Video Surveillance Signs, Security Camera Signs - security camera signage
Masscareers
For people without heart isssue, the electrical discharges of the TASER device are too short to affect the heart muscle or cause abnormal heart rhythms. Even for those with heart conditions, the proper use of the device does not appear to cause issues. One of the first study of TASERs on humans, published by the Academy of Emergency Medicine in 2006, looked at their effect on individuals with a known heart disease or diabetes. The study participants were shot in the back with a TASER and researchers measured blood markers of heart damage and did a test called an EKG, or electrocardiogram. They did not find any negative effects.
However, TASER currents don’t reach the heart. Humans have protective mechanisms: The skin, which provides high resistance to electricity, and soft tissue, which surrounds muscles and organs like the heart, also reduce the current.
CIBCcareers
Interesting assignments and job rotations enable you to deepen your skills as you consult with clients and communities to create value through innovative solutions that effect change.
You put a premium on your professional development and health and well-being. So do we. Known for our friendly and collaborative environment and focus on continuous learning, we help you thrive professionally and personally.
TASERS, also called "electrical control devices," have been used by law enforcement since the mid-1970s, with the intention to help subdue resistant suspects without physical contact or the use of firearms.
MBTAcareers
Careerscanada
On skin, the most common affects are superficial burns or small puncture wounds, caused by the metal probes that deliver the current not being immediately pulled off after a person has been tased. Scrapes are often seen across the skin surface because the person shocked by the TASER my convulse uncontrollably.
Serious injuries represent less than one percent of injuries from TASERs, as noted in a 2009 study published in the Annals of Emergency Medicine that looked at more than 1,200 uses of conducted electrical weapons by law enforcement officers against criminal suspects.
RBCcareers
At CGI, you are more than an employee. You are invited to be a company owner to benefit from the rewards of our collective success and actively shape the future direction of your company.
Visit our Careers FAQ for more information on how to apply for a job, internships, employment verification, former employee queries, technical issues, etc.
City of Bostoncareers

The widespread use of ECDs, with more than a 1,070 estimated worldwide uses per day, as reported by TASER manufacturer Axon, has led many to wonder: What happens to the human body after being tased?
Founded in 1976, CGI is among the largest IT and business consulting services firms in the world. We are insights-driven and outcomes-focused to help accelerate returns on your investments.
The current -- either direct, DC, or alternating, AC -- is the rate at which electrons going down a wire travel per second. Alternating current is what is typically used in wall sockets and it's more dangerous, according to the Journal of the American Medical Association, causing more extreme muscle contraction.
Being a partner of choice for our clients means offering the value and richness that diverse teams bring — from commitment and engagement to innovation and out-of-the-box thinking. Our DE&I initiatives and programs are focused on building diverse teams where our professionals can be their authentic selves, receive support to develop and advance their careers and work in a respectful, empowering and collaborative environment. Here are some examples of our global and local programs that celebrate diversity and help build an equitable and inclusive culture.
TASERs cause muscle contractions, but do not appear to trigger the release of the muscle enzyme associated with muscle cell damage -- creatine kinase. If levels of that enzyme are high, it causes a condition called rhabdomyolysis, which can lead to kidney failure. Current research has shown that the muscle contractions induced by the TASER cause a small increase in CK, but do not appear to pose a direct risk for rhabdomylosis, according to a review of research by Forensic Science International.
Of course, police officers and medical personal should assess subjects subdued by a TASER for injuries. Existing medical or psychiatric conditions and the use of alcohol or drugs in the suspect may lead to behavior or reactions after the use of the TASER that need medical evaluation.
Googlecareers
The taser delivers 19 short pulses per second over 5 seconds, with an average current of 2 milliamps, according to TASER manufacturer Axon. It creates an electric field, which stimulates nerve cells called alpha motor neurons to send an electrical impulse. The impulse travels to muscles and causes short, sustained muscle contractions.
Complications related to the brain or nervous system are rare, but do occur, including loss of consciousness, seizures, abnormal brain activity and confusion. This is more likely to occur if a subject is shot at a close distance or directly to the head, which is not usually the case since those are not the recommended targets. The probability of causing a seizure is very low.
For example, a current applied to the arm will be reduced to .001 percent of the original signal by the time it reaches the heart. TASERs have a 2 milliamp current and it takes at least 1,000 milliamps -- 1 amp -- to injure muscles, nerves and the heart. Higher amps, starting at 10,000 milliamps or 10 amps, cause the heart to stop and produce severe burns, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The taser has two modes: the first, pulse mode, causes neuromuscular incapacitation as the neural signals that control muscles become uncoordinated, and muscles contract at random. The second mode, drive-stun, uses pain to get compliance.
Careerslogin
A taser is a battery-powered, handheld device which delivers a short, low-energy electrical pulse. Two electrode wires are attached to the gun's electrical circuit. Pulling the trigger breaks open a compressed gas cartridge inside the gun and flings the electrodes into contact with a body and a charge flows into the muscles.
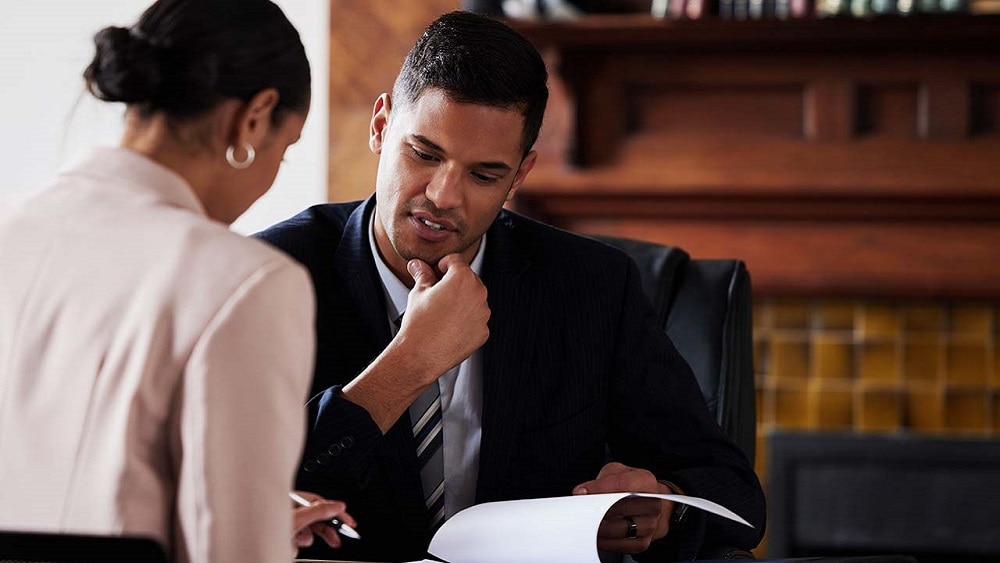

An ampere, or amp, is the unit used to measure current. A small current -- 200 microamps –- applied directly to the heart can cause a fatal rhythm called ventricular fibrillation.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500