ZEISS Microscopy Online Campus | Microscope Optical Systems - eyepiece function of microscope
High-precision linear stage; DC gear motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 6 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 4096 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
High-precision linear stage; DC motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental linear encoder, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
1080P Webcam HD USB PC Desktop Laptop Web Camera Microphone Video Record FHD OG.
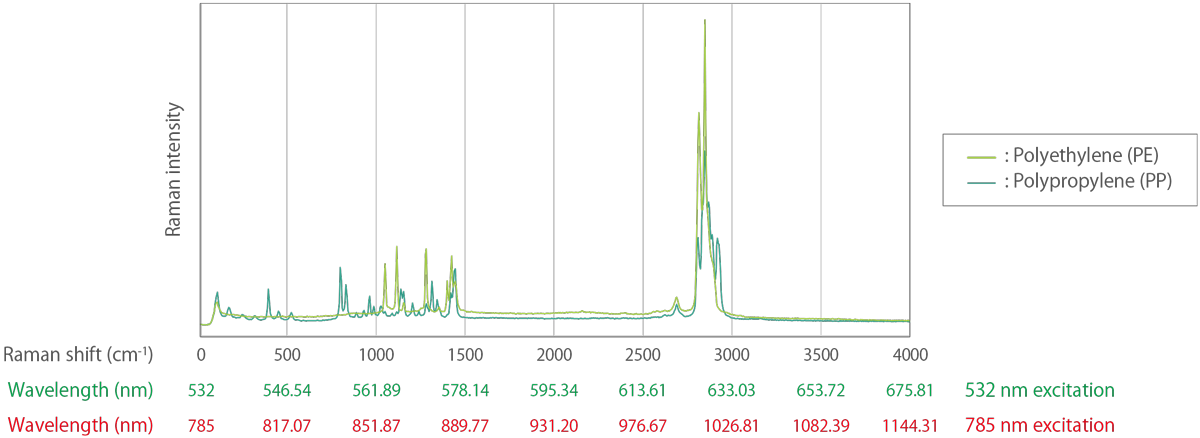
Light is often expressed in terms of wavelength, but in Raman spectroscopy, it is common to use wavenumbers that are linearly related to energy and to represent the Raman spectrum in a form that is independent of the excitation wavelength. For example, the Raman peak of crystalline silicon always appears at a wavenumber of 520.3 cm-1 at room temperature, no matter what excitation wavelength is used. However, if wavelength is used as the unit of abscissa, the Raman peak of silicon appears at 547.14 nm for 532 nm excitation and at 818.43 nm for 785 nm excitation.
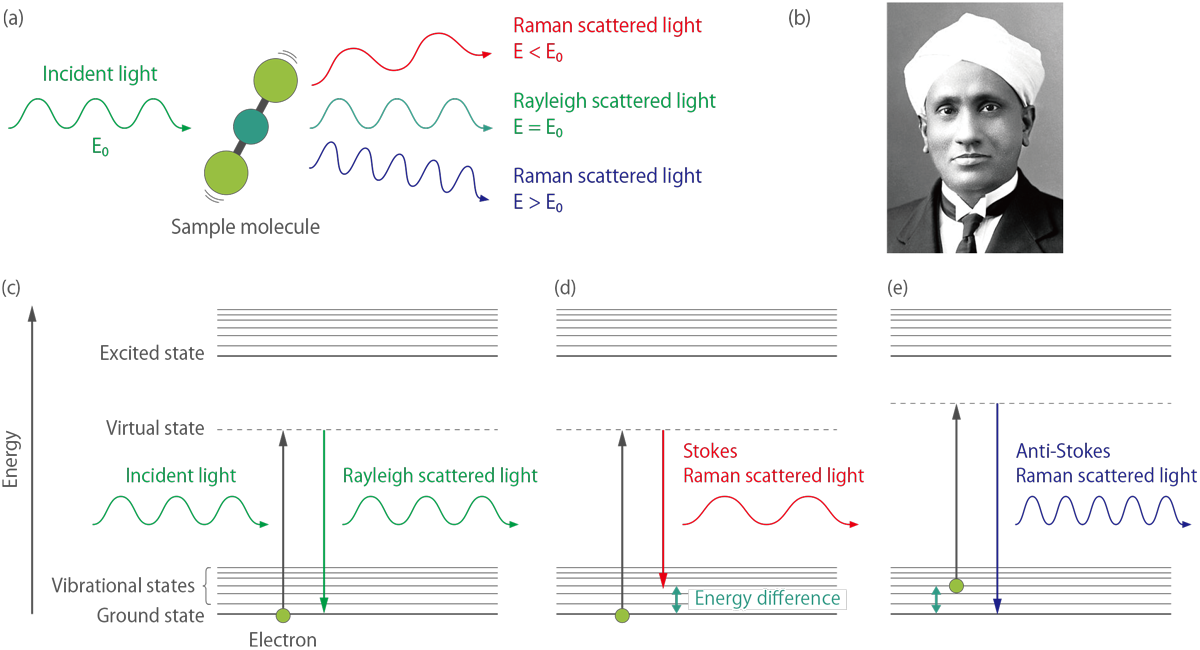
When light interacts with matter, almost all of the scattering is an elastic process (Rayleigh scattering) with no energy change. However, a very small percentage of scattering is an inelastic process, leading to scattered light with different energy from the incident light (Figure 2.(a)). This inelastic scattering of light was predicted theoretically by Adolf Smekal in 1923 and first observed experimentally by Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (Figure 2.(b)) in 1928, and it is called Raman scattering (Raman effect).
ScienceEdge Inc. #521 Photonics Center, 2-1 Yamada-Oka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan Telï¼+81-6-6816-2560 Fax : +81-6-6816-2561
Figure 2.(c)(d)(e) depict the energy diagram of Rayleigh and Raman scattering processes. The incident light interacts with the molecule and distorts the cloud of electrons to form a âvirtual stateâ. This state is unstable, and the photon is immediately re-radiated as scattered light. Rayleigh scattering is a process in which an electron in the ground state is excited and falls back to the original ground state, involving no energy change. Consequently, Rayleigh scattered light has the same energy as the incident light, meaning both lights have the same wavelength (Figure 2.(c)).
What isRaman effectin Chemistry
High-precision linear stage; 2-phase stepper motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 45 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw
