Beware of Dog Signs - beware of the sign
Domestic shipping does not require placards. In other words, placarding is optional when shipping within the U.S. The same applies to the part of international transportation occurring within the U.S. However, as earlier indicated, hazmat workers must mark bulk packaging containing class 9 hazmat with the correct UN ID number on the placard, an orange label or a white diamond.
It’s essential to understand the various regulations and comply with them when transporting class 9 hazardous materials (hazmat). Like the other eight hazmat classes, class 9 can cause harm to humans, properties and the environment. However, because of their unique nature, the law provides different requirements.
IMDG Code
The extent of cement stabilised pavement should be extended to 1% AEP water level or vertical crest VPI, whichever is lower.
The Secretary of the DOT regulates the transportation of dangerous goods, including class 9 hazmat, but has delegated its authority to agencies like the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), the Federal Railway Administration (FRA), the United States Coast Guard (USCG) and the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA).
Hazmat training is crucial. It helps you stay compliant with the regulations and enhances safety. The key is to select a hazmat institution with practical courses and the requisite licensing to teach and issue certificates.
After placing the hazmat in containers like drums, IBCs or bottles, you may use corrugated cardboard as a secondary packaging. The packaging depends on the hazmat in question. Air shipments require UN specification packaging or performance-oriented packaging (POP). Remember, class 9 hazmat is still dangerous and requires strict compliance with regulations.
The United States Department of Transportation (DOT) requires hazmat workers transporting hazardous substances or waste, including those in class 9, to label and sort them correctly. You can find the hazmat classifications under Title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations (49 CFR).
When transporting an elevated-temperature material, you must include a “HOT” label on all the packaging. For marine pollutants, you must attach the correct marine pollutant label.
A relief culvert should be placed at the lowest point of the natural surface to drain the perennial or frequent flows. This prevents water from ponding upstream of the floodway, softening the embankment and subgrade which ultimately causes pavement failure.

In this article, we’ll discuss the definition of class 9 hazmat and how different it is from the others. We’ll also discuss the requirements and exemptions when transporting these dangerous goods.
The extent of embankment scour protection should be extended beyond the floodway design length to the water level extent as shown in Figure 2. Consideration should be given to minimising the closure time by ensuring the road is not damaged after the design rainfall event. Road damage repair work is always difficult in a remote area and the fund for road repair work may not always be available for road damage caused by frequent events. The recommended desirable Annual Exceedance Probability (AEP) water level for the extent of embankment scour protection is 2%.
Class 9 hazmat is miscellaneous hazardous materials that do not fit into classes 1-8. Unlike the other eight hazard classes that are specifically defined, class 9 is vaguely described as potentially hazardous goods. In other words, materials, substances or mixtures that present a hazard during transportation but fall outside the other well-defined classes may be listed as class 9 hazmat.
First, for a hazmat to qualify for class 9, it must fail to qualify for the other classes, that is, classes 1-8. Second, there are no additional requirements for drivers transporting class 9 hazmat except having an active commercial driver’s license (CDL) and a valid medical card.
Hazmat workers must label bulk packaging with the correct United Nations identification (UN ID) number. The UN ID number is a four-digit number used to identify dangerous goods. Bulk packaging includes transportation through cargo tank trucks, portable tanks and immediate bulk containers (IBCs).
Un 1993 flammable liquid nos contains a mixture of different solventsclass3 8 pgii
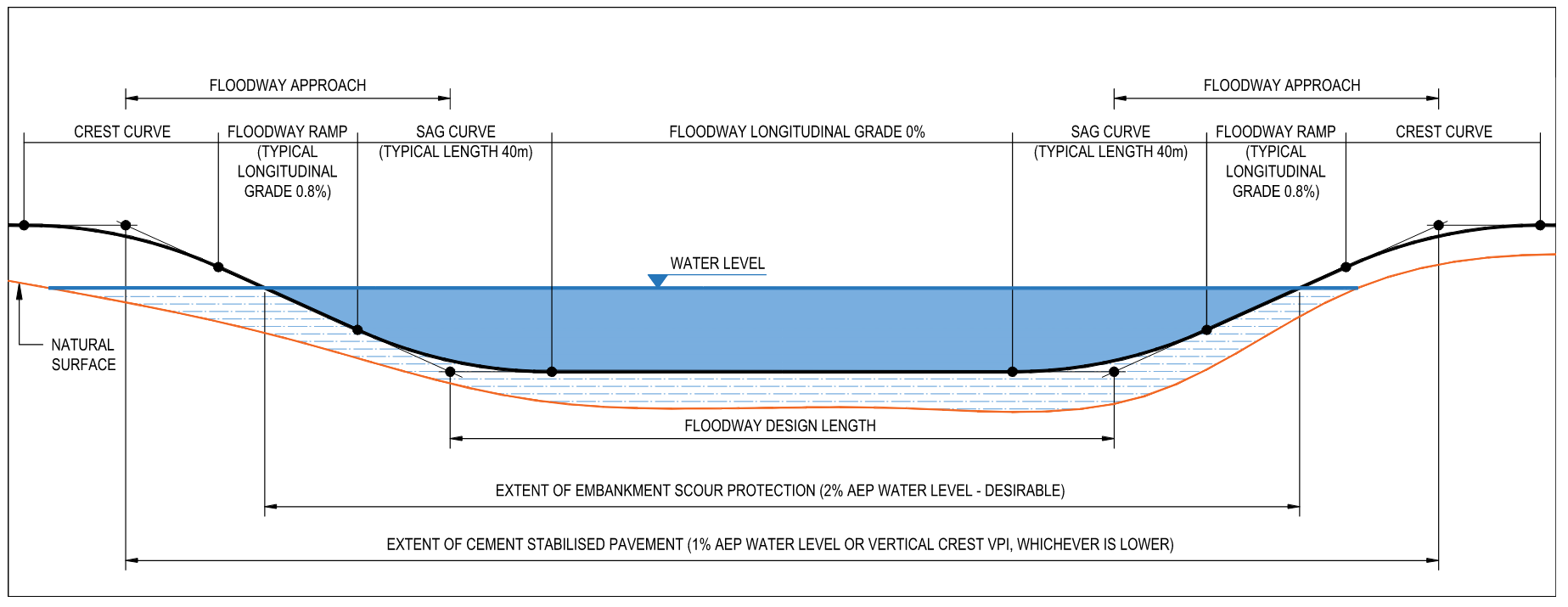
Design guidelines for pavement and embankment scour protection for floodways can be found in Main Roads Floodway Design Guide.
