Illumination in machine vision system - different illuminations
Unpolarizedlight
Energy must be supplied from an external source into the gain medium to produce the population inversion. (This process leads to stimulated emission, which produces laser output). The method depends on the gain medium. Most commonly, the energy is supplied in the form of electricity or light. A less common method is the energy released from an exothermic chemical reaction.
State AL AK AZ AR CA CO CT DE DC FL GA HI ID IL IN IA KS KY LA ME MD MA MI MN MS MO MT NE NV NH NJ NM NY NC ND OH OK OR PA RI SC SD TN TX UT VT VA WA WV WI WY
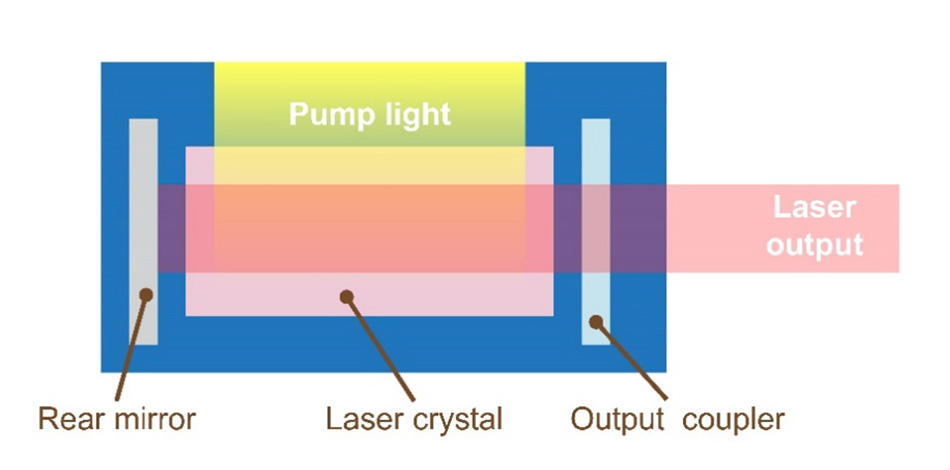
The main elements of a laser resonator. A pump source supplies energy into a gain medium which is placed between mirrors. The mirrors provide feedback, making emitted photons pass multiple times through the gain material for amplification.
To understand what a laser gain material is, it’s first necessary to understand the process of stimulated emission. Quantum mechanics tells us that atoms and molecules can only exist at certain specific, discrete energy levels. The lowest energy level is called the ground state, while higher energy levels are known as excited states.
The simplest type of resonant cavity is built with two mirrors facing each other, and the laser gain medium placed in between them. The rear mirror reflects as near to 100% as possible. The front mirror – called the output coupler – might have a reflectance of anywhere from 30% to 99% depending on the gain medium.
Mar 31, 2022 — 1. Aputure LS 1200D Pro · 2. Aputure Lightbox 60 x 90 · 3. Aputure Light Storm C120D II LED Light · 4. Aputure Amaran AL-H198 LED Light · 5. Aputure ...
But flashlamps produce a broad spectrum of light. The laser gain material can only utilize a very narrow spectrum of this light – specifically, the wavelength that corresponds to the energy difference between the ground state and highest excited state. In fact, most of the flashlamp pump energy is wasted, and this makes these lasers electrically inefficient, which means they produce a lot of waste heat. As a result, fairly substantial cooling system is needed to eliminate this heat.
The earliest solid-state lasers used flashlamps as a pump source, and these are still in use for some applications. Their main advantage is low cost and the ability to deliver high laser-pulse energy.
The first laser was demonstrated in 1960. While it generated some interest and excitement, it largely remained a “solution in search of a problem” for the first several years. But, bit-by-bit, practical applications for laser were developed. Today, lasers are common and found in an extraordinarily diverse range of applications.
Electrical pumping of gas lasers is somewhat more complex. Gas lasers usually consist of several gases contained within a laser tube. A high voltage is used to create an electron discharge within the laser tube. These high-energy electrons impact the gas molecules and impart energy to them.
In some materials, it is possible to supply energy (a process called “pumping”) to create a population inversion. This means that more than 50% of the atoms or molecules are in the excited state – the opposite of the normal thermal equilibrium situation.
80 LED Compact Ring Light with Built-in Dimmer for Stereo Microscopes. 5.0 star rating. 1 Review. Regular price $49.99. Regular price $59.99. Sale price $49.99.
