LED Inspection Light Penlight HL 100 with clip and magnet ... - led inspection
Waveopticsformulas
SINGAPORE OptoSigma SEA 83 Science Park Drive, #02-01.The Curie, 118258 TEL. +65 6909 9318 sales@optosigma-sea.com SINGAPORE
4. Periodic WavelengthIt is used for other kinds of waves as well. In linear media, any wave pattern can be described in terms of the independent propagation of sinusoidal components. The wavelength λ of a sinusoidal waveform traveling at constant speed v is given by this equation.
9. Depth of fieldIn optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. (You can find a more detailed blog post about the Depth of field here)
5. FrequencyThis equation couldn’t be absent from this list. Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time.It is also referred to as temporal frequency, which emphasizes the contrast to spatial frequency and angular frequency. The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency.
Opticsformula Sheet
3. Thin lens formula Also known as Image location formula. It basically sais that if the distances from the object to the lens and from the lens to the image are S1 and S2 respectively, for a lens of negligible thickness, in air, the distances are related to the length of the focus of the lens.
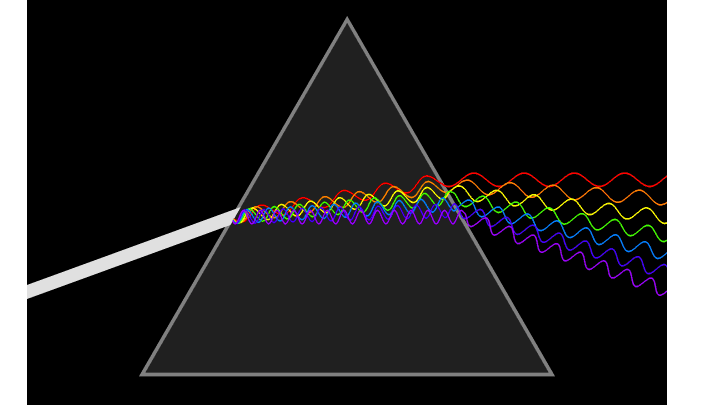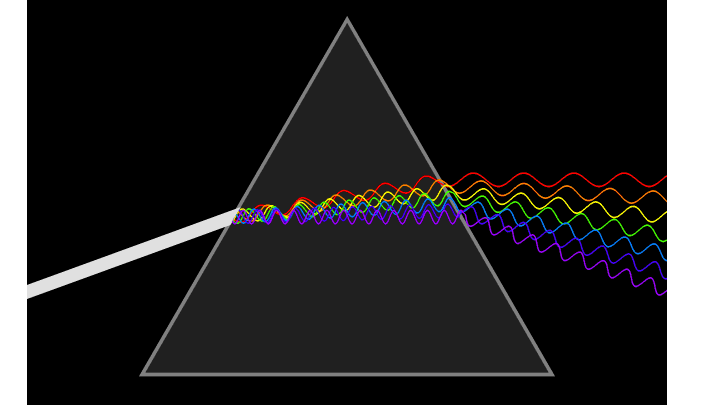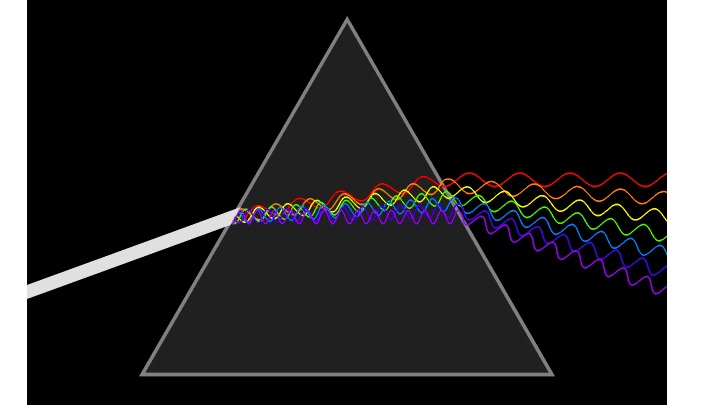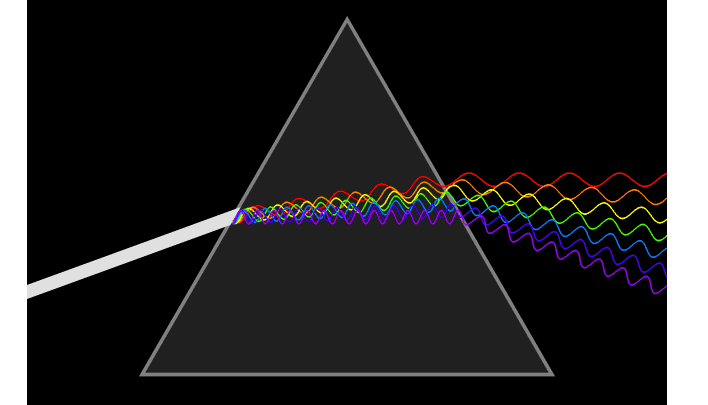
