ffp1, ffp2 and ffp3 respiratory masks - moldex
Several factors are driving increased drone use, including cost savings and increased availability, as well as updated agency policies and FAA guidelines governing law enforcement UAV deployment.
The eye-catching colors of a fire hydrant are hard to miss, whether you're walking through a city or driving around a neighborhood. What many don't realize, however, is that these colors are integral in helping emergency responders identify and assess their available resources when preparing to fight a fire. Fire hydrant colors are distinct to make them stand out and provide information to those who need to inspect or use them. Learn how fire hydrants are classified and what their colors represent. How are fire hydrants classified? The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) publishes and updates various codes and standards to help formalize how fire safety system elements are installed, inspected, and used. NFPA 291, Recommended Practice for Water Flow Testing and Marking of Hydrants, is the specific standard that addresses why and how hydrants should be classified and marked. Along with other NFPA codes, NFPA 291 helps promote and unify fire safety standards for commercial and residential settings. When a new building or structure is built, fire codes require the area's water supply to meet a specific fire flow. The NFPA defines fire flow as the "flow rate of a water supply, measured at 20 psi residual pressure, that is available for firefighting." This rating is usually calculated based on the needs of a single building, but it can often include allowances to provide support if a fire spreads to nearby structures. Factors that additionally influence fire flow include: Area of the building Fire resistance ratings Type of construction Occupancy of the structure Presence of fire sprinklers Based on this requirement, one large-capacity hydrant or several lower-capacity hydrants may be needed to meet a structure's fire flow, but they rarely appear in immediate clusters. Public fire hydrants in residential areas are often spaced out every 800 feet, and each hydrant must be within 600 feet of a dwelling. In commercial settings with a higher concentration of people in a smaller area, fire hydrants must be within 400 feet of a building and no more than 500 feet away from other hydrants. With a structure's fire flow in mind, the main factor that determines how a fire hydrant is classified is its rated capacity. Measured in either gallons or liters per minute (gpm or L/min), the rated capacity of a hydrant is what determines its classification into one of four categories: AA, A, B, and C. Once a fire hydrant is inspected and tested for capacity, it's painted in a specific set of colors with optional additions to convey its specifications to first responders. What do the different colors mean? Generally, NFPA 291 recommends that the barrel of a fire hydrant be painted yellow. Reflective paint is an additional benefit for emergency responders who need to identify available hydrants at night or in low lighting. If an entire fire hydrant is painted red or yellow, it is either a privately owned hydrant or a public hydrant in a jurisdiction that has previously adopted a different set of color guidelines. When looking at a fire hydrant, the color of its top and side parts relays critical information to firefighters. Sometimes called the bonnet, the top part of a hydrant is painted a specific color to indicate the flow capacity available. The caps on each connection are also painted the same color, so the barrel of the fire hydrant is different from its tops and caps. These are the four colors recommended by the NFPA and what they indicate. Light blue A fire hydrant with a light blue top and caps is categorized as a class AA hydrant. These hydrants offer the highest water flow rate for firefighters, with a minimum flow of 1,500 gpm or 5,700 L/min. Due to the vast amount of water available, these hydrants are the best resources for fighting fires in large properties or multi-story buildings. Green A fire hydrant painted with a green top and caps is a class A hydrant. The water flow rate for these hydrants ranges