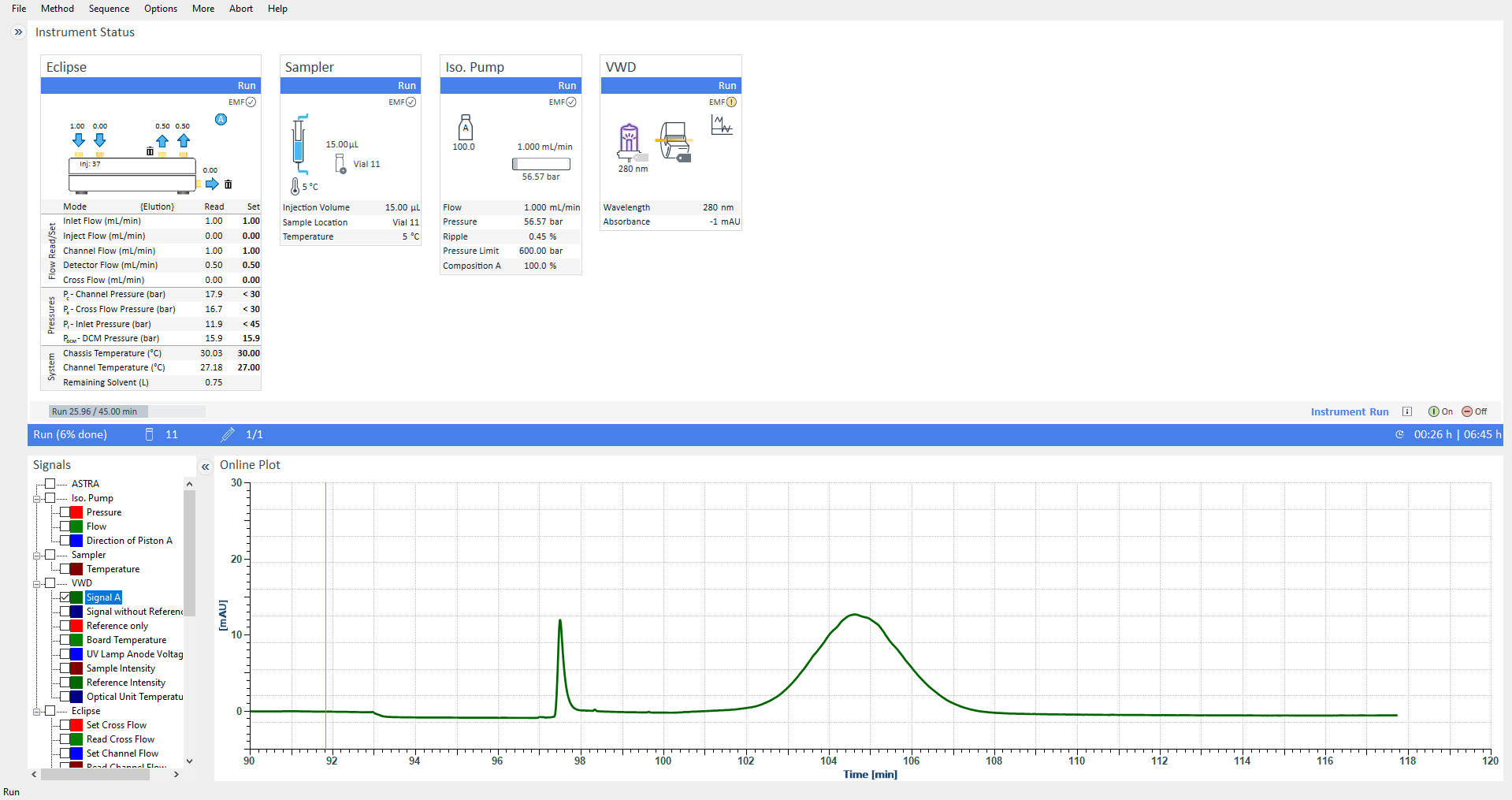
Status information from the Eclipse instrument’s Health Indicators are displayed; should any warnings come up, you will receive actionable recommendations.
Understanding the factors affecting depth of field — including the relationship between aperture, f-stop, focal length, and distance — allows us to create images with the desired focus and blur. By considering these elements, we can effectively control the aesthetic and composition of our photos.
