What is a Power over Ethernet (PoE) injector? - power over ethernet poe injector
Now, if you’re shooting a closeup of something extremely cute and still, like a closeup of a sleeping dog, then you’ll want to crank that aperture all the way down. With a lower aperture, you’ll be able to have a dynamic depth of field in your shot.
But, aperture doesn’t only matter in physics. It affects how your video looks and even how the tone of your video feels. So, how does this light-controlling hole affect your videos? Let’s dive in and learn more!
Our hair extension glue set is a game-changer for all hair extension enthusiasts. With our advanced UV light technology, you can achieve seamless and long- ...
The beauty of DSLRs is that you can play around with your aperture and instantly see the results to find just the right setting for what you’re trying to achieve.
Basically, f-stops are a quantitative measure of the lens speed and are often specific to what type of lens you’re using. For example, some lenses don’t go below an f/4 and others can go down to an f/1.2.
A small aperture has a higher f-stop, so less light will come through the lens to reach the sensor (larger number = smaller hole).
If you’re shooting landscape, you may want to use a higher aperture (f/16). With a higher aperture, more things in the shot will be in focus.
Some zoom lenses have a fixed aperture throughout the range of the zoom. These lenses include a 24–70mm f/2.8, a 24–105mm f/4.0, and a 70–200mm f/2.8. Some newer lenses even have a lower aperture, like the 28–70mm f/2.0. These lenses tend to be more expensive than zoom lenses with a variable aperture. An example of a lens with a variable aperture is an 18–55mm f/3.5–5.6. This means that as you zoom in, the aperture gets smaller, and the number gets bigger.
Totalmagnificationofmicroscope
Mar 21, 2023 — It is a mechanism that connects the camera body to the lens and plays a significant role in determining the compatibility and functionality of ...
by J Yu · 2019 · Cited by 2 — Particularly, MTF has been enhanced sharply in meridian direction. In the best case, MTF vales of progressive addition lenses increase by 15.06%, 39.37%, 94.32% ...
Let’s start at the very beginning: What is aperture? Great question! Aperture is often referenced in optics — a branch of physics focused on the study of light. In optics, aperture is the name for a hole through which light can travel.
Aperture is one of the three main adjustments for exposure/brightness on your camera, with the others being shutter speed and ISO. Setting the right aperture also depends on what the shutter speed and ISO are set at; they all work together to create one balanced-looking shot.

Here’s what we mean by that: Each lens is different and has different characteristics. So, depending on whether you use a macro, zoom, prime, or telephoto, one setting is going to look different across each one of these lenses.
A higher aperture (e.g., f/16) means less light is entering the camera. This setting is better for when you want everything in your shot to be in focus — like when you’re shooting a group shot or a landscape.
Please take a few minutes to fill out a brief survey about your experience using the Virtual Edge: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1yGbkF0KM92WBSk-IgS-EkjxkTKTQwhzuXmDsVpwRDoU/viewform
A lamp (i.e., bulb) sits on a movable track behind a Fresnel lens and in front of a spherical reflector. The reflector directs most of the light towards the ...
40xmagnification microscope
AR coatings enhance the way you see the world by allowing more light to pass through the lens while eliminating glare, ensuring you have clear vision on the job ...
When it comes to physically using aperture on your camera, adjusting your aperture should be simple! Every camera has an f-stop number digitally displayed on an LCD screen, or on the dialog box on the top of the camera.
Immersion Oil: Clear, finely detailed images are achieved by contrasting the specimen with their medium. Changing the refractive index of the specimens from their medium attains this contrast. The refractive index is a measure of the relative velocity at which light passes through a material. When light rays pass through the two materials (specimen and medium) that have different refractive indices, the rays change direction from a straight path by bending (refracting) at the boundary between the specimen and the medium. Thus, this increases the image’s contrast between the specimen and the medium.