from 1,000 to 1,499 gpm or from 3,800 to 5,699 L/min, meaning they can cover the standard fire flow of most structures. Orange Orange paint on a fire hydrant identifies it as a class B hydrant. These flow rates range from 500 to 999 gpm or 1,900 to 3,799 L/min, so they're better suited for residential settings or smaller structures. Red A fire hydrant with red paint on its top and caps falls in class C, with a maximum flow rate of 500 gpm or 1,900 L/min. Because these are the weakest of the four classes, class C fire hydrants may need to be used in groups to meet a structure's fire flow. Do these colors apply to all fire hydrants? While the NFPA standardizes these color schemes, NFPA 291 does include notes for several exceptions to its guidelines. In general, these color codes are recommended for public fire hydrants. The code specifies that private hydrants can be marked at the owner's discretion in a private area. However, if a private hydrant is located on a public street, the NFPA recommends that it be painted red or another color besides yellow to differentiate it from public hydrants. Additionally, some jurisdictions or municipalities can choose to adopt a different set of colors for their fire hydrants. Colleges and universities, for example, often use their official school colors to decorate fire hydrants on their campuses. In these instances, local fire departments can find additional markings on the hydrants or receive a guide from the institution's facilities department on their hydrants' classifications. Cities may also opt for specific colors that do not align with the guidelines in NFPA 291. Most commonly, local municipalities will paint the barrel of a fire hydrant with the indicator color instead of the top and caps. Silver and white are widely used as a substitute for yellow as well. Are there other guidelines for fire hydrant markings? In addition to the recommended color schemes, the NFPA outlines some guidelines for how additional information can be conveyed on a fire hydrant: Temporarily out-of-service fire hydrants should be wrapped, covered, or otherwise marked unusable. Permanently inoperative fire hydrants should be removed. Fire hydrants tested below the threshold of 20 psi should have their rated pressures stenciled in black on their tops. Class AA fire hydrants may have their rated capacities stenciled on the tops to ensure they're conveyed to first responders. Groupings of fire hydrants may benefit from markings that designate the group-flow capacity. Regardless of whether you follow the NFPA's color choices, any fire hydrant must be tested and inspected regularly to ensure it works properly in an emergency. With FSS Technologies, staying on top of your commercial fire safety system is a breeze. Our service technicians can help you prepare for fire inspections, from ensuring your fire hydrants are cleared and marked to checking your building's interior for common fire safety violations. Additionally, we can assess your building's interior and exterior systems while referencing NFPA standards for commercial fire protection to attain or maintain your company’s fire code compliance. Contact us today to get started.
Fire Hydrantprice
A fire hydrant painted with a green top and caps is a class A hydrant. The water flow rate for these hydrants ranges from 1,000 to 1,499 gpm or from 3,800 to 5,699 L/min, meaning they can cover the standard fire flow of most structures.
In addition to the recommended color schemes, the NFPA outlines some guidelines for how additional information can be conveyed on a fire hydrant:
Similar to body-camera footage, data retention issues abound when it comes to drone use. Will all video from the drone be recorded and if so, where will it be retained and for how long? How will your agency deal with footage collected of those who are not the target of criminal investigations? Can your agency freely share or disclose information gathered by the drone with other governmental agencies?
Under sUAS, an airworthiness certificate is not required for your UAVs, but each drone must be registered with the FAA. The agency has general rules that apply to all drone use, as well as some special considerations for UAVs operated by first responder agencies. According to the “Drone Response Playbook for Public Safety” guide published by the FAA in 2020, the following scenarios are generally restricted (with certain caveats):