Another challenge when it comes to DOF is managing the trade-off between aperture size and diffraction. Larger aperture sizes generally create a shallower DOF, while smaller apertures increase DOF and lead to a more detailed image3. However, increasing aperture size beyond a certain point might introduce diffraction, causing a loss of sharpness and reduced image quality4. One way to overcome this is by staying within the sweet spot range of the lens, which is typically between f/5.6 and f/11, where diffraction is minimal.
VISION DESIGN immediately displays the predicted fractogram using fundamental FFF theory to calculate retention times, including the effects of band broadening and dilution of the sample in the FFF channel. It only takes a few minutes to explore the effect of different cross-flow rates and timings to improve resolution and find the best method - all from the comfort of your desk.
Flagship software for comprehensive characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles by SEC/FFF-MALS. Acquires, analyzes and reports measurements from multi-angle light scattering, dynamic light scattering, UV/Vis, dRI and differential viscometry detectors. Building on over 40 years of light scattering research, ASTRA includes an unrivaled range of analysis features.
We offer visual artists a community of resources filled with the top advice, workflows, tips, tricks, advice, and business mentorship so that you can become your next level of PRO.
VISION software is the intelligent human interface to an FFF-MALS system built on Wyatt Technology’s Eclipse™ FFF instrument and DAWN™ MALS instrument. VISION comprises two primary modules: VISION DESIGN for in silico method design and optimization and VISION RUN for running FFF methods.
Electrical/asymmetric-flow field-flow fractionation (EAF4) separates by both size and particle charge to determine zeta potential distributions, even of multimodal and polydisperse populations.
VISION RUN transfers UV/VIS signals directly to ASTRA. Set UV parameters and acquire all signals digitally, without any external cabling required. Select up to two UV channels for analysis in ASTRA – even post-collection.
21 CFR Part 11 requires that electronic data be persistent, and that any changes to the data be recorded in an audit trail. VISION employs two methods to ensure this:
In portrait photography, depth of field plays a vital role in highlighting the subject, often by creating an aesthetically pleasing background blur, called bokeh. By using a shallow depth of field, we can isolate the subject and capture sharp, focused portraits with smooth, out-of-focus backgrounds. This separation directs the viewer's attention to the subject's features; while a wider aperture, longer focal length, and closer camera-to-subject distance work together to create a more dramatic effect.
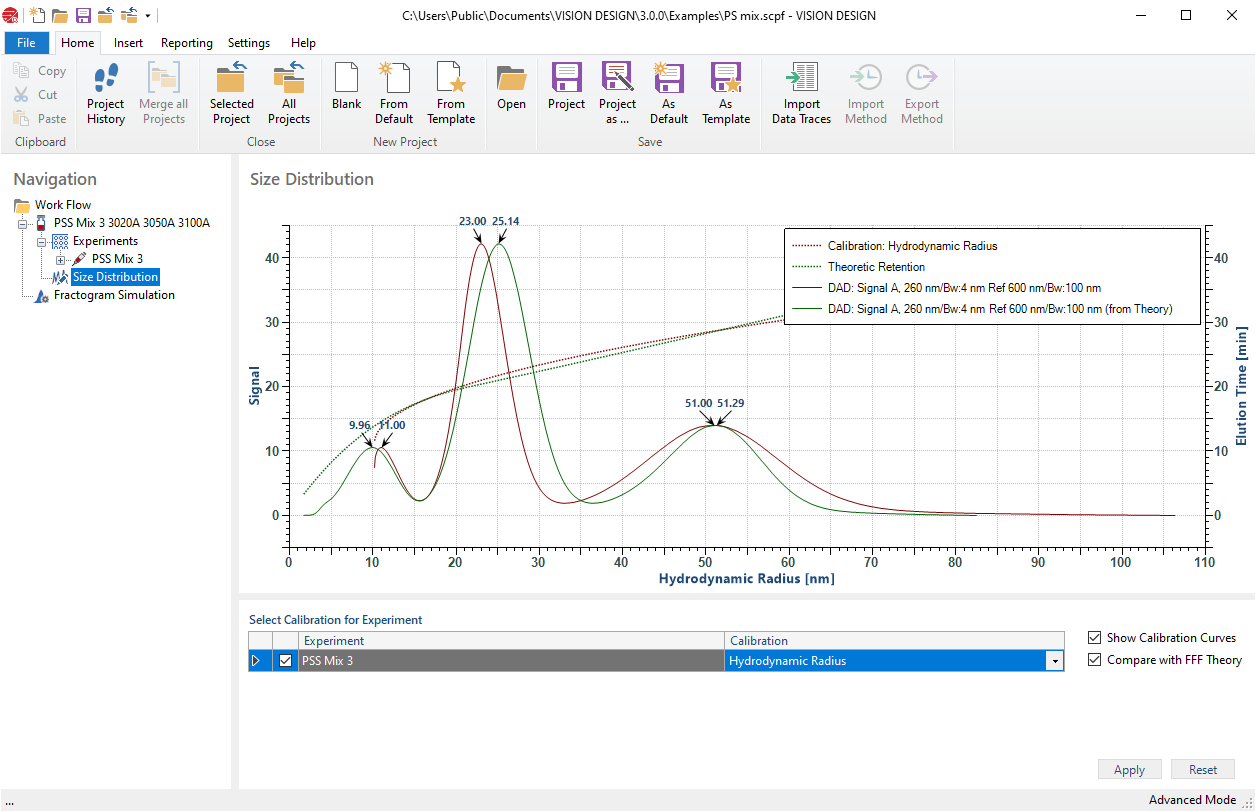
Determine the hydrodynamic radius (Rh) and its distribution from a calculation based on fundamental FFF theory or a calibration with reference standards.
Union Park Capital is a private equity investment firm focused solely on lower middle-market Industrial Technology companies. They partner with management ...