1. Snell’s law It is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass and air.
Lensequations
Laser Beam Expanders, also known as collimators, are optical devices used to collect a collimated beam of light to expand or reduce its size, depending on the orientation used. They are used for reducing power density, minimizing beam diameter, and reducing laser spot size. Beam expanders are useful in a variety of applications including interferometry, laser scanning, remote sensing, laser machining, laser ranging, high power lasers and more. We offer both variable (zoom) and fixed laser beam expanders. In this section, find a variety of off the shelf standard beam expanders or ask us about custom OEM beam expanders.
2. Refractive IndexThe refractive index or index of refraction of a substance is a dimensionless number that describes how light, or any other radiation, propagates through that medium. The refractive index determines how much light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
10. Malu’s lawThis equation describes the intensity of the light that passes through a perfect polarizer when it is placed in a polarized beam of light.
What is f inOptics
Optics equationsMCAT
UK Elliot Scientific Limited Unit 11 Sandridge Park, Porters Wood, St Albans, AL3 6PH TEL. +44 (0)1582 766 300 sales@elliotscientific.com United Kingdom
Lists and Dummy guides of useful stuff are always great. Lists of formulas and equations are educational as well. Here is the first list of top Equations, powered by the fxSolver team.Behold, the Top 10 Optics equations.
Written by Dimitris on April 12, 2016 .
7. ParallaxApart from the fact that Parallax is an awesome supervillain name, is also a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines.
OpticsFormulas PDF
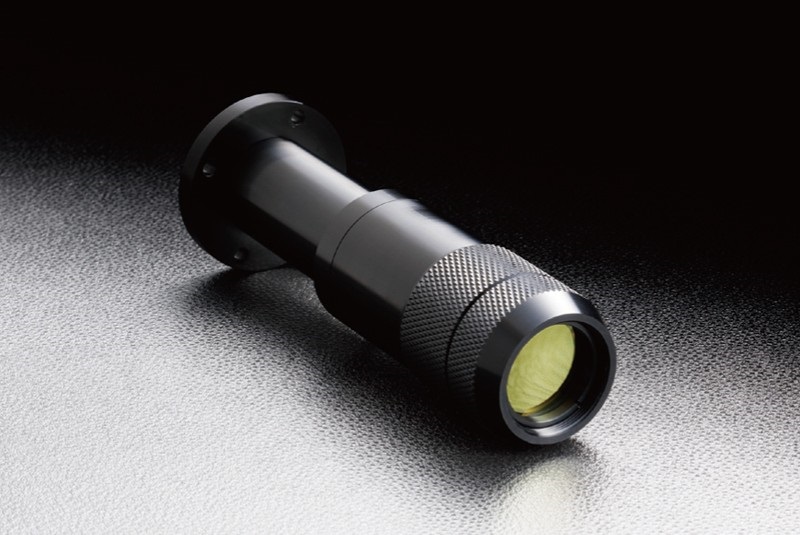

8. Magnification of the telescopeThe angular magnification of the telescope is related to the focal length of the objective lens and the focal length of the eyepiece. Optical magnification is the ratio between the apparent size of an object and its true size, and thus it is a dimensionless number.
USA OptoSigma Corporation 1540 Scenic Avenue, Suite 150, Costa Mesa, CA. 92626 TEL. +1-949-851-5881 sales@optosigma.com USA
6. Polarization angle – Brewster’s angleThe angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized.
If you need any help, you will find some in our fxSolver video.Also remember to follow or interact with us in our social media pages. You will find links below.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500