What is an Airy pattern? How does it arise in diffraction? - Vaia - airy pattern
Figure 3: Matching camera FOV to microscope FOV. Top . An 18 mm FOV microscope is matchedby an 18 mm FOV camera, which fits within the microscope circular FOV. Bot . Having a camerawith a larger FOV than the microscope leads to more image capture but introduces vignetting artifacts.
Adapters can have lenses in them to magnify or demagnify the image before it reaches the camera. This can be used to better match the camera FOV to the microscope FOV. For example, if the camera has an 11 mm diagonal FOV but the microscope is capable of an 18 mm FOV, a 0.67x adaptor would demagnify the image and allow it to be displayed on the 11 mm camera. However, this increase in FOV comes at the cost of reduced resolution.
Jun 14, 2000 — In a real converging lens light bends at both surfaces as shown by the upper ray, in the thin lenses used in ray tracing we model light bending ...
Adaptors can also affect the microscope and camera FOV depending on the type of adaptor used. A C-mount adaptor is the most popular microscope camera adaptor and is restricted to a maximum 22 mm FOV. The F-mount adaptor is a larger format adaptor capable of reaching >30 mm FOV.
VUVBandpass Filter
Our IR filters are designed to hold up for years of regular use in the field. Each filter completes the weather-sealing of the lens and can withstand extreme wind, salt water, dust and other abrasive elements and conditions.
The IR filters work by blocking light up to certain wavelengths and only passing light higher on the spectrum into infrared. The result is otherworldly landscapes and subjects that couldn’t normally be seen with the naked eye. Bright white foliage, a surreal glow and dark, dramatic skies are hallmarks of infrared photography that can be creatively explored with IR filters.
Opticalbandpass filter
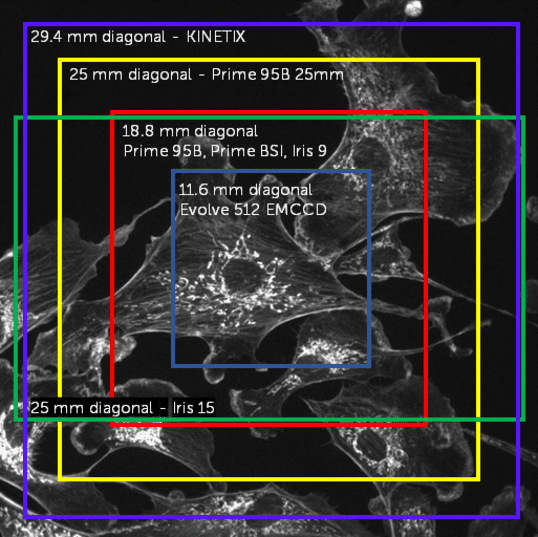
At Teledyne Photometrics, we aim to create cameras that can optimally match the FOV of all modern microscopes (Table 1). For this reason, the Prime 95B Series comprises a 19 mm camera, a 22 mm camera and a 25 mm camera. Additionally, the Prime BSI and Iris 9 both fit a 19 mm microscope FOV and the Iris 15 fits a 25 mm microscope FOV. The Kinetix is our largest format sensor which is able to be used to get the maximum FOV out of any system up to 29 mm.
Both film and digital cameras can be used for infrared photography. In film photography, the sensitivity of the film itself is one of the most important factors in determining the effect. It is necessary to learn how the film and filters interact to alter the image. Digital cameras have numerous advantages such as increased IR sensitivity and less grain in the image.
These larger sensors typically have more pixels, so while an EMCCD would have 0.25 megapixels (MP), CMOS cameras contain anywhere from 1-15 MP depending on the pixel size.
A camera with 25 mm diagonal FOV can only image an area this large if the magnification is 1x. With a typical life science magnification of 40x, the camera FOV decreases by a factor of 40, resulting in a 625 µm diagonal FOV.
IRpassfilterSheet
While a few cameras are full-spectrum out-of-the-box, most cameras must be converted to shoot infrared. The process involves removing and replacing the original cover glass so IR light can reach the sensor. If you go this route, you have several options to choose from and the modification can be done with a wide variety of cameras.
The CCD and CMOS sensors used in digital cameras are sensitive to UV, visible and IR light. Since most photography uses only visible light to create images, camera manufacturers always use filter cover glass over the sensor to block IR and UV and pass only visible light. Without the filters, there would be strong color shifts and a hazy look when trying to take standard, visible light photographs.
Your system supports progressive scan for NTSC video, which generally provides a better picture from video plays through your system.