VISION provides two levels of audit trail to independently record all operator actions that create, modify, or delete electronic records. Each entry in the audit trail is time-stamped, and records the operator performing the actions, as well as the computer where the actions are performed.
Flatten the learning curve and increase your productivity. Wyatt offers unmatched software tools for designing, performing and analyzing FFF-MALS experiments.
VISION offers an optional 21 CFR Part 11 compliant security and database package for use in GMP and GLP laboratories, and synchronizes data acquisition with ASTRA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance package.
To achieve a shallow depth of field, use a large aperture (lower f-number), which allows more light to enter the camera lens. This will create a smaller area of focus in your image, resulting in a blurred background. Using a longer focal length and getting closer to your subject will also help achieve a shallow depth of field. This Shotkit guide offers examples and a depth of field calculator to help.
Seamlessly coordinates the pump and autosampler front-end with the Eclipse, detectors and ASTRA, and records FFF, electrical and digital UV signals for diagnostics and analysis in VISION DESIGN and ASTRA.
Spherical Aberration Spherical aberration is an axial aberration, affecting the entire field equally, including stars at the center.
The blue experiment is the result of simulations tested to improve the resolution. With a modified cross-flow gradient, the peaks are expected to exhibit baseline resolution.
depth offield中文
Incoming Qualification and Operational Qualification documents are provided with VISION SP software, ensuring validation at the lab site.
Depth of fieldcalculator
Natural light portraiture has a certain look and feel that is unmistakable. In this tutorial, you'll learn how Dani Diamond produces his beautiful and recognizable natural light portraits. You'll implement Dani's workflow into your own workflow, and be stunned by the final images. This tutorial is perfect for photographers who want to learn how to make post-production retouching look natural. It also teaches you how to integrate key components that work together to create great natural light portraiture. With over 10 hours of content, this tutorial provides everything you need to know about shooting in natural light and retouching your photos in Photoshop.
To achieve a shallow depth of field, use a larger aperture (lower f-stop number) to create a narrow area of focus within your image. In contrast, using a smaller aperture (higher f-stop number) will result in a larger zone of focus, leading to a deeper depth of field.
VISION RUN uses the ICF instrument control framework for Agilent® modules from the 1260 series. The complete feature sets of autosamplers, isocratic or quaternary pumps, UV detectors, fluorescence detectors and fraction collectors are supported.
Sep 29, 2023 — Luckily, when it comes to digital cameras, you really have only three sensor sizes to consider: full-frame, APS-C, and Four Thirds. Here's what ...
To sum up, mastering depth of field requires a combination of aperture settings, focusing techniques, and making appropriate camera and lens choices. By understanding these elements and their relationships, we can produce stunning images with desired focus and blur effects.
