LED Spotlights - All You Need to Know - led spotlight lamp
Because the two processes are similar, the name “greenhouse effect” was coined to describe Fourier's explanation. However, part of a greenhouse's warmth results from the physical barrier of the glass, which prevents the warmer air from flowing outward. So despite the fact that the atmospheric greenhouse effect has some processes in common with an actual greenhouse, the overall mechanisms driving the greenhouse effect are different and more complex.
On a 35mm film camera, it turns out that the angle of view afforded by a 50mm lens provides a field of view that is approximate to the field of view produced by the human eye. (When we say “35mm film camera” we are referring to the size of the frame of film, not the focal length.) We all know that our eyes have a wide field of view and that we also see things off to the periphery of where we are looking—peripheral vision—but, when you look through a 50mm lens on a 35mm camera, what you see is very similar to what your eye sees. Therefore, the 50mm lens, and lenses measured close to 50mm (say 35mm to 70mm, opinions vary) are known, collectively, as “normal” or “standard” lenses.
So your use of the term "distort" is misleading as well. It runs the risk of being conflated with barrel and pincushion distortion - genuine distortions that are indeed a property of the lens.
The use of the term perspective here is unfortunate. The only thing that can alter perspective is moving the position of the camera. A wide angle lens does not distort geometric perspective. That's what people look like up close. Take that photo of your friend and print it big. Now stand close enough so that it fills the same angle of view as the lens provided to the sensor. Nothing will be distorted. Check out the skull in Holbein's The Ambassadors. It looks undistorted from a certain angle, as would the corners of a wide angle shot when presented to a viewer in such a way as to match the FOV of the original shot.
The general rule for maintaining sufficient shutter speed for a given focal length, to avoid the appearance of image shake, is to simply use a shutter speed quicker than 1/focal length. Therefore, you should try to shoot a 300mm lens at a shutter speed quicker than 1/300 of a second and adjust aperture and/or ISO to help you achieve that shutter speed.
Ozone (O3) is also a relatively minor greenhouse gas because it is found in relatively low concentrations in the troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere). In the troposphere, it is produced by a combination of pollutants — mostly hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxide compounds.
Focaldistance vsfocal length
Before I go on, I need to say a quick word about “crop factor.” Different digital cameras have different-sized sensors. This causes an effective change in the field of view of the camera, but not in the focal length of a given lens. Because the sensor size is independent of focal length, we often speak of the different field of view produced by a smaller sensor as a “35mm equivalent” field of view or focal length. I will be covering crop factor in an upcoming article but, for the purposes of this article, we will be talking about focal length in relation to 35mm film or a full-frame digital sensor, as it is a standard baseline for discussions on focal length.
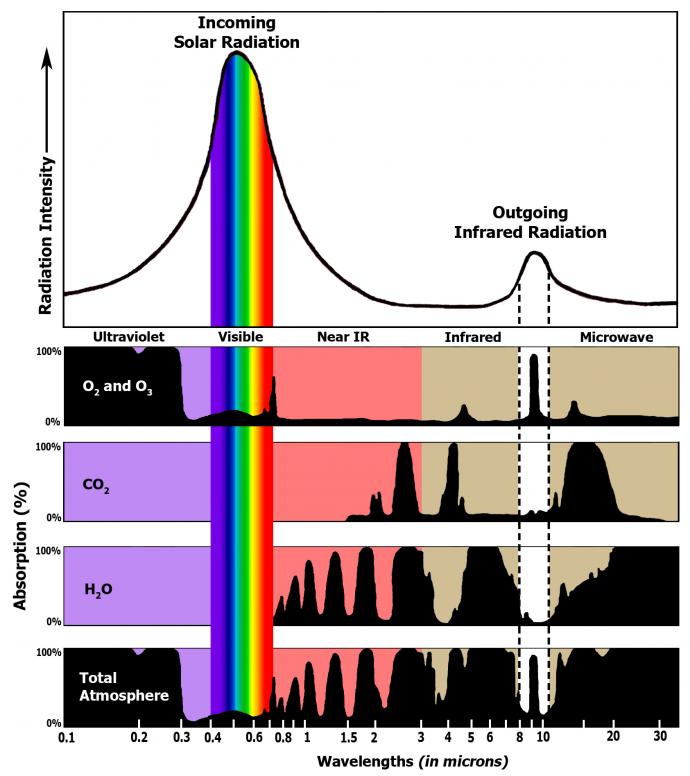
The relative importance of a greenhouse gas depends on its abundance in Earth's atmosphere and how much the gas can absorb specific wavelengths of energy.