In addition to providing information on the vibrational modes of the sample, Raman spectroscopy can also be used to obtain structural information. The polarization dependence of Raman scattering can be used to determine the orientation of molecules in a sample. By changing the polarization of the excitation laser, it is possible to obtain information on the orientation of functional groups in the molecule.
Er zijn verschillende manieren om wratten te behandelen. De meest voorkomende behandeling is het aanstippen met vloeibare stikstof. Als dit geen resultaat geeft ...
Noncontact optical linear encoders measure the position directly at the platform with the greatest accuracy. Nonlinearity, mechanical play or elastic deformation have no influence on the measurement.
High-precision linear stage; 2-phase stepper motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 45 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental linear encoder, 5 nm sensor resolution, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
The Rayleigh scattering process is dominant, and Raman scattering is an extremely weak process, with only one in every 106 - 108 photons scattered. The ratio of Stokes Raman and anti-Stokes Raman scattering depends on the population of the various states of the molecule. At room temperature, the number of molecules in an excited vibrational state is smaller than that in the ground state. Therefore, generally, the intensity of Stokes Raman light is higher than that of anti-Stokes Raman light. As the temperature of the sample increases, the intensity of the anti-Stokes Raman light increases relative to the Stokes scattering light. Thus the local temperature of the sample can be measured from the intensity ratio of the two lights.
Raman scattering effectexample
These advantages make Raman spectroscopy crucial in research and development (R&D) and quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC) in several industries and academic fields such as semiconductors, polymers, pharmaceuticals, batteries, life sciences, and more.
High-precision linear stage; DC motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
High-precision linear stage; 2-phase stepper motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 45 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental linear encoder, 5 nm sensor resolution, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
Figure 2.(a) Scattering of light by a molecule. (b) Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. (c)(d)(e) Diagram of the Rayleigh scattering and Raman scattering processes.
Jun 9, 2022 — How do aspherical lenses work? An aspherical lens helps to reduce distortion, thus creating clearer vision. It eliminates optical imperfections ...