Ideally, a 21 CFR Part 11 compliant application should be usable for quality assurance in a manufacturing process. To meet this goal, it is necessary that the application support "operational system checks to enforce permitted sequencing of steps and events". In other words, it should be possible for a technician in quality assurance to run the application with minimal input and limited possibility to affect the results through incorrect decisions.
Depth of field
https://www.bhphotovideo.com/explora/photography/tips-and-solutions/the-challenge-of-depth-of-field-in-macro-or-close-up-photography ↩
Similarly, in wildlife photography, a shallow depth of field is helpful to isolate an animal against its surroundings and make it stand out. However, when photographing animals within their habitat or interacting with each other, a wider depth of field allows the viewer to appreciate the context, the landscape, and the circle of life in which these animals live. Each unique situation and desired outcome will dictate the depth of field necessary to achieve the photographer's vision.
The distance between the camera and the subject is another factor that affects depth of field. The closer you are to your subject, the shallower the depth of field, resulting in a blurred background. Conversely, moving farther away from your subject will increase the depth of field, keeping more of the scene in focus. This TechRadar article further explains how distance and focus control sharpness in photos.
Depth of field (DOF) in photography is a critical aspect of capturing visually stunning images by controlling focus and blur in your shots. Essentially, it refers to the area within a photograph that appears acceptably sharp and in focus. A strong understanding of DOF allows photographers to purposely guide their viewers' attention to specific elements within an image, making it a powerful tool for storytelling and creating compelling compositions.
Wyatt's line of multi-angle static light scattering products couple to size exclusion chromatography (SEC-MALS), field-flow fractionation (FFF-MALS) and stop-flow composition-gradient systems (CG-MALS). Our dynamic light scattering (DLS) products operate in traditional cuvette as well as on-line and automated, high-throughput modes. We also offer unique instruments for electrophoretic light scattering (ELS), differential refractometry and differential viscosity. Wyatt Technology was acquired by Waters Corporation.
The Zebra Aurora suite of machine vision software enables users to solve their track-and-trace, vision inspection and industrial automation needs.
Combines simplified, rationalized FFF method development with FFF data analysis to optimize separations based on FFF theory.
VISION offers a seamless workflow in a few simple steps, starting with developing and optimizing the FFF method in silico, then running a sample sequence, followed by data processing, refining the separation method, reporting and consolidating the data files in projects.
The aperture, which is an adjustable opening in the camera lens, plays a significant role in determining depth of field. A wider aperture allows more light to enter the camera, and a smaller aperture permits less light. The size of the aperture is measured by the f-stop number, with lower f-stop numbers corresponding to a wider aperture and higher f-stop numbers indicating a smaller aperture.
Generative AI in Photoshop is revolutionizing design and photo editing by providing tools that streamline workflows and enhance creativity. This technology enables quick removal of unwanted objects...
All data that VISION generates are made available to the user in human readable form. Using powerful data export and presentation capabilities, all data can graphed, shown in tables, or exported to text.
When it comes to landscape photography, we generally want a wide depth of field to showcase the sharpness, texture, and details across the entire scene. This often involves using a narrow aperture, such as f/8 or f/11, to maintain focus from foreground to background. It's crucial to carefully choose a focal point and balance depth of field with other factors like angle of view, field of view, and camera settings. A more expansive depth of field helps tell a story of the landscape, emphasizing the natural beauty and bringing it to life for the viewer.
The latest generative AI advancements in Photoshop, powered by Adobe Firefly Image 3 Model, revolutionize digital art by offering features like Text to Image and Generative Fill, enh...
VISION software is the central hub for your FFF-MALS system built on the Eclipse FFF instrument and DAWN MALS instrument.
Focal length has a significant impact on depth of field. Longer focal lengths result in a shallower depth of field, while shorter focal lengths produce a deeper depth of field. This means that using a telephoto lens will create more background blur, while a wide-angle lens will keep more of the scene in focus. Shotkit provides examples of the difference in depth of field based on focal length.
There are three main factors that affect depth of field in photography: aperture, focal length, and distance to the subject. Changing any one of these factors will alter the appearance of the depth of field in your images. This TechRadar article provides an in-depth explanation of each factor's impact.
The flexibility of FFF allows users to achieve excellent separations for most applications, but in some cases finding the optimal method for the separation run may require tedious trial-and-error.
The results of a physical experiment can then be fed back into VISION DESIGN to further refine the method. Usually a single test run will give VISION DESIGN the information it needs to help you fully optimize your method.