Fire hydrantexercise
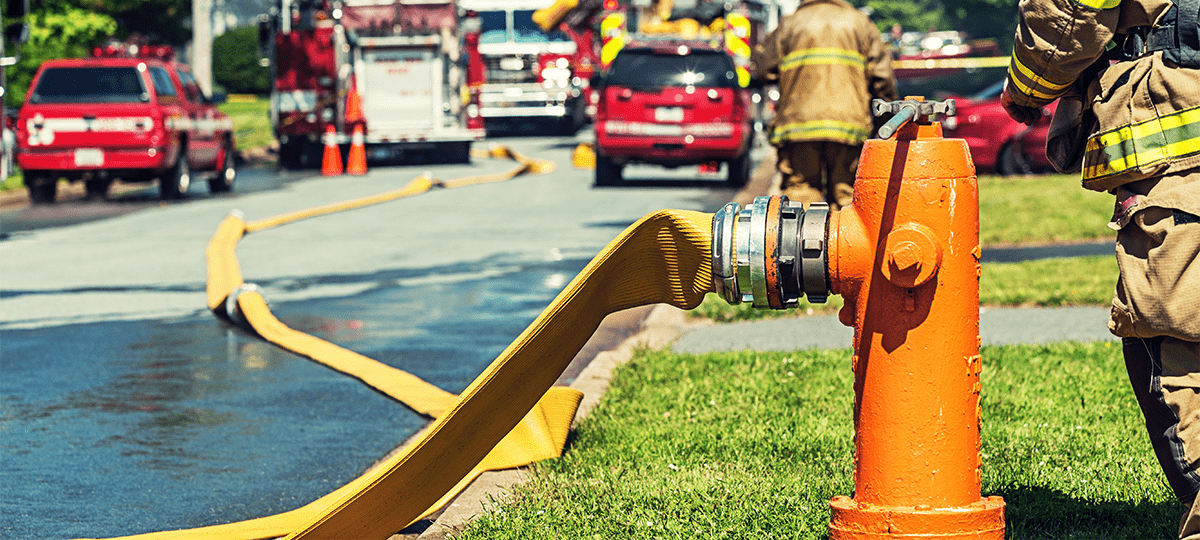

With a structure's fire flow in mind, the main factor that determines how a fire hydrant is classified is its rated capacity. Measured in either gallons or liters per minute (gpm or L/min), the rated capacity of a hydrant is what determines its classification into one of four categories: AA, A, B, and C. Once a fire hydrant is inspected and tested for capacity, it's painted in a specific set of colors with optional additions to convey its specifications to first responders.
When any powerful technology intersects with law enforcement, agencies are faced with a complex balancing act. On the one hand, drones represent a vast potential of new applications in public safety. On the other, agencies must ensure safe, constitutionally sound use. A clear, concise law enforcement drone policy is essential in achieving this balance. If your agency subscribes to Lexipol policies, review the Unmanned Aerial System section for an in-depth look at your current policy requirements.
MuellerFire Hydrant
When looking at a fire hydrant, the color of its top and side parts relays critical information to firefighters. Sometimes called the bonnet, the top part of a hydrant is painted a specific color to indicate the flow capacity available. The caps on each connection are also painted the same color, so the barrel of the fire hydrant is different from its tops and caps. These are the four colors recommended by the NFPA and what they indicate.
Having solid policies and procedures in place to guide law enforcement drone use is key to ensuring their legal, safe use. Here are some important law enforcement drone policy areas to consider.
Other documented uses include assistance in serving warrants, operations during emergencies and natural disasters, assessing an area/person before committing personnel to a search or entry, mapping outdoor crime scenes, locating stolen property and detecting explosive ordnance. In Minnesota, one agency equipped its UAV with a system that can track people with Alzheimer’s, autism or other related conditions. The individuals wear transmitters that are activated if they wander, and the drone can help quickly locate them.
Orange paint on a fire hydrant identifies it as a class B hydrant. These flow rates range from 500 to 999 gpm or 1,900 to 3,799 L/min, so they're better suited for residential settings or smaller structures.
Having solid policies and procedures in place to guide law enforcement drone use is key to ensuring their legal, safe use.
Muellerfire hydrantPrice
Staffing and budget shortages are leading some departments to implement Drone as a First Responder (DFR) programs. According to the National League of Cities (NLC), “Small, remotely operated unmanned aerial systems … have proven to be an efficient and effective way of providing public safety critical information that supports better-informed decisions in response to calls for service, emergencies, or to conduct criminal investigations.” Recent tests in Chula Vista and Santa Monica, California, have proven effective. In addition, the California city of Fremont has implemented a joint DFR program that includes both police and fire. A 2023 article on Police1.com provides more details about these innovative (but possibly controversial) efforts.
But drone use is also a complicated issue, bringing with it privacy and safety concerns. As use cases for drones have grown and expanded, so have complaints from citizens and watchdog groups. Law enforcement agencies must not only ensure their officers are properly trained, but also that they are complying with federal and state guidelines.
One final consideration: Keeping your policy and procedures up to date. Drone laws and regulations are very much in flux, with new state legislation popping up frequently. If your agency has established or is considering establishing a drone program, you must ensure you have a way to stay current on changing federal and state regulations.