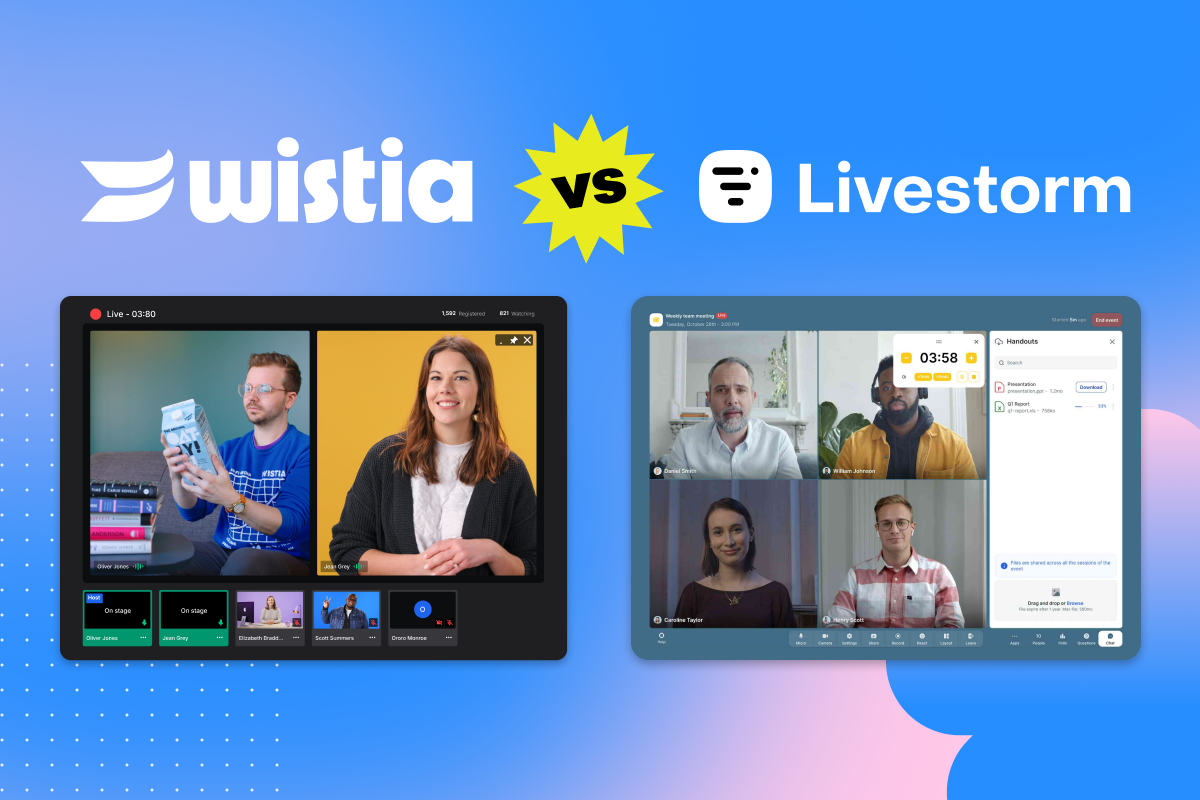
Here's a quick recap of our live event where our co-founders shared how we're making Wistia an all-in-one video marketing ...
Microscope magnificationchart
The Virtual Edge by http://www.uwyo.edu/virtual_edge/ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License
Resolution ofmicroscope
To increase or decrease the aperture, simply adjust the camera’s circular jog wheel. If all else fails, check your camera’s manual!
Parfocal: the objective lenses are mounted on the microscope so that they can be interchanged without having to appreciably vary the focus.
Jan 6, 2022 — Allen wrenches come in lots of different lengths, including short-arm and long-arm variations. The long arms can reach recessed screws more ...
Most people will probably say lower apertures are the best. That’s because, in a lot of cases, more expensive lenses typically have lower f-stops (e.g., 1.2, 1.4, 3, etc) and a more expensive lens can sometimes equate to better quality. For example, prime lenses (i.e., those with a fixed focal length), like a 24mm, 35mm, or 50mm, can have apertures as low as 1.2 and can create some dynamic looking shots.
If you’re still fuzzy on what setting to pick, go ahead and try a couple of shots! Take a couple shots at one f-stop, and if you don’t like that look, adjust accordingly.
Traditionally, a lens that goes below an f/4 is classified as a “fast lens,” which refers to the maximum aperture diameter (or f-stop).
