1.8: Polarization - polarized of light
Where possible, scientists try to find natural ways to classify things. UV is subdivided according to the effect it has on atoms. Even then, there is still debate about whether 320 nm or 315 nm should be used to mark the division between UVA and UVB.
Stereomicroscope
Optical microscopes are the most common type of microscope.By using an optical lens constructed of multiple objective lenses, they enable observations of the target at magnifications that are 100, 200, or 300 times higher than those performed with a microscope having a single lens.This section explains optical microscopes in detail.
Ultraviolet (UV) light is part of a family of radiations called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. UV is just beyond the violet end of visible light and has smaller wavelengths and greater energy.
Invertedmicroscope
In the Netherlands in the latter half of the 17th century, Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek created the single-lensed microscope (a microscope with one lens) and discovered microorganisms and sperm. At the same time in the United Kingdom, Robert Hooke created the compound microscope, with a combination of two lenses: an objective lens and an eyepiece, and used it to observe the structure of cork. Because the structure appeared to be a collection of small rooms like a beehive, he named these rooms cells. This led to the use of the word cell in biology. The currently used optical microscopes are generally compound microscopes that combine an objective lens and an eyepiece. With typical optical microscopes, the light source is located below the sample, and it is observed by using the objective lens to magnify the light that is transmitted through the sample. Therefore, it is not possible to observe objects that do not transmit light. To observe such samples, it is necessary to cut them into thin slices and secure these slices on glass slides or similar objects. Stereoscopic microscopes are used to observe objects that cannot be processed into thin slices. Stereoscopic microscopes are optical microscopes that project light down onto the sample. The reflected light is then magnified by the objective lens for observation. Stereoscopic microscopes have two eyepieces, allowing for 3D observation that is the same as viewing the sample with the naked eye. Stereoscopic microscopes are used for relatively low-magnification observation. Metallurgical microscopes are used to observe the light reflected from samples at high magnification.
UV is produced naturally by very hot objects such as our Sun. About 10% of the Sun’s energy output is UV. UV shines on the Earth along with heat and visible light. Our atmosphere reflects much of the incoming UV back out to space and absorbs most of the rest. Overall, then, only a small proportion of the Sun’s UV reaches us. The ozone layer at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere and oxygen within the atmosphere absorbs the more energetic UV with shorter wavelengths. It is some of the longer wavelength UV that reaches the Earth’s surface.
Light microscopevs electronmicroscope
It is important to monitor the amount of UV that reaches us at various places on the Earth. This can help us see how the UV level varies during the day, over a year and from year to year, so we can make predictions and give warnings when the UV level is high. A UV Index has been developed that uses the monitored UV to estimate the exposure level for humans. A UV Index number of 2 or less is a low exposure level and rises progressively to a UV Index number of 11+ (an extreme exposure level). One unit in this index is roughly equivalent to 25 millijoules of UV energy falling per second on a one square metre area.
Electronmicroscope
It is said that the minimum distance between two points that can be distinguished with the naked eye is 0.1 mm, the thickness of a strand of hair. Optical microscopes can distinguish a minimum distance of 200 nm. Electron microscopes are generally used to observe objects smaller than 200 nm.
As with all electromagnetic spectrum radiations, UV travels at the speed of light. Humans cannot see it, but some animals, especially some insects, can see UV light and have body markings that reflect UV light.
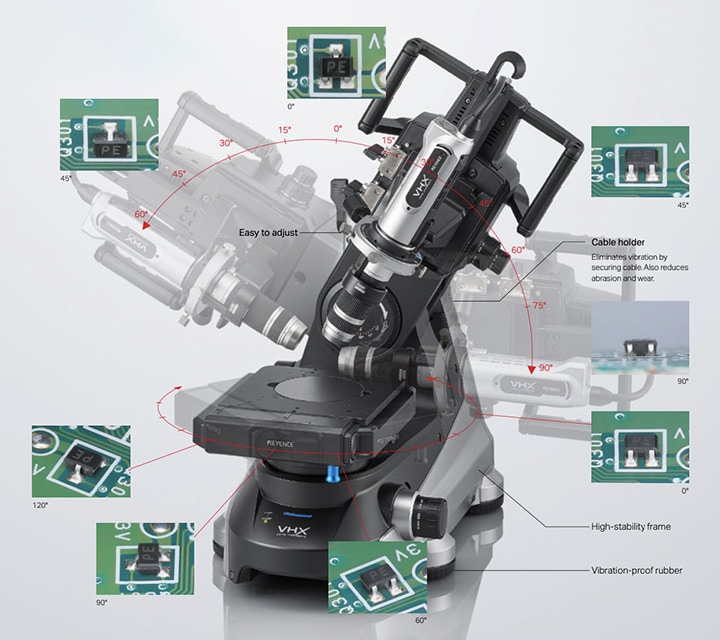
Optical microscope
In the article, Monitoring ozone levels find out more about NIWA’s research programme into monitoring atmospheric ozone and understanding and predicting the relationship between ozone depletion and climate change.
Optical microscope is the general term used for microscopes that use visual light and glass lenses to perform magnified observation of objects. Because they have historically been used to observe organisms such as microorganisms and the cells of plants and animals, they are also called biological microscopes.
There are a variety of ways we put ultraviolet (UV) radiation to good use – vitamin D production, sterilisation and disinfection, astronomy, fluorescence and lighting, and curing.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500