Water vapor (H2O) is the strongest greenhouse gas, and the concentration of this gas is largely controlled by the temperature of the atmosphere. As air becomes warmer, it can hold more moisture or water vapor. When the air becomes saturated (or holds as much moisture as the air can at that temperature), the excess moisture will condense into cloud droplets. And if these droplets are large enough, they will fall as precipitation.
To have an average temperature of 15°C (59°F), Fourier knew that there had to be another process occurring in the atmosphere –– something similar to the way a greenhouse retains heat. A greenhouse's glass enclosure allows visible light to enter and be absorbed by the plants and soil. The plants and soil then emit the absorbed heat energy as infrared radiation. The glass of the greenhouse then absorbs that infrared radiation, emitting some of it back into the greenhouse and thus keeping the greenhouse warm even when the temperature outside is lower.
The sun's visible wavelengths of radiation pass easily through the atmosphere and reach Earth. Approximately 51% of this sunlight is absorbed at Earth's surface by the land, water, and vegetation. Some of this energy is emitted back from the Earth's surface in the form of infrared radiation.
Remember, when you are comparing a camera lens/photograph to looking at someone up close with your eyes, you are still viewing them through a wide angle lens...your own wide-angle lens—the eyeball. Your eye experiences that same larger delta between light rays at the edges and the center of the "frame." You would see it more if the eye had a closer minimum focus distance.
At first, you might think that to achieve the same field of view with different focal length lenses, all you need to do is move closer or farther from the subject. This is partially true, but the way your image changes will be very obvious, even if the subject is about the same size in an image taken with a wide-angle lens and then a telephoto lens.
Carbon dioxide constantly moves into and out of the atmosphere through four major processes: photosynthesis, respiration, organic decomposition or decay, and combustion or the burning of organic material. You will learn more about carbon dioxide and the carbon cycle in Module 4.
III. Much of this infrared radiation does not reach space, however, because it is absorbed by greenhouse gases in atmosphere, and is then emitted as infrared radiation back toward the Earth's surface. This process is known as the greenhouse effect.
In fact, if we were really being careful, the second image should be projecting an upside down car on the sensor as lenses flip the image!
You have already learned that Earth's atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen. These gases are transparent to incoming solar radiation. They are also transparent to outgoing infrared radiation, which means that they do not absorb or emit solar or infrared radiation. However, there are other gases in Earth's atmosphere that do absorb infrared radiation. These gases are known as greenhouse gases. Below are the most important greenhouse gases that influence Earth's climate system.
If you get close to a subject with a wide-angle lens, the distortion characteristics of that lens will distort the subject. If you don’t believe me, take a portrait of a friend up close with a wide-angle or fisheye lens, and ask them if they like the image. Chances are, they will not.
A 50mm lens is a 50mm lens all the time, regardless of what camera it is attached to...or even if it is attached to a camera!
FOV tofocal lengthcalculator
The family of wide-angle lenses includes fisheye lenses that can provide more than a 180-degree field of view; much greater than the human eye, including the periphery, so much that if not conscious of it, you can photograph your feet in the frame when holding the camera to eye level. Telephoto lenses, especially extreme “super telephoto” lenses, can narrow the field of view to where it feels like you are looking through a soda straw, albeit a really big and heavy soda straw!
A lens with a focal length longer than 50mm will give the photographer a telephoto perspective—making it appear that you are closer to your subject by producing a field of view that is narrower than that of a standard lens.
field ofview中文
One “side effect” of focal length is image, camera, or lens shake. When you handhold a camera, no matter how steady your hands, between your hands and arms and the mechanicals of the camera, things will be moving when you depress the shutter release. This movement causes blur in an image at varying degrees; sometimes not noticeable and other times, ugh.
fov和焦距的关系
We already said that the 50mm lens gives us the “normal” field of view perspective. What about lenses of different focal lengths?