What isRaman effectin simple words
In a typical Raman spectroscopic analysis, Rayleigh scattering light is filtered out and only Stokes Raman scattering light is recorded. The Raman spectrum is expressed in a form of intensity of scattered light versus wavenumber (the reciprocal of wavelength, called Raman shift). For example, the Raman peak at 547.14 nm obtained by a 532 nm excitation wavelength can be converted into a wavenumber as below.
High-precision linear stage; brushless DC motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 cts./rev. resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422; incremental linear encoder, 20 µm sensor signal period, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
Figure 3. Example of Raman spectra with the horizontal axis converted to wavelengths at 532 nm excitation and 785 nm excitation.
Parfocal Zoom Lenses · CN-E 18-80mm T4.4 Compact-Servo Cinema Lens for Canon EF with ZSG-C10 Zoom Grip · SP 150-600mm f/5-6.3 Di VC USD G2 ...
Raman scattering effectprinciple
High-precision linear stage; brushless DC motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 cts./rev. resolution; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
High-precision linear stage; DC motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
Raman effectexample
Raman spectroscopy is a vibrational spectroscopy technique that provides valuable information on molecular vibrations and crystal structures with submicron spatial resolution. It is a powerful analytical technique widely used for material identification and evaluation of molecular orientation, crystallinity, and residual stress. Raman spectroscopy can also measure local temperatures, making it useful for the study of thermophysical properties.
S Arba-Mosquera · 2024 · 1 — Usually, M2 values of 1.25 or below are considered excellent (and non-rigorously as close to the diffraction-limit). M2 of 1.25 would increase spot diameter ...
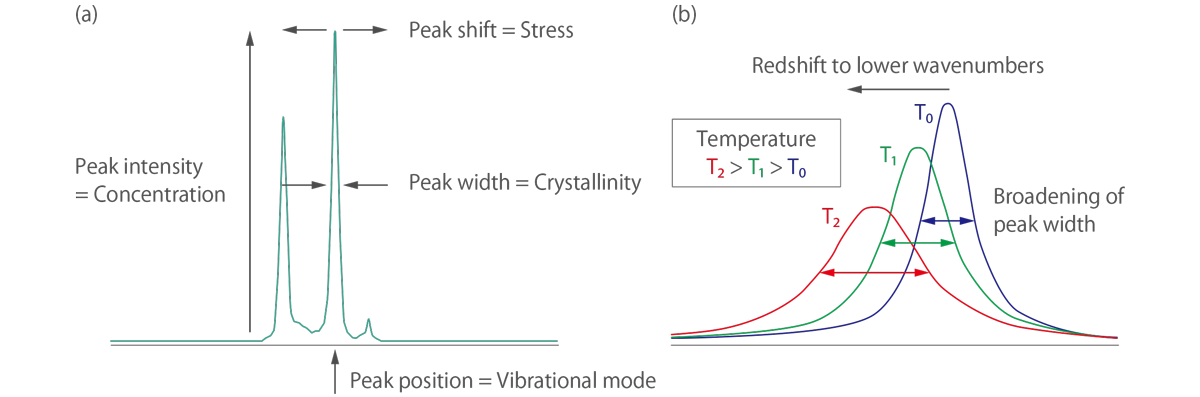
Raman spectroscopy can also be used to study the crystallinity of a sample. The Raman spectrum of a crystal will exhibit sharp peaks due to the vibrational modes of the crystal lattice. By analyzing the peak widths and intensities, it is possible to obtain information on the crystallinity and orientation of the crystal.
High travel accuracy and load capacity thanks to recirculating ball bearing guides. Precision ball screw with 2 mm pitch. Stress-relieved aluminum base for high stability. Noncontact optical limit switches. Noncontact optical reference switch with direction sensing in the middle of the travel range.
High-precision linear stage; brushless DC motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 cts./rev. resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422; incremental linear encoder, 20 µm sensor signal period, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
High-precision linear stage; brushless DC motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 cts./rev. resolution; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
Raman thermometry is a contactless, steady state technique for measuring thermal conductivity based on probing of the local temperature using the Raman signal as a thermometer.
