Real Life Applications of Light Absorption - absorption light
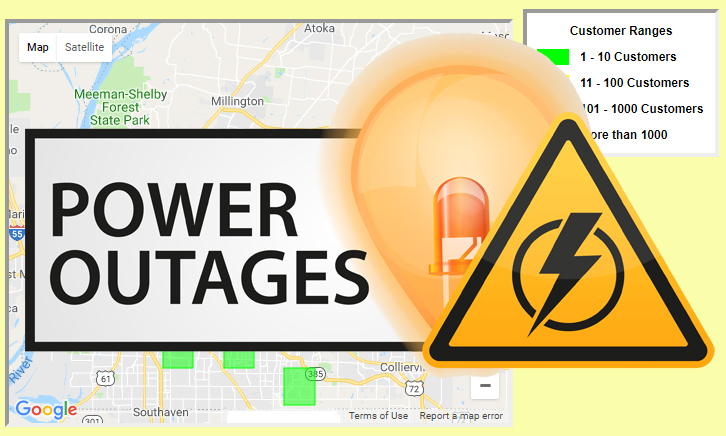
Memphis Light, Gas and Water's Electric Outage Summary Map provides you general information about the outage level across Shelby County. Detailed information about specific addresses is not available for home safety and security measures. All information displayed on this site is based on reported and known outages. For information about your specific outage, or if you have an outage and the section of the map you are in doesn't show any outages, call MLGW's Electric Outage Hotline, (901) 544-6500. Important Note: Customers using Internet Explorer 8 or older may not be able to access the outage map due to compatibility issues between IE 8 and Google Maps.
Remember to keep your telephone number(s) updated with MLGW so we can provide you with faster service when reporting outages. Updated information will:
Color When atoms or compounds absorb light of the proper frequency, their electrons are excited to higher energy levels. Colored compounds absorb visible (colored) light and this absorption is responsible for their color. Our eyes perceive a mixture of all of the colors, as in the proportions in sunlight, as white light. The following figure shows how the mixture of colors that the eye perceives as white light is separated as the light passes through a prism. As shown in the next figure, an object is seen as black if it absorbs all colors of white light. A white object reflects all colors of white light equally. If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
As shown in the next figure, an object is seen as black if it absorbs all colors of white light. A white object reflects all colors of white light equally. If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
When atoms or compounds absorb light of the proper frequency, their electrons are excited to higher energy levels. Colored compounds absorb visible (colored) light and this absorption is responsible for their color. Our eyes perceive a mixture of all of the colors, as in the proportions in sunlight, as white light. The following figure shows how the mixture of colors that the eye perceives as white light is separated as the light passes through a prism. As shown in the next figure, an object is seen as black if it absorbs all colors of white light. A white object reflects all colors of white light equally. If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
As shown in the next figure, an object is seen as black if it absorbs all colors of white light. A white object reflects all colors of white light equally. If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.
Our eyes perceive a mixture of all of the colors, as in the proportions in sunlight, as white light. The following figure shows how the mixture of colors that the eye perceives as white light is separated as the light passes through a prism. As shown in the next figure, an object is seen as black if it absorbs all colors of white light. A white object reflects all colors of white light equally. If an object absorbs all colors but one, we see the color it does not absorb. The yellow strip in the following figure absorbs red, orange, green, blue, indigo and violet light. It reflects yellow light and we see it as yellow. The eye also uses complementary colors in color vision. When a color is removed from white light we see the complementary color. The following table shows the colors seen when a complementary color is removed (for example, by a color filter). Wavelength (Angstroms) Removed Color Removed Color Seen (Complementary color) 6800 6100 5800 5600 5300 5000 4800 4300 4100 Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow Green Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Blue-green Blue Indigo Violet Purple Red Orange Yellow Lemon Yellow The yellow strip in the following figure looks yellow because it absorbs indigo light from white light. Indigo is the complementary color of yellow. A solution containing the complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, is blue because the complex absorbs red and orange light, the complementary colors of blue and blue-green. Computer monitors produce colors by producing mixtures of light. For more information, click here.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500