GreenBandpass Filter
Combining our IR filters with our best-in-class polarizer, the IR CPL gives more versatility to infrared photographers without the need to stack filters. As with standard photography, polarizers let you control reflections and darkens the sky during infrared shoots. We incorporated the world’s first polarization indicators, which make precisely controlling the amount of polarization simple and fast. This is especially helpful for IR filters since they are so dark that you can't see through to make polarization adjustments. Also some view finders rely solely on visible light and are rendered useless if an IR filter is on the lens.
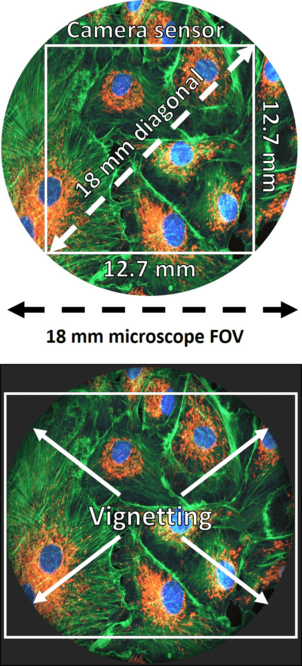
Figure 1: Different camera FOVs displayed on the same sample. While CCD/EMCCDs have small FOVs, CMOS cameras range from 18.8-29 mm in FOV, and can be square or rectangular.
CCDs and EMCCDs typically had smaller sensors measuring around 11 mm, this limits what you can image and is well below the maximum of most microscopes.
The greater the magnification, the smaller the FOV, as shown in Figure 2. However, high resolutions depend on high magnifications (see our resolution article for more), and high camera speeds can also be obtained with smaller FOVs. So in order to image at a large FOV, it will affect other factors in your imaging. Luckily, most biological samples are small (from cells to molecules) and often don 't need the entire FOV the camera can offer.
... Wavelength (nm). %T. 400. 450. 500. 550. 600. 0. 10. 20. 30. 40. 50. 60. 70. 80. 90. 100. All transmission and blocking (OD) data are actual, measured spectra ...
The field of view of the camera determines how much of your sample you can see. With larger FOVs, cameras can image more effectively and capture a sample in fewer images. However, FOV is decreased at higher magnifications and in order to improve speed, and it should be matched to the model of microscope. By keeping this in mind, you can maximize your FOV and perform more efficient imaging.
IR bandpass filter850nm
CMOS cameras offer much larger sensors, typically around 18.8 mm diagonal which matches up well to certain microscope models. Some microscopes can go above 20 mm diagonal, so CMOS cameras are also available with sensor sizes of 22 mm, 25 mm, and even 29 mm.
Featuring durable, weather-sealed traction frames, the IR and IR CPL have an ultra-slim, double threaded design that eliminates vignetting on wide-angle, full-frame setups down to 16mm. We use high purity H-K9L® glass made in Japan and our state-of-the-art MRC8 and nanotec® Nano Coatings protect the filters from the elements while improving optical performance. And like all of our filters, the IR filters are guaranteed to be free from manufacturing defects for 25 years.
Unlock the ethereal world outside of the visible spectrum with our all-new line of IR filters designed for full-spectrum and IR converted cameras. Featuring rugged, weather-sealed traction frames, MRC8 and nanotec® Nano Coatings, our IR filters are engineered for incredible optical performance and durability.
Similarly to resolution, FOV is dependent on both the microscope and the camera, both of which have upper limits on their max FOV. By pairing a large FOV camera with a large FOV microscope much of your sample can be captured at once, while using a smaller FOV camera with a large FOV microscope will limit the amount of data you can receive even if the microscope can deliver much more.
Each filter incorporates our state-of-the-art nanotec® Nano Coating technology which repels dirt, water and other debris by beading up on the surface rather than absorbing and smearing.
The area across which your camera can image is known as the field of view or FOV, the larger the FOV the more of your sample you can see. Having a large FOV allows you to take more efficient images containing more data, and take fewer images in order to capture the entire sample. But as with all camera specifications, changes to FOV will affect other vital factors such as resolution and imaging speed.
Jul 20, 2023 — Anti-glare (AG) or anti-reflective (AR) lens coatings are specific coatings designed to decrease the amount of reflective light in your lenses.
A microscope C-mount or F-mount adaptor is needed to connect a scientific camera to the microscope camera port. The mount threading is standardized which means that a C-mount adaptor will connect to all scientific cameras that connect via C-mount. However, the adaptors are microscope specific which means that although any C-mount camera will connect to a C-mount adaptor, the adaptor will only fit microscopes of the matching brand.
