Which colors absorb more light energy? - what absorbs light
UVcure Adhesive
Like any important laboratory instrument, you should be sure to take care of your microscope. Bumps, scratches, and dust can easily impair microscope performance. Be sure to clean up your work area and microscope after use and store the microscope appropriately.
Please note: Your browser does not fully support some of the features used on Addgene's website. If you run into any problems registering, depositing, or ordering please contact us at [email protected]. Learn more
You may be wondering why there are multiple objective lenses. Each objective performs essentially the same task but has different magnifying powers. When you look at the side of an objective, you will see several pieces of information, but the most important (for now) is the magnification power, such as 4x, 10x, or 20x. A 4x objective magnifies the image four times the actual size, the 10x objective magnifies it 10 times, and so on.
UVcuringGluefor Plastic
Microscopes are emblematic of biological research and are found in many different types of laboratories. These tools allow you to observe specimens much smaller than you would be able to with your naked eye, like microbes in a drop of pond water or the cells in your cell culture dish. Microscopes come in a huge range of shapes and sizes - from phone-sized, foldable microscopes that aren't very powerful (but are cheap and accessible) to massive transmission electron microscopes that allow us to see cellular components with science-fiction levels of detail. You can take entire courses on microscopy and still have more to learn, so, for this protocol, we'll focus on one of the most common types that you're likely to encounter: the compound light microscope.
The light that does pass through the sample then travels through the objective lens which magnifies the image, then the ocular lens, where the image is further magnified before it finally reaches your eyes. These lenses determine the magnification of the image and the resolution your microscope can achieve. You achieve the highest resolution when your image is in focus, which you can control using the focus knobs on the side of the microscope.
UVadhesive for Glass
The ocular lens also provides magnification and the power should be provided on the microscope; often this lens provides 10x magnification. To determine the final magnification of your image, multiply the magnification of your objective lens by the magnification of your ocular lens. For example, if you observe something using the 10x objective and your ocular lens is also 10x, you would actually be seeing a 100x magnified image of that object!
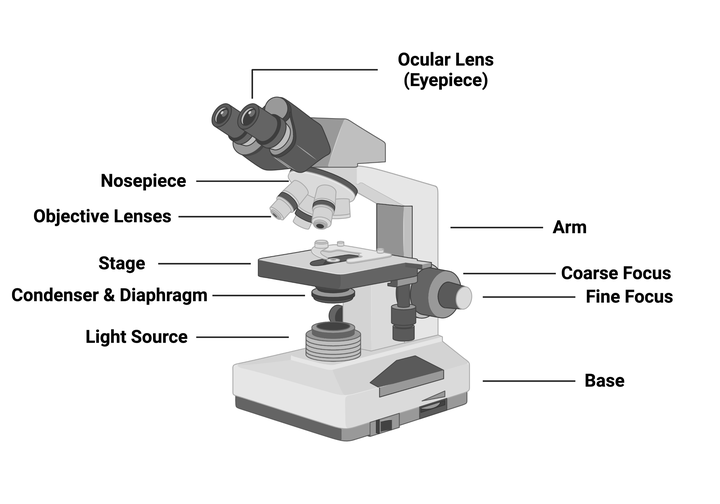
As the name suggests, light microscopes take advantage of the physical properties of light to detect small objects. Two of the most important properties of a microscope are magnification (the ability to make an image larger) and resolution (the ability to distinguish between two discrete objects). Figure 1 depicts an image of a compound light microscope with the main components labeled:
Please note: Your browser does not support the features used on Addgene's website. You may not be able to create an account or request plasmids through this website until you upgrade your browser. Learn more
The route the light follows from the source to your eyes is called the light path. Light travels from the light source through a condenser that helps concentrate the light onto the sample, and then through the sample. However, some of that light won’t make it through the sample because different components of the specimen will refract and reflect the light. These differences create contrast, which allows you to distinguish objects within the sample. You can increase contrast by a) adjusting the aperture of the condenser diaphragm to limit the amount of light hitting the sample or b) using dyes or stains that add color to some components of the sample but not others.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500