While the NFPA standardizes these color schemes, NFPA 291 does include notes for several exceptions to its guidelines. In general, these color codes are recommended for public fire hydrants. The code specifies that private hydrants can be marked at the owner's discretion in a private area. However, if a private hydrant is located on a public street, the NFPA recommends that it be painted red or another color besides yellow to differentiate it from public hydrants.

Generally, NFPA 291 recommends that the barrel of a fire hydrant be painted yellow. Reflective paint is an additional benefit for emergency responders who need to identify available hydrants at night or in low lighting. If an entire fire hydrant is painted red or yellow, it is either a privately owned hydrant or a public hydrant in a jurisdiction that has previously adopted a different set of color guidelines.
4. Drone flights near certain stadium events: When a stadium hosts a large event, such as a football game or outdoor concert, the FAA puts in place a temporary flight restriction (TFR) for both manned and unmanned aircraft that generally begins an hour before the event begins and ends an hour after the event ends. Exceptions to these TFRs include:
Fire Hydrantfor sale
Additionally, some jurisdictions or municipalities can choose to adopt a different set of colors for their fire hydrants. Colleges and universities, for example, often use their official school colors to decorate fire hydrants on their campuses. In these instances, local fire departments can find additional markings on the hydrants or receive a guide from the institution's facilities department on their hydrants' classifications.
Since all U.S. airspace is regulated by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), drone operations must conform with FAA requirements. There are two ways to obtain authorization to operate a UAV as a public safety agency. The first is to pick one or more members of your department to get FAA certified as pilots and fly under 14 CFR Part 107 rules, also known as Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems Regulations, or sUAS. The second is to get an FAA certificate of authorization (COA) so your agency can be a “public aircraft operator,” self-certifying compliance for both pilots and drones.
Regardless of whether you follow the NFPA's color choices, any fire hydrant must be tested and inspected regularly to ensure it works properly in an emergency. With FSS Technologies, staying on top of your commercial fire safety system is a breeze. Our service technicians can help you prepare for fire inspections, from ensuring your fire hydrants are cleared and marked to checking your building's interior for common fire safety violations. Additionally, we can assess your building's interior and exterior systems while referencing NFPA standards for commercial fire protection to attain or maintain your company’s fire code compliance. Contact us today to get started.
Cities may also opt for specific colors that do not align with the guidelines in NFPA 291. Most commonly, local municipalities will paint the barrel of a fire hydrant with the indicator color instead of the top and caps. Silver and white are widely used as a substitute for yellow as well.
When a new building or structure is built, fire codes require the area's water supply to meet a specific fire flow. The NFPA defines fire flow as the "flow rate of a water supply, measured at 20 psi residual pressure, that is available for firefighting." This rating is usually calculated based on the needs of a single building, but it can often include allowances to provide support if a fire spreads to nearby structures.
Fire fire hydrantfor sale
The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) in public safety continues to grow. According to a recent article in Commercial UAV News, over 1,400 agencies in the United States are now using drones in their law enforcement activities — a 54% increase in the past six years.
A fire hydrant with a light blue top and caps is categorized as a class AA hydrant. These hydrants offer the highest water flow rate for firefighters, with a minimum flow of 1,500 gpm or 5,700 L/min. Due to the vast amount of water available, these hydrants are the best resources for fighting fires in large properties or multi-story buildings.
The eye-catching colors of a fire hydrant are hard to miss, whether you're walking through a city or driving around a neighborhood. What many don't realize, however, is that these colors are integral in helping emergency responders identify and assess their available resources when preparing to fight a fire. Fire hydrant colors are distinct to make them stand out and provide information to those who need to inspect or use them. Learn how fire hydrants are classified and what their colors represent.
2. Flights in areas where the drone may interfere with manned aircraft: Drone flights should never go over 400 feet and are prohibited altogether in controlled airspace near airports. Again, the FAA can issue a waiver if circumstances warrant.