In relation to focal length, there is not much more you can say about a zoom versus a prime, but it is important to know that there are usually optical tradeoffs for the convenience of a zoom. For a more thorough discussion about the applications of different focal length lenses and the debate between prime lenses and zoom lenses, see my article “Going Beyond the Kit Lens.”
Focal length
I wrote this article as an introduction for photographers new to the world of photography. Therefore, I chose not to dive too deeply into the technical.
Prime lenses are those that have fixed focal lengths. Zoom lenses are those that have variable focal lengths. This is accomplished by physically changing the length of the lens, internally or externally.
If you're still craving more, be sure to watch this episode of FocusEd, which discusses lens focal length for photographers. You will learn about what focal length is, how sensor size and lens focal length affects your angle of view, and more!
When capturing a photograph of an object at very close range with a wide angle lens, you do experience distortion. This distortion is not caused by a rectilinear lens is suddenly distorting the view—recilinear is recilinear— the distortion happens because of the more oblique angles that the light is entering the lens. The closer the subject is to the lens, the more variation there is in the angles of entry of the light rays from an object. Subject-lens distance is the cause...not really a distorting lens. For the beginner, this is difficult to describe without encouraging the audience to study the inside of their eyelids instead of a lens diagram.
FOV tofocal length
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is also an important greenhouse gas. It has a long lifetime in Earth's atmosphere. Carbon dioxide strongly absorbs energy with a wavelength of 15 μm (micrometers). This makes carbon dioxide a good absorber of wavelengths falling in the infrared radiation region of the spectrum.
Unfortunately, when you venture into the telephoto realm of focal lengths, this movement is amplified by the fact that the field of view of the lens is smaller than that of wide-angle or normal lenses. Therefore, it is more difficult to get a sharp image at telephoto focal lengths, especially extreme focal lengths.
In the 1860s, John Tyndall, an Irish scientist who was fascinated by the growth and formation of glaciers, wanted to test his ideas explaining how Earth maintained a fairly constant temperature. He began a series of experiments to measure the amount of radiant heat (infrared radiation) that certain gases could absorb and transmit. Tyndall found that water vapor and carbon dioxide were good absorbers and emitters of infrared radiation.
In 1827, Joseph Fourier, a French mathematician and physicist, wondered why Earth's average temperature is approximately 15°C (59°F). He reasoned that there must be some type of balance between the incoming energy and the outgoing energy to maintain this fairly constant temperature. His calculations indicated that Earth should actually be much colder (-18°C or 0°F).
If the concentration of greenhouse gases increases, then more infrared radiation will be absorbed and emitted back toward Earth's surface, creating an enhanced or amplified greenhouse effect.
If the lens is shorter than 50mm, say, a 24mm lens, then the image produced by that lens will give the photographer a wide-angle perspective of the world before them—wider than your “normal” vision. The field of view of the lens is wider than that of the standard lens.
To counteract this shake, you can stabilize the camera on a tripod or other support and reduce the duration your shutter is open. The faster the shutter speed, the less movement will be captured. In order to maintain the same exposure, you may need to increase the size of your aperture opening or increase your ISO sensitivity.
The top image simulates a single point of light being focused onto the sensor. The second image illustrates how the lens collects the light from a scene and sends it into the camera to cover the sensor.
This is exactly the answer I was looking for. Just to put it another way, this means if I have a shot taken on a 50mm prime, with a 1.6 crop factor sensor, it is still correct to say the lens' focal length for the image was 50mm, rather than 80mm? It's the field of view that has changed, effectively cropping the image, although it might be convenient to say the produced image "looks like it's been shot with an 80mm lens and 35mm sensor."
Halocarbons are composed of carbon, chlorine, fluorine, and hydrogen. They include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are man-made gases commonly used in refrigerators and air conditioners. Concentrations of CFC gases in the atmosphere are the highest of any of the halocarbons, and they can absorb more infrared radiation than any other greenhouse gas. The impact of 1 molecule of a CFC gas is equivalent to 10,000 molecules of carbon dioxide.