Total magnification: In a compound microscope the total magnification is the product of the objective and ocular lenses (see figure below). The magnification of the ocular lenses on your scope is 10X.
The aperture on your camera is a hole in the lens that controls the amount of light that passes through the camera lens to fall on the sensor.
400xmagnification microscope
The aperture setting is typically identified by an f-number, often called an f-stop, which is a ratio comparing the focal length to the effective aperture diameter.

What is the magnification on a microscopeexplain
A lower aperture means more light is entering the camera, which is better for low-light scenarios. Plus, lower apertures create a shallow depth of field, making the background blurry. You want to use a low aperture when you want a more dynamic shot. For example, we use low apertures like (f/1.8) in our Wistia studio to create that cinematic look.
Simply put, the f-stop number is tied to aperture. The higher the f-stop number, the smaller the aperture, which means less light enters the camera. The lower the f-stop number, the larger the aperture, and the more light enters the camera.
The compound microscope has two systems of lenses for greater magnification, 1) the ocular, or eyepiece lens that one looks into and 2) the objective lens, or ...
4K wireless security cameras are invaluable. Their high-resolution video captures detailed images, making it easier to identify people and activities at a ...
Here are some examples: If your subject is running or moving a lot, then you probably want a higher aperture where more of the scene is going to be in focus, so your subject doesn’t become blurry.
You can use many different apertures for recording quality video. If you’re familiar with photography, aperture for video follows the same rules you’re already familiar with.
by VD Tang · 2023 — Focal length is the distance between the lens and the focal point, where the light rays converge or diverge. · The concept of vergence is crucial ...
You might be wondering why f-stops are displayed using decimals (e.g., 1.4, 2.8, and more). Well, that’s because they’re a fraction that stands for the ratio of the focal length of a lens to the diameter of the entrance pupil.
Electronmicroscopetotalmagnification
One way to change the refractive index is by staining the specimen. Another is to use immersion oil. While we want light to refract differently between the specimen and the medium, we do not want to lose any light rays, as this would decrease the resolution of the image. By placing immersion oil between the glass slide and the oil immersion lens (100X), the light rays at the highest magnification can be retained. Immersion oil has the same refractive index as glass so the oil becomes part of the optics of the microscope. Without the oil the light rays are refracted as they enter the air between the slide and the lens and the objective lens would have to be increased in diameter in order to capture them. Using oil has the same effect as increasing the objective diameter therefore improving the resolving power of the lens.
If so, you may want to use a lower aperture (f/1.8). The lower the number, the more shallow the depth of field. Less things will be in focus, and the setting will create a dynamic-looking shot.
Yaw, Pitch and Roll Angles. The yaw (direction), pitch (tilt) and roll values for the camera, plane and objects are defined as described in the following ...
Learn how this multi-product SaaS company used the power of video, analytics, and Wistia to increase their engagement by 60% ...
Resolving power or resolution: the ability to distinguish objects that are close together. The better the resolving power of the microscope, the closer together two objects can be and still be seen as separate.
Think of it like your eyes: When you squint, less light comes through to the pupil, and when the eye is opened fully, all of the light enters.
There are benefits to having either a higher aperture or a lower aperture. It all depends on what kind of look you are going for — because high and low apertures create distinct looks that help you dial in that “sweet spot” for your style.
If your background is messy or busy, it can be distracting for the viewer and pull their attention away from the subject of your shot. Use a low aperture to blur your background! Stick to as low of an aperture as possible to focus on your subject and keep the background blurry.
Something to keep in mind is that the aperture on your camera not only affects the brightness or exposure of your image, but it affects depth of field, too.
At the end of the day, when it comes to aperture, the main thing to remember is that it controls how much light comes into your shot — and you want to use that knowledge to choose the best aperture based on the context of what you’re shooting.
Magnificationofmicroscopeformula
Get free, unlimited access to our video asset library! Download royalty-free music, color grade presets, webinar bumpers and overlays, script templates, and more — curated for marketers, created by us!
Finally, with autofocus tracking recently taking over the DSLR game, you don’t have to worry too much about your shot being in focus, but these rules above still apply when properly exposing for a shot.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500