What Makes the Best Anti-Reflective Coatings - anti reflective coating
C- to CS-mount adapter.
Coarse adjustmentmicroscopefunction
Polarization definition: a sharp division, as of a population or group, into opposing factions.. See examples of POLARIZATION used in a sentence.
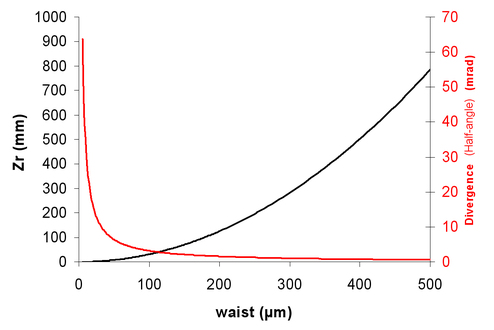
If we consider a “big” waist (1 mm), we find ZR = 3,14 m and a divergence (half-angle) of 0,018 degrees. We then obtain a so-called “collimated beam”.
Comments Section · Optimum Opti-Coat Pro starts at $1000 with wash, clay/decon, 1 polishing step and coating for smaller vehicles. · You have to ...
The developer, Lens Distortions, LLC, indicated that the app's privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see ...
Revolving nosepiecemicroscopefunction
Let's take again the origin at the waist position w0, corresponding to a plane wave (infinite radius of curvature). We have defined the Rayleigh length : .
When z increases, the beam expands in the transverse direction while its amplitude on the z-axis decrease (energy conservation). The profile shape remains Gaussian.
Function of objective lens inmicroscope
Infrared Linear Variable Filters are narrow band filters where the Centre Wavelength (CWL) changes with distance along it's length, this is shown in the ...
Jun 29, 2022 — Deep Dive into Optics: Camera Lens Field of View (FOV) ... Field of view (FOV) is defined as the maximum area that a device can capture. The ...
The divergence of a Gaussian beam is inversely proportional to the size of its waist. In the framework of Gaussian optics, “collimating a beam” is the same thing as “having a big waist”.
Fine adjustment knobmicroscopedefinition
Armmicroscopefunction
Analysis · Average the right and left angles for each color. · Use the grating equation with d=(1/6000) cm to find the wavelength · Calculate the percent ...
Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of ...
Oct 24, 2024 — Polarization, property of certain electromagnetic radiations in which the direction and magnitude of the vibrating electric field are ...
The Gaussian characteristics of the beam are essentially important in the vicinity of the beam waist. Indeed, when z increases, the complex radius of curvature becomes close to R and the wave could be considered spherical.
For a tightly focused laser beam (w0 = 10 µ) and a 1 µm wavelength, we find ZR = 314 µm and a divergence (half-angle) of 1,8 degrees.
The Rayleigh length is the distance (from the waist) where the beam area is twice the beam area at the waist (the radius is times bigger). This parameter is useful to define a “collimated” beam : over this length, the beam size is nearly constant (between and ) - see figure 11.
Body tube microscopefunction
w(z) is the dimension of the laser spot (the “radius” if the spot is circular) in the plane perpendicular to the propagation, at a distance z from the origin. Precisely, it is the radius (at 1/e for the amplitude, or 1/e² for the intensity) of the transverse Gaussian profile at the z abscissa.
Fine adjustment knobmicroscopefunction
Body tubedefinition
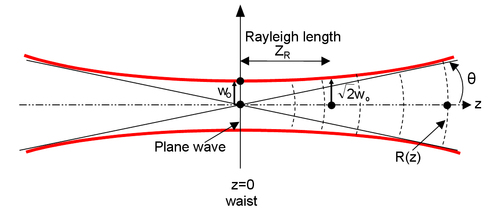
The main basic expressions related to Gaussian beams were mathematically obtained in the previous paragraph. We will now describe their physical signification.
Prices from $8 - Enquire for a fast quote ☆ Visit our Medical Aesthetics Clinic - 20 Queen Street East, Downtown Brampton, Ontario, L6V 1A2, Canada.
The size of the beam at the origin, w0, is minimal : the beam will diverge from this point (see figure 11). This minimal dimension is called “beam waist” (the waist is the radius of the spot. The diameter is of course given by 2 w0).




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500