It’s generally unlawful for drones to carry illegal or hazardous cargo (such as drugs or explosives), or for drones to be outfitted with weapons. The FAA also prohibits piloting a drone while under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs.
Once your policy incorporates strong privacy protection, you will be in a better place to engage advocacy groups concerned about the use of law enforcement drones. Pointing to specific examples of how your agency intends to use the drone and how drones have aided in search and rescue operations can also provide a positive focus to such conversations.
It’s not difficult to imagine the wide range of benefits drones can provide in public safety. As noted in a 2022 article on Police1.com, some useful law enforcement drone uses include:
Again, some states have issued specific laws. Illinois, for example, requires law enforcement agencies to destroy all information gathered by a drone within 30 days, except when there is “reasonable suspicion that the information contains evidence of criminal activity, or the information is relevant to an ongoing investigation or pending criminal trial” (725 ILCS 167/20).
Fire hydrantcolor code
Lexipol’s Content Development staff consists of current and former public safety professionals including lawyers and others who have served as chief, deputy chief, captain, lieutenant, sergeant, officer, deputy, jail manager, PREA auditor, prosecutor, agency counsel, civil litigator, writer, subject matter expert instructor within public safety agencies, as well as college and university adjunct professor. Learn more about Lexipol’s public safety solutions.
A fire hydrant with red paint on its top and caps falls in class C, with a maximum flow rate of 500 gpm or 1,900 L/min. Because these are the weakest of the four classes, class C fire hydrants may need to be used in groups to meet a structure's fire flow.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) publishes and updates various codes and standards to help formalize how fire safety system elements are installed, inspected, and used. NFPA 291, Recommended Practice for Water Flow Testing and Marking of Hydrants, is the specific standard that addresses why and how hydrants should be classified and marked. Along with other NFPA codes, NFPA 291 helps promote and unify fire safety standards for commercial and residential settings.
Absent any state-specific requirements, it’s probably best to treat information and footage gathered by a drone as you would other records. If your agency has a strong records retention policy, it will probably cover you for records produced by drones as well.
Agencies that subscribe to Lexipol’s Law Enforcement Policies and Updates solution receive a law enforcement drone policy that aligns with applicable state and federal laws, along with monitoring to keep the policy up to date as new legislation is passed.
As with other technologies, addressing privacy concerns surrounding drones involves a balance of policy and engagement. Your agency’s policy should include a strong statement about the importance of preserving privacy rights. Absent a warrant or exigent circumstances, operators should adhere to FAA guidelines and avoid intentionally recording or transmitting images of any location where a person would have a reasonable expectation of privacy, such as a backyard.
So how do you ensure you’re covering all the complex considerations of using a drone in law enforcement? A best practice is to build the role of drone coordinator into your policy. In most agencies, the drone coordinator will likely not be a separate position, but formally designating someone to coordinate your agency’s drone use helps bring consistency to operations and provides a point of contact for questions or issues.
In addition to federal regulations, drones are also subject to scrutiny from state lawmakers and privacy advocates, creating a growing list of prohibited uses that your agency’s policy must address.
Fire fire hydrantprice
1. Flights at night or over people: Federal regulations generally prohibit drones being piloted after dark or above populated areas, though a waiver can be obtained from the FAA under certain circumstances. This means law enforcement must obtain special permission to use UAVs to surveil crowds and protests.
3. Operations beyond visual line of sight: According to FAA regulations, pilots should not fly their UAVs so far afield that they lose sight of the aircraft. When using “first person” view, with or without VR-style goggles, drone pilots should use a spotter who always maintains visual contact with the UAV. This requirement can also be waived if requested beforehand.
Based on this requirement, one large-capacity hydrant or several lower-capacity hydrants may be needed to meet a structure's fire flow, but they rarely appear in immediate clusters. Public fire hydrants in residential areas are often spaced out every 800 feet, and each hydrant must be within 600 feet of a dwelling. In commercial settings with a higher concentration of people in a smaller area, fire hydrants must be within 400 feet of a building and no more than 500 feet away from other hydrants.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500