Someone standing 2 feet from you will be just as distorted at 200mm focal length as at 16mm... you'll just see a narrower slice of the scene in front of you. Maybe a nostril!
fov是什么
Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and other trace gases in Earth's atmosphere absorb the longer wavelengths of outgoing infrared radiation from Earth's surface. These gases then emit the infrared radiation in all directions, both outward toward space and downward toward Earth. This process creates a second source of radiation to warm to surface – visible radiation from the sun and infrared radiation from the atmosphere – which causes Earth to be warmer than it otherwise would be. This process is known as the natural greenhouse effect and keeps Earth's average global temperature at approximately 15°C (59°F).
Methane (CH4) is 30 times stronger than carbon dioxide as an absorber of infrared radiation. Methane, however, is present in smaller concentrations than carbon dioxide, so its net contribution to the greenhouse effect is not as large. Methane is also relatively short-lived (lasting approximately 8 years) in the atmosphere. Methane is produced when bacteria decompose organic plant and animal matter in such places as wetlands (e.g., marshes, mudflats, flooded rice fields), sewage treatment plants, landfills, and the guts of cattle and termites. Scientists are concerned about the concentration of methane increasing in regions where the Arctic and alpine permafrost is thawing and releasing methane as it warms.
Again, unless you are designing a lens from scratch, you, as a photographer, are free from knowing the nuances of measuring focal length and you should keep in mind how lenses of different focal lengths affect the way your images look in terms of proximity, distortion, and perspective. Thankfully, on this subject, the bulk of the math can remain with the engineers!
Field of view
I. The sun's visible wavelengths of radiation pass easily through the atmosphere and reach Earth. Approximately 51% of this sunlight is absorbed at Earth's surface by the land, water, and vegetation.
Nitrous oxide (N2O), a relatively long-lived gas, has increased in atmospheric concentration due mainly to agriculture. Nitrate (NO3-) and ammonia (NH4+) are used as fertilizers. Bacteria convert a small amount of this nitrate and ammonia into the form of nitrous oxide. Internal combustion engines also produce nitrous oxide.
Different digital cameras have different-sized sensors. This causes an effective change in the field of view of the camera, but not in the focal length of a given lens.
Hello - Was hoping you could clarify something me. In some instances (in the top image in the article) the focus point is shown at the image plane. In other cases ( the lower image in this article) the image plane is shown to be behind the focal point, which would be out of focus.
When you shoot through a telephoto lens, you will see the image get virtually “flattened.” This means that the image will appear to have less depth—the background behind your subject will appear much closer, and your portrait will be more flattering to the subject.
The other thing that lenses of different focal lengths have an effect on is what is known as “perspective.” To put it very simply, wide-angle lenses distort the scene, and telephoto lenses compress the view.
An effective absorber of infrared radiation has a broader absorption profile, which means that it can absorb a wider spectrum of wavelengths. Water vapor and carbon dioxide can absorb radiation wavelengths in the range of 4 μm to 80 μm, except those between 8 μm and 12 μm. Ozone can absorb wavelengths between 9 μm and 10 μm, but as you have learned, it is found in low concentrations. The sun's ultraviolet wavelengths are strongly absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere.
When averaged over the course of a year, the amount of incoming solar radiation received from the sun has balanced the amount of outgoing energy emitted from Earth. This equilibrium is called Earth's energy or radiation balance. Relatively small changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere can greatly alter that balance between incoming and outgoing radiation. Earth then warms or cools in order to restore the radiative balance at the top of the atmosphere.
The primary measurement of a lens is its focal length. The focal length of a lens, expressed in millimeters, is the distance from the lens’s optical center (or nodal point) to the image plane in the camera (often illustrated by a "Φ" on the top plate of a camera body) when the lens is focused at infinity. The image plane in the camera is where you will find your digital sensor or film plate. If you are an optical engineer, this is important stuff. For the photographer, however, we do not need to know about nodal points or why the 200mm lens in our closet is only 193mm long, to make great photos. What we need to know, as photographers, is what focal length means to our images. When we talk about lenses, the focal length is not only related to the lenses’ physical length, the linear measurement is representative of an angular field of view.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500