Ozito Detail bootable Sander Assorted Grits - Evans Company - bunding bunnings
A few other examples of elemental oxidizing agents include diatomic oxygen (O2), diatomic chlorine (Cl2), and ozone (O3). These oxidizers are the elemental forms of the second and the third most electronegative elements (oxygen and chlorine respectively), making them good electron acceptors.
Oxidisingin chemistry
To learn more about oxidizing agents and the part they play in oxidation-reduction reactions, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
As an atom-transferring substance – An oxidizing agent is a substance that transfers at least one electronegative atom to a chemical species in a chemical reaction. The transferred atom is typically an oxygen atom. Several combustion reactions and organic redox reactions involve the transfer of an electronegative atom between two reactants.
The group 17 elements of the periodic table are collectively referred to as Halogens. They are said to have a strong ability to gain electrons, attributed to their high electronegativities when compared to elements from other groups. This implies that they have the ability to easily attract electrons towards their respective nuclei. Examples of the halogens that are good oxidizing agents include iodine, bromine, chlorine, and fluorine. Fluorine is said to be the strongest elemental oxidizing agent due to its highest electronegativity, as discussed earlier.
Forcepoint Data Security Posture Management: Automate data discovery, classification and orchestration to get total control and visibility of your data across the enterprise.
Oxidisingchemicals
Some compounds that exhibit large oxidation states can also be considered good oxidizing agents. Ionic examples include the permanganate ion, the chromate ion, and the dichromate ion. Acidic examples of good oxidizers include nitric acid, perchloric acid, and sulphuric acid. The electronegativity of the molecules increases with the increase in the oxidation states of the atoms, increasing their ability to oxidize other substances.
Replace broad, sweeping rules with individualized, adaptive data security that doesn’t slow down your employees. Block actions only where you need to, and drive productivity
By accepting electrons from other substances, oxidizing agents cause their oxidation states to become more positive. Oxidizing agents are reduced as well.
Oxidisingprocess
Many other oxidizing agents are commonly used industrially as well as in the day-to-day lives of humans. Examples include household bleach (NaClO), Potassium Nitrate (KNO3), and Sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
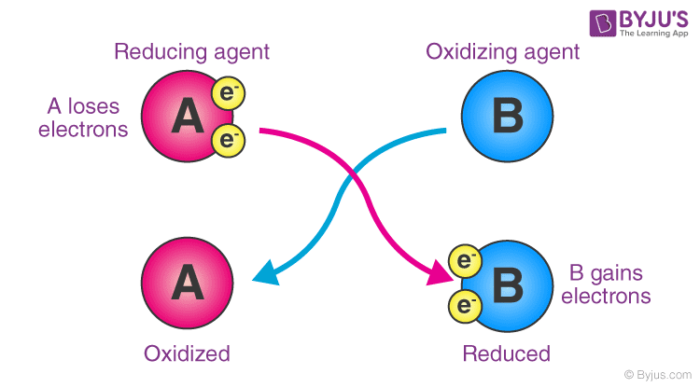
As an electron acceptor – They are chemical substances whose atoms remove at least one electron from another atom in a chemical reaction. As per this definition, oxidizing agents are the reactants that undergo reduction in redox reactions. An illustration detailing the electron-accepting properties of oxidizing agents is provided below.
Protect PII and PHI, company financials, trade secrets, credit card data, and other pieces of sensitive customer data-even in images. Follow intellectual property (IP) in both structured and unstructured forms, and stop low & slow data theft even when user devices are off-network.
When it comes to electron transfers, an oxidizing agent gains electrons while oxidation is the process of losing electrons. Reduction, on the other hand, means gaining electrons. As a result, the oxidizing agent gains electrons from the species being oxidized, implying that it undergoes reduction (as it gains electrons).
In the example illustrated above, the Fe2O3 molecule acts as an oxidizer by transferring an electronegative oxygen atom to the carbon monoxide molecule.
Create data security policies once and apply them to the web, cloud and private applications through the Forcepoint ONE Security Service Edge (SSE) platform integration.
Strongoxidisingagent meaning
Elemental fluorine is said to be the strongest elemental oxidizing agent. This is perhaps due to the fact that fluorine is the most electronegative element in the modern periodic table, and therefore exerts the strongest attractive force on electrons amongst all the elements. In fact, the oxidizing power of diatomic fluorine (F2) is strong enough to cause metals such as asbestos and quartz (and even molecules, such as water) to burst into flames when exposed to it.
Secure data everywhere with Forcepoint. Prevent breaches, simplify compliance, unify policy management and adapt to risk in real time with our data security solutions.