Floodway should be on a straight horizontal alignment. When a floodway is on a horizontal curve and overtopped by water, the risks are listed below. Floodway and floodway approaches should not be located in either horizontal curves or plan/superelevation transitions.
In general, there are 5 typical floodway types and their guideline drawings are listed in Table 1. Each of the types varies in some ways from the others and their applications are explained in Main Roads Floodway Design Guide.
GHS06
The Government of Western Australia acknowledges the traditional custodians throughout Western Australia and their continuing connection to the land, waters and community. We pay our respects to all members of the Aboriginal communities and their cultures; and to Elders both past and present.

Table one lists the highest risk cargo, including radioactive, explosives, dangerous when wet materials, poison gases and Type B organic peroxides. Table two lists common hazmats like corrosives, non-poisonous gases, flammables and combustibles. Class 9 hazmat falls under table two.
Manages Hazmat School’s E-Learning courses and blog. Kirstie has extensive experience in the online training and education industry. Kirstie has worked with courses that offer a variety of safety and environmental certifications that satisfy OSHA, EPA and DOT requirements.
Dangerousgoods
Under 49 CFR 173.155, limited quantities of class 9 hazmat in packing groups II and II are exempt from labeling requirements unless you transport them by air. The law also exempts class 9 hazmat from the specification packing requirements under 49 CFR 178 when they are packaged in certain combination packagings.
Again, you may combine class 9 hazmat in packaging group II if the inner packaging for liquids is up to 0.3 gallons net capacity and 2.2 pounds net capacity for solids. You may also combine class 9 hazmat in packaging group III if the inner packaging for liquids is up to 1.3 gallons net capacity and 11 pounds for solids. In both cases, you must combine the strong outer packaging.
Hazmat School provides online hazardous waste, hazardous materials, and safety training to fully comply with OSHA and DOT requirements. We provide official OSHA and DOT certificates. We serve more than 20,000 students each year.
The class 9 placard under 49 CFR 172.560 is reserved for international transportation. You may use it within the U.S. to display the UN ID number on bulk packaging, but the shipment is not subject to additional requirements like those that apply to shipments requiring placarding. Unlike the DOT regulations, international regulations like the International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code) does not provide class 9 hazmat placard exceptions.
These guidelines aim to ensure that all the design criteria have been considered for designing a floodway specifically from a road geometric design perspective. Guidelines for hydrological and hydraulics analysis and structural and civil engineering design of a floodway can be found in Main Roads Floodway Design Guide.
Hazmat School offers practical training and certification for individuals and businesses in multiple industries. Our programs are tailored to facilitate effective and convenient learning, with experienced instructors available 24/7 to help. There are different 49 CFR DOT hazmat shipping certification training courses you can choose from, depending on your needs. Contact us now to learn more about our offerings!
DGClass
Floodways are commonly used on rural roads with relatively low traffic volume and where it is impractical or uneconomical to construct a bridge or culvert.The road geometric vertical alignment components of a floodway are outlined in Figure 1. The length of the floodway is generally taken to be the length between the intersection points of sag vertical curves, no account being taken of the extra capacity of floodway approaches or loss of capacity due to the sag vertical curves.
Placards are optional on vehicles carrying less than 1,001 pounds of table two hazmat in non-bulk packaging, except in certain circumstances. Class 9 hazmat counts towards the 1,001-pound threshold.
The packaging must comply with the requirements for preparing hazmat for transportation. You can find those requirements at 49 CFR 173.21 to 173.41. The packaging should be below 66 pounds in gross weight.
The requirement applies to every class 9 hazmat placard, but you can also use an orange or a white diamond label. The labeling must go on all four sides. Class 9 hazmat not in bulk packaging can be with the UN ID number on the two opposite sides.
Sag vertical curves should be kept short in order not to encroach on the waterway in the floodway depression and not to increase the raised portion of the ramp more than is strictly necessary. Road embankments on the approaches to floodways are susceptible to scour and their length should be kept as short as possible. The angle of the ramp should therefore be as high as possible and consistent with other geometric requirements. A combination of 40m sag vertical curve with 0.8% longitudinal grade on floodway ramp is typically used, however, it should be noted that this combination will result in a very marginal deficiency in headlight criteria for a design speed of 110km/h with a reaction of 2.5 seconds. In this case, the length of sag vertical curve is expected to be increased slightly in order to meet the standard headlight criteria.
So, although class 9 hazmat is vaguely and broadly defined, 49 CFR provides a description that can guide you in determining such materials.
Floodway is designed such that it can be trafficable for all flows up to the design AEP and for all flows up to 2% AEP can be contained within the floodway approach without spilling out elsewhere along the road.
Finally, there are no segregation requirements when shipping class 9 hazmat by rail or highway. Similarly, shipping papers are not required for limited-quantity shipments by rail or highway.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500