+1 805-681-9009 Headquarters | 6330 Hollister Ave, Santa Barbara, CA 93117 © 2024 Waters Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Mastering depth of field requires the ability to manipulate various factors such as aperture, focal length, and distance from the subject. By adjusting these elements, photographers can create images with a shallow DOF, where only the subject is in focus and the background is blurred, or a deep DOF, where both the subject and background appear sharp. Experimenting with different settings and techniques can help you achieve the desired effect for your photography style, whether it's portraits, landscapes, or anything in between.
Creating a deep depth of field requires using a small aperture (higher f-number), which allows less light to enter the camera lens. This results in a greater area of focus, keeping more subjects in sharp focus. Using a shorter focal length and increasing the distance between the camera and the subject will also contribute to a deeper depth of field. Reference this B&H Explora article to understand the basics.
Various camera settings and lens choices can also impact depth of field. For instance, focal length of the lens influences the depth of field: a wide-angle lens typically results in a deeper depth of field, while a telephoto lens creates a shallower depth of field. Sensor size also plays a role in controlling depth of field, with larger sensors (such as those found in full-frame cameras) producing a shallower depth of field compared to smaller sensors (e.g., APS-C or Micro Four Thirds).
The decision to use a shallow or deep depth of field depends on the desired outcome and mood you want to convey in a photograph. For instance, a shallow depth of field is often used in portrait photography, highlighting the subject while blurring the background. Alternatively, deep depth of field works well in landscape photography, where the primary goal is to capture everything in sharp focus from foreground to background.
General description of the script. Short wave infrared (SWIR) measurements can help scientists estimate how much water is present in plants and soil, as water ...
By understanding and addressing these challenges, photographers can take better control of their depth of field, ultimately creating more captivating and appealing images6.
VISION offers an optional 21 CFR Part 11 compliance package, including IQ/OQ documents and procedures, which are described below and more fully in the 21 CFR Part 11 White Paper. VISION SP launches and synchronizes with ASTRA SP and employs a secure, joint SQL database for VISION and ASTRA data.
An additional benefit of VISION DESIGN is the analysis of fractograms collected in VISION RUN to determine size distributions based on FFF retention time, even without the use of light scattering data.
With method and sequences technology, VISION supports moving macromolecular and nanoparticle characterization into everyday manufacturing and quality assurance applications.
VISION SP has strong support for enforcing permitted sequences through the methods. A user with Researcher privilege level can create a new experiment, and then save it as a Method. A user with Technician privilege level can only use the Method to collect and analyze data, and cannot make changes to the Method configuration, analysis, or results reporting.
Depth of fieldsimulator
Thirteen key questions to ask when buying a Multi-Angle Light Scattering (MALS) or Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) instrument.
In street and wildlife photography, depth of field varies across different images and styles. For more candid moments, street photographers often use a shallow depth of field to draw emphasis to a single subject, with a background blur that helps evoke a sense of intimacy and emotion. On the other hand, when photographing scenes that feature multiple subjects or convey a broader context, a deeper depth of field may be used to keep everything in focus.
To better understand the relationship between aperture and depth of field, you can experiment with various f-stop settings on your camera and observe the resulting changes in focus and blur. Keep in mind that a wider aperture also allows more light into the camera, which can affect other settings like ISO and shutter speed.
DoF calculators are valuable tools for determining depth of field. These can be standalone devices, apps on your smartphone, or online resources. By inputting information such as focal length, aperture, and camera sensor size, these calculators can estimate the depth of field for your specific scenario. This can help guide your decisions when adjusting camera settings to achieve an ideal depth of field.
In photography, controlling the depth of field (DOF) is essential to achieve desired levels of blur and detail in an image. Shallow DOF can be achieved with larger aperture lenses, but in macro or close-up photography, maintaining the right balance can be challenging 1. One solution to maintain an ideal DOF is to use bracketing2. Bracketing involves taking multiple shots of the same subject, with gradually changing aperture settings, to later select the best image with the intended blur and detail.
Electronic signatures can be executed on any data collected. As such, electronic signatures will be performed in ASTRA in Security Pack mode. Please see the ASTRA product page for more details.
The dashboard shows instrument status with instrument configurations, settings, real-time status and signal display and sample sequences.
