Was ist 4K-Auflösung? Ist 8K 2x besser? - 4k pixelgröße
Telescope lensconcave or convex
This site uses cookies to improve your experience with us. By closing this banner, or interacting with our site, you permit us to recognize our cookies and our partners' and identify you for marketing.