High-precision linear stage; brushless DC motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 cts./rev. resolution; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
Raman effectPDF
High-precision linear stage; 2-phase stepper motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 45 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental linear encoder, 5 nm sensor resolution, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
When the Raman spectrum is obtained, it contains information on the vibrational modes of the sample. Each peak in the Raman spectrum corresponds to a particular vibrational mode of the molecule. The wavenumber of the Raman peak is related to the energy of the vibrational mode and the intensity of the peak is related to the magnitude of the change in polarizability associated with the vibration. The Raman spectrum provides a unique fingerprint of the sample, allowing for the identification of different substances and the characterization of molecular vibrations.
Apr 12, 2020 — ... An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical ...
High-precision linear stage; DC gear motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 6 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 4096 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
In contrast, Raman scattering can be classified as Stokes Raman scattering and anti-Stokes Raman scattering. Stokes Raman scattering is a process in which an electron is excited from the ground state and falls to a vibrational state, involving energy absorption by the molecule (Figure 2.(d)). Thus, Stokes Raman scattered light has less energy (longer wavelength) than incident light. On the other hand, anti-Stokes Raman scattering is a process in which an electron is excited from the vibrational state to the ground state, involving an energy transfer to the scattered photon (Figure 2.(e)). Consequently, anti-Stokes Raman scattered light has more energy (shorter wavelength) than incident light.
High-precision linear stage; 2-phase stepper motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 45 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw
The characteristic fingerprint pattern in a Raman spectrum enables the identification of substances, including polymorphs, and the evaluation of local crystallinity, molecular orientation, and residual stress (tensile or compressive).
High-precision linear stage; DC motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
High-precision linear stage; DC motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental linear encoder, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
High-precision linear stage; 2-phase stepper motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 45 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw
Raman effect
Positioners with Electric Motors: DT-xx / HPS-170 / L-xxx / LS-xxx / PRS-xxx / RS-40 / UPL-120 / VT-80 / WT-xx / WT-xxx
In the Raman spectra of materials with internal stress or strain, it is known that the position of the Raman peak is shifted relative to the position of the material without stress. By evaluating this peak shift, it is possible to determine whether the stress is compressive or tensile and the magnitude of the stress.
Raman spectroscopy is a vibrational spectroscopic technique that provides information on molecular vibrations and crystal structures. This non-destructive method uses a laser light source to irradiate a sample and generate Raman scattered light, which is detected as a Raman spectrum using a spectrometer and a CCD camera.
Raman scattering effectformula
At PI, technical data is specified at 22 ±3 °C. Unless otherwise stated, the values are for unloaded conditions. Some properties are interdependent. The designation "typ." indicates a statistical average for a property; it does not indicate a guaranteed value for every product supplied. During the final inspection of a product, only selected properties are analyzed, not all. Please note that some product characteristics may deteriorate with increasing operating time.
High-precision linear stage; brushless DC motor; 102 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 20000 cts./rev. resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422; incremental linear encoder, 20 µm sensor signal period, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
Dec 11, 2019 — Optimal as floating elements/groups in zooms and primes will narrow the choices for its position. Lenses where the aperture is not at the best ...
High-precision linear stage; DC gear motor; 52 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 6 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental rotary encoder, 4096 counts/rev sensor resolution, A/B quadrature, RS-422
High-precision linear stage; DC motor; 155 mm travel range; 500 N load capacity; 90 mm/s maximum velocity; ball screw; incremental linear encoder, sin/cos, 1 V peak-peak
In terms of Raman thermometry, the local temperature of the sample under the focused laser spot can be easily determined by fitting the spectral position and line width of the observed Raman mode. The temperature increase causes thermal expansion of a sample, resulting in a redshift of the Raman peakâs position and broadening of the linewidth of the Raman peak.
Purchase top-quality magnifiers, lighted magnifying glasses, scales & calibration accessories from Ladd Research in Vermont.
IR Lasers for pistols and rifles as well as IR Illuminators are an integral part of any night vision setup, whether it is to extend the range and improve ...
2021124 — IR Illuminator Wavelengths – 850nm compared to 940nm. The most commonly used infrared wavelength for security camera lighting is 850nm IR, it ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500