FOVand focal length
VISION coordinates data collection in ASTRA™, the most powerful and versatile software available for the characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles via multi-angle and dynamic light scattering.
Another technique for controlling depth of field is focus stacking. This involves taking multiple images at different focus distances, then combining them in an editing program like Photoshop. The result is a single, sharp image with an extended depth of field. A tripod is essential for this technique, ensuring that the camera remains steady between shots.
One technique that photographers use to maximize sharpness across an image is calculating the hyperfocal distance. This is the point at which everything from half the distance to the hyperfocal point to infinity is in focus. It's especially useful in landscape photography, where you want to achieve maximum depth of field.
Each FFF method, sequence and configuration has a separate log that records all actions performed. The logs are always linked with their respective method, sequence or configuration, and cannot be reset. The logs record actions such as:
Telecentriclens
To calculate hyperfocal distance, we need to know the focal length, aperture, and circle of confusion. Alternatively, you can use a DoF calculator or app, which makes the process much easier.
Unleash your individuality with Sleepaxa's revolutionary Custom Lens Fit service, where you can now bring your own frames to life with our exceptional ...
One of the primary ways to control the depth of field is by adjusting the aperture setting of your camera. A wide aperture (represented by a small f-stop number, such as f/2.8) will create a shallow depth of field, resulting in a blurred background. On the other hand, a narrow aperture (larger f-stop number, like f/16) will produce a deeper depth of field, keeping more of the image in focus.
In addition to the aperture, the depth of field is influenced by the focal length of the lens and the distance between the camera and the subject. A lens with a longer focal length tends to produce a shallower depth of field, while a lens with a shorter focal length generally results in a greater area of focus. Additionally, the closer the camera is to the subject, the shallower the depth of field will be.
VISION DESIGN is an indispensable tool for FFF method development which utilizes in-silico, "virtual" experiments based on FFF theory to eliminate most of the time and effort required for FFF method development.
Aperture is one of the main factors affecting depth of field. A larger aperture (lower f-number) results in a shallower depth of field, while a smaller aperture (higher f-number) creates a deeper depth of field. Adjusting the aperture allows you to control the amount of focus and blur in your image. This Digital Camera World cheat sheet demonstrates how to affect depth of field using aperture.
Shallowdepth of field
Accurate focusing plays a crucial role in controlling depth of field. When focusing on a subject, consider using techniques such as manual focus, autofocus points, or focus peaking to ensure the desired area of the image is sharp. Additionally, the distance between you and your subject affects the depth of field: objects closer to the camera will have a more shallow depth of field than those farther away.
Depth of fieldgithub
Once a sample sequence table is defined, VISION RUN will coordinate FFF operation and MALS analysis methods. Samples can be added to sequences on the fly for maximum convenience.
When discussing depth of field in photography, it is important to distinguish between shallow depth of field and deep depth of field. A shallow depth of field results in only a small range of the image appearing sharp and in focus, while the rest of the scene is blurred. Conversely, a deep depth of field achieves a broader range of focus, where more of the scene appears sharp and clear. This distinction plays a crucial role in the overall aesthetic and composition of a photograph.
20101023 — Enough is a simple word that is used often by everyone (a commonly used word). Adequate is a higher level word that is used to say "enough" at a ...
La surround view camera a 360 gradi fornisce assistenza durante le manovre di parcheggio grazie alle quattro telecamere dislocate intorno alla tua Maserati.
VISION calculates zeta potential and electrophoretic mobility from EAF4 measurements made with different applied electrical fields. VISION DESIGN offers fully automated processing plus determination of peak retention time and its shift with the electrical field.
A final consideration is the size of the image sensor. Larger sensors typically produce a shallower DOF when compared to smaller sensors, given the same aperture and focal length settings5. Understanding the impact of sensor sizes on DOF can help photographers make better choices when choosing a camera and settings[^;width:400px;height;border;padding:3^6^px;text-align
Using the depth of field (DoF) preview button on your camera allows you to see what areas of the image will be in focus. This helps you make adjustments to your aperture or focus distance to achieve the desired effect. When using live view, you can also zoom in on specific areas to check focus, making it even easier to visualize the depth of field.
The graph shows size distributions of a polystyrene latex mix reference standard calibration and comparison with FFF theory.
Enter the estimated particle sizes of your sample of interest, select your channel and predict your fractogram based on:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500