DISCLAIMER: Product comparison is based off of in-product capabilities and cross-portfolio integrations available from the same vendor as of Feb 1st, 2024. Comparisons do not include integrations with third-party vendors. Feature comparison is based off of each vendor’s most recent and modern version available as of Feb 1st, 2024. Information is based off of data collected from public websites and forums, analyst papers, and product datasheets as of Feb 1st, 2024.
Here, substance ‘A’ undergoes oxidation, resulting in an increase in its oxidation number. On the other hand, the oxidation state of substance ‘B’ becomes smaller (since it gains electrons by undergoing reduction).
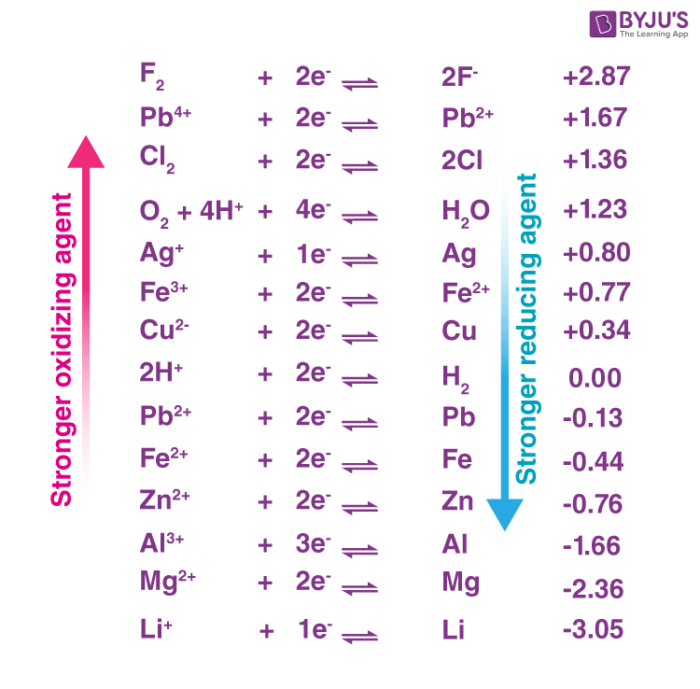
The standard electrode potential of a half-reaction in a redox process provides insight into the oxidizing power of the chemical substance. An illustration ranking some oxidizers in terms of their oxidizing powers is provided below.
Data security is a persistent challenge. Forcepoint Data Loss Prevention (DLP) enables businesses to discover, classify, monitor, and protect data intuitively with zero friction to the user experience. Audit behavior in real-time with Risk-Adaptive Protection to stop data loss before it occurs.
Oxidisingsubstance symbol
Types ofoxidising
An oxidizing agent is a substance that causes oxidation by accepting electrons and thus becoming reduced. A reducing agent is a substance that causes reduction by losing electrons, causing it to be oxidized.
Oxygen is the element corresponding to the atomic number 8 and is denoted by the symbol ‘O’. It belongs to the chalcogen group of the periodic table and is a highly reactive non- metal with good oxidizing properties. In general, metals tend to form metal oxides by reacting with atmospheric oxygen, due to the strong oxidizing power of oxygen. Oxygen is observed to be a part of a majority of combustion reactions.
Oxidizing agents normally exist in their highest possible oxidation states and, therefore, have a strong tendency to gain electrons and undergo reduction. Ions, Atoms, and molecules having a strong affinity towards electrons are considered to be good oxidizers. The stronger the electron affinity, the greater the oxidizing power.
Hydrogen peroxide is the chemical compound having formula H2O2. It appears to the human eye as a colourless liquid which has a greater viscosity than water. Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest compound having a peroxide functional group with an oxygen-oxygen single bond. It finds its uses as a weak oxidizing agent, disinfectant, and bleaching agent.
View and control all your data with the industry's largest pre-defined policy library. Ensure regulatory compliance across 80+ countries for GDPR, CCPA and more. Deploy data classification with Forcepoint Data Classification as well as Microsoft Purview Information Protection.
An oxidizing agent (often referred to as an oxidizer or an oxidant) is a chemical species that tends to oxidize other substances, i.e. cause an increase in the oxidation state of the substance by making it lose electrons. Common examples of oxidizing agents include halogens (such as chlorine and fluorine), oxygen, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Oxidisingexamples
An oxidizing agent is a compound or element that participates in a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction and accepts electrons from a different species. An oxidant is a chemical compound that easily transfers oxygen or another substance atoms in order to gain an electron.
What isoxidisingagent
Many organisms make use of electron acceptors, or oxidizers, to collect energy from the redox reactions such as in the process of hydrolysis of glucose.
""Forcepoint DLP delivers unified data and IP protection for hybrid and multi-cloud enterprises with a focus on understanding the people who create, touch, and move data, in order to protect users and data across endpoints, networks and cloud apps.""
Forcepoint ONE Data Security: Safeguard sensitive information and enforce compliance with DLP Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500