ACHIEVE® PRO WITH CRYPTEX® CALF PASTE 60 GM TUBE.
ThorlabsIR Bandpass Filter
Online conversion from Millimeter (mm, Metric) to Pixel (px, Typographical (British And U.S. - ATA System)). Distance And Length Converter.
As in standard, visible light photography, choosing the right lens for IR will go a long way in determining the quality of your images. There is a lot of variability in the way lenses capture infrared light so researching and experimenting with different options is crucial to avoid issues such as hot-spots in the center of frame and blurry corners.
Choose from IR bandpass filters in wavelengths of 590, 665, 720, 830 and 900nm or the IR CPL which combines the same bandpass options with our circular polarizer. The IR CPL also features the world’s first frame with polarization indicators that allows precise and easy polarization control.
The development of larger FOV microscopes and scientific cameras that can take advantage of the F-mount is relatively recent - at the time of writing only one commercially available 25 mm microscope exists. Most modern microscopes have a 19 mm or 22 mm FOV and are therefore still able to use the C-mount. The largest format spinning disk confocal systems are also limited to a 22 mm FOV.
Some rectangular camera sensors can often occupy the microscope FOV more effectively depending on the size, but if the camera FOV is larger than the microscope FOV there will be vignetting, an effect seen at the corners of the image due to the lack of light, as seen in Fig.3 Bot. While this may capture more of the microscope FOV, the substantial image artifacts at the corners of each image can lead to decreased image quality.
Find reviews of customer favorites · seowidget. CVS Health Home Drug Test Kit, 14 Drugs. CVS Health. 5.0. (89). This is good quality and definitely accurate.
Ir bandpass filterfor sale
A detective board with crime investigation materials. · Close up shot of investigation board. · Background image of evidence board with pictures of criminals in ...
The camera FOV depends on two factors: the size of the camera sensor and the total magnification. Sensor size can be measured in a number of ways but a commonly used measure is the size of the diagonal across a sensor, as some sensors are square and others rectangular. This is typically displayed in millimeters, and a range of camera sensor sizes can be seen in Figure 1.
A 'lightpath' is a continuous path in a distributed WDM optical ... fiber link at periodic locations to amplify the light signal. ... route chosen by a lightpath ...
One thing to keep in mind is that a microscope FOV is circular, and a camera FOV is square/rectangular, as seen in Fig.3 Top. Pairing an 18 mm FOV camera with a 18 mm FOV microscope does result in some areas that are not imaged, but this is largely a common factor with all imaging systems unless circular camera sensors emerge in the future. So for now, the camera FOV should aim to fit within the microscope FOV, meaning that it is best to match the FOV between camera and microscope.
UVBandpass filter
We recommend using Life Pixel for all camera conversion services. They offer a variety of conversion options and some great information about infrared photography.
One option is to make your camera full-spectrum by removing the sensor filter and passing UV, visible and IR light. A full-spectrum conversion is versatile since you can use a variety of filters to pass or cut wavelengths and shoot in visible, infrared or a combination of both.
If the goal is simply to attach the camera to the microscope, a 1x adaptor contains no additional lenses and provides no additional magnification or demagnification. This is often the preferred method as it introduces no additional lenses into the system. Every extra lens reduces the number of photons reaching the camera by 3-4% so many researchers will try to avoid this.
By recognizing that FOV requirements can be highly variable, we are able to better serve the needs of our customers and offer a broad range of camera FOV options.
Plastic Guide. Canadian Customers: Take a look at our simplified Returns Process Attention: Our ecommerce shop is experiencing problems with product and ...
With IR conversions, all or most of visible light is cut with the replacement cover glass. In the majority of cases, the original cover glass is swapped for an IR pass filter that blocks all UV and visible light up to 720 nm. The other available options change the pass wavelength either deeper into the IR spectrum or into the visible spectrum.
Due to the extremely dark glass of IR filters, composition, metering and focus adjustments are difficult with the filter on. Polarization percentage is also impossible to distinguish - that's why we added polarization indicators on the frame to eliminate the guesswork. Also some cameras rely on visible light for auto-focus and exposure settings, so they can't be used with an IR filter that blocks the entire visible range. It is important to set your composition before you attach the filter and to use manual focus in these situations. You may also need to take multiple exposures of the same scene to produce the desired result.

Photographer Lloyd Chambers has an excellent site for information about infrared photography. Check out his Digital Infrared Photography Guide for great tips for how to get started or perfect your craft.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500