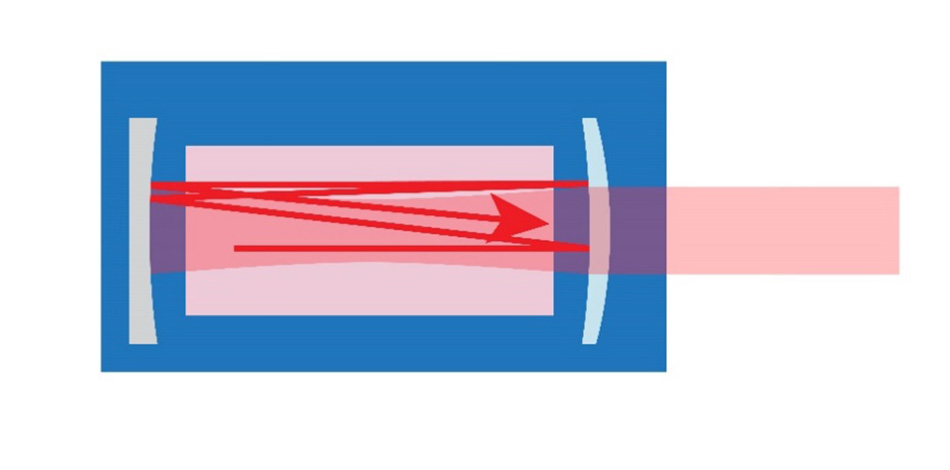
In operation, light bounces back and forth between these mirrors, gaining intensity with each pass through the laser medium. Some of the light exits the resonator through the output coupler. As a result, the light intensity within the laser resonator is always much higher than the intensity of light that comes out of the device.
Making one or both of the mirrors concave better confines the beam to within the resonator, and also yields a laser with a small, well-formed beam. Variations on this resonator design are common for many solid-state and gas lasers.
However, not all materials can support a population inversion and stimulated emission. The capability to do this depends on several factors, including the allowable energy levels in the atoms or molecules, the transition probabilities between these energy levels, the lifetime of excited states (how long the atom or molecule tends to remain in that excited state), and several other factors.
Typically, a resonant cavity (or resonator) is used to make photons pass through the gain medium numerous times before exiting the laser. This is necessary to build up a useful level of laser output, because the amount of amplification on each pass through the gain medium is relatively small. One major exception to this is the excimer laser, which imparts a very large amount of gain (amplification) in even a small number of passes.
It's also possible to optically pump a semiconductor laser. In this case, the output of another diode laser is focused into the active region of the diode. This supplies the pump energy, instead of using electrical current. Optical pumping makes the semiconductor laser more complex but can deliver a wider choice of laser output wavelengths, higher output power, and better efficiency (meaning less heat generation).
Tungsten lights are a reliable and inexpensive option for beginners that will provide even lighting for interior shoots.
Coherence analysis
This first photon passes near another atom or molecule and stimulates it to emit a second photon. The second photon has identical energy, direction, phase, and polarization as the stimulating photon. These two photons then cause stimulated emission of two more photons – so now there are four photons. This process rapidly cascades to create a large number of identical photons. This cascade of photons – called amplification or gain – is the basis of laser action. It allows pump energy to be converted into coherent laser light.
Region * United States Canada Afghanistan Aland Islands Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory British Virgin Islands Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo (Brazzaville) Congo, (Kinshasa) Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Curaçao Cyprus Czech Republic Côte d'Ivoire Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic East Timor Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hong Kong, SAR China Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran, Islamic Republic of Iraq Ireland Isle of Man Israel Italy Ivory Coast Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao PDR Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao, SAR China Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island North Korea North Macedonia Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestine Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Russian Rwanda Réunion Saint-Barthélemy Saint Helena Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint-Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Korea South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania, United Republic of Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu U.S. Virgin Islands Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican City Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic) Vietnam Wallis and Futuna Islands Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
The end mirrors often have a curvature on them to spatially confine the light (to keep photons from “walking out” of the resonator after multiple passes) and to define the shape of the beam.
In the case of CO2 lasers, the electrons collide with nitrogen molecules and vibrationally excite them. These nitrogen molecules subsequently collide with CO2 molecules, transferring energy to the CO2 molecules to create a population inversion.
All the various solid-state crystal and optical fiber gain media are electrical insulators; in other words, they can’t conduct an electric current. So, these laser materials must be pumped optically. That is, an external light source is focused into the gain medium, and the atoms or molecules of the laser material absorb this light. The result: the atoms or molecules reach the necessary excited state.
Infrared light therapy is a procedure that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to relieve pain caused by acute or chronic injury. By using low intensity light in ...
Partiallycoherent
A resonator using two flat mirrors is simple to construct, but is very sensitive to misalignment since it causes a photon to "walk-off" after a small number of passes. However, if the resonator is physically small, this isn't a problem. This configuration is commonly used in diode lasers.
There’s an additional advantage to the use of a laser as a pump source. Most lasers produce an easily focused beam. This allows the pump light to be concentrated in the gain medium right where it does the most good. That is, within what is called the “mode volume.” This is the region within the gain medium actually occupied by the laser beam. Pump light that goes into other parts of the laser medium is wasted. Effectively filling the mode volume maximizes laser efficiency, and also improves the output beam quality.
It is now more common to pump solid-state and fiber lasers with yet another laser – typically, a diode or solid-state laser. The wavelength of the pump laser is specifically chosen to match the absorption of the gain medium. This produces much higher overall pumping efficiency and reduces the cooling requirements.
Let’s look at the underlying principles of each of these elements, and some of the forms they take in various types of lasers.
Stimulated emission produces photons that are all in phase with each other. This is called “coherence.” This property enables laser light to produce well-defined interference fringe patterns.
In a fiber laser, the mirrors are often high-reflectance Fiber Bragg Gratings (FGBs) integrated directly into the fiber. In this case, the fiber itself spatially confines the beam and defines its shape. In diode lasers, the mirrors are formed by cleaving the ends of the semiconductor device and applying optical thin film coatings to them.
To understand ultraviolet radiation (UV) one needs to know UV's placement in the electromagnetic spectrum. Ultraviolet light is located between X-radiation and ...
Coherence
Lasers count your blood cells when you have lab tests. Lasers are used to project movies at many theaters. Lasers are used to perform countless surgeries and other medical procedures every year. Lasers weld automobiles and are key in the production of electric vehicles. Lasers carry virtually every phone call and all internet traffic over fiber optic cables. Lasers make the microelectronic circuits that power all modern technology. Many people carry lasers with them all the time – since they’re incorporated into some cell phones for distance measurement. Lasers mark many of the packages used for consumer goods with information like date codes and serial numbers. Lasers have numerous uses in scientific research, from cutting-edge neuroscience, microscopy, and spectroscopy, to gravity wave astronomy. Today, lasers really do light the way towards a brighter future.
Fiber lasers that use fiber-coupled diode lasers as the pump source are a good example of this principle. These can easily be configured so the pump light is directed primarily into the core or cladding of the gain fiber, as needed — and the result is a highly efficient laser system.
The mechanism of stimulated emission and the characteristics of most laser resonators frequently combine to yield a highly directional beam that does not spread quickly over distance.
State AL AK AZ AR CA CO CT DE DC FL GA HI ID IL IN IA KS KY LA ME MD MA MI MN MS MO MT NE NV NH NJ NM NY NC ND OH OK OR PA RI SC SD TN TX UT VT VA WA WV WI WY
20161219 — The power of magnification for a compound light microscope is the product of the power of magnification of the ocular lens and the power of ...
coherence中文
Region * United States Canada Afghanistan Aland Islands Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory British Virgin Islands Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo (Brazzaville) Congo, (Kinshasa) Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Curaçao Cyprus Czech Republic Côte d'Ivoire Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic East Timor Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hong Kong, SAR China Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran, Islamic Republic of Iraq Ireland Isle of Man Israel Italy Ivory Coast Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao PDR Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao, SAR China Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island North Korea North Macedonia Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestine Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Russian Rwanda Réunion Saint-Barthélemy Saint Helena Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint-Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Korea South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania, United Republic of Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu U.S. Virgin Islands Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican City Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic) Vietnam Wallis and Futuna Islands Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
Constructing the largest visible-light telescope in the world. The Giant Magellan Telescope will provide an unprecedented view of the sky, allowing ...
Another example is the ion laser. In these, an electron discharge again creates collisions with the Argon or Krypton gas within the laser tube. The first collision ionizes the gas. Then, further collisions with the ions provide energy to put them in an excited state and produce a population inversion.
Materials that can support gain come in virtually every form of matter – solid, liquid, and gas. By convention, these are typically grouped into categories as shown in the table.
The word “laser” is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. All lasers convert input energy into light through the process of stimulated emission.
Choose the Elegant and Luxurious Spot Lighting Made by the Best Designers. Spot lighting is a unique type: it's almost invisible, but extremely functional and ...
A population inversion creates favorable circumstances for the process of stimulated emission. The process starts when one atom or molecule emits a photon and drops from a higher to a lower energy state. This is called spontaneous emission.
The phenomenon of “stimulated emission” is at the heart of laser operation. To create the conditions that produce and maintain stimulated emission, lasers incorporate three key functional elements. These are:
Lasers have become indispensable tools in a diverse range of applications. The truth is their operating principles and construction offer a unique set of beam characteristics that cannot be duplicated by any other technology. Some of the most important properties are described here.
Monochromaticlight
Normally, the temperature of a material determines how its atoms or molecules are distributed among the possible energy levels. In a typical thermal equilibrium situation, most atoms or molecules are in the lower energy states, and progressively fewer are in the excited states.
UV lights help eliminate mold, bacteria, and other microorganisms that can accumulate on the AC coils and in the air handler, leading to cleaner air and more ...
However, the form and implementation of these three elements differ greatly from one type of laser to another. Specifically, this includes the use of different types of laser materials (gain media that support stimulated emission), how the energy is supplied to this material, forms of the laser cavity, and the output characteristics.
Coherent light
Electrical pumping can be used with semiconductor (diode) lasers, since these are devices specifically intended to conduct electricity. In particular, they consist of a semiconductor p-n junction which is forward-biased. The applied voltage supplies energy to promote enough electrons from the semiconductor’s valence band into its conduction band to create a population inversion. Photons are emitted when the electrons and holes (absence of an electron in the valence band) recombine, and the population inversion enables stimulated emission to occur.
Lasers range in size from small semiconductor devices to huge systems that fill an entire building. They also utilize diverse gain materials – from free electrons to solids. But all these different lasers operate on the same underlying principles.
20231215 — Measuring light color – CCT. If you measure for color or CCT, the distance between the spectrometer and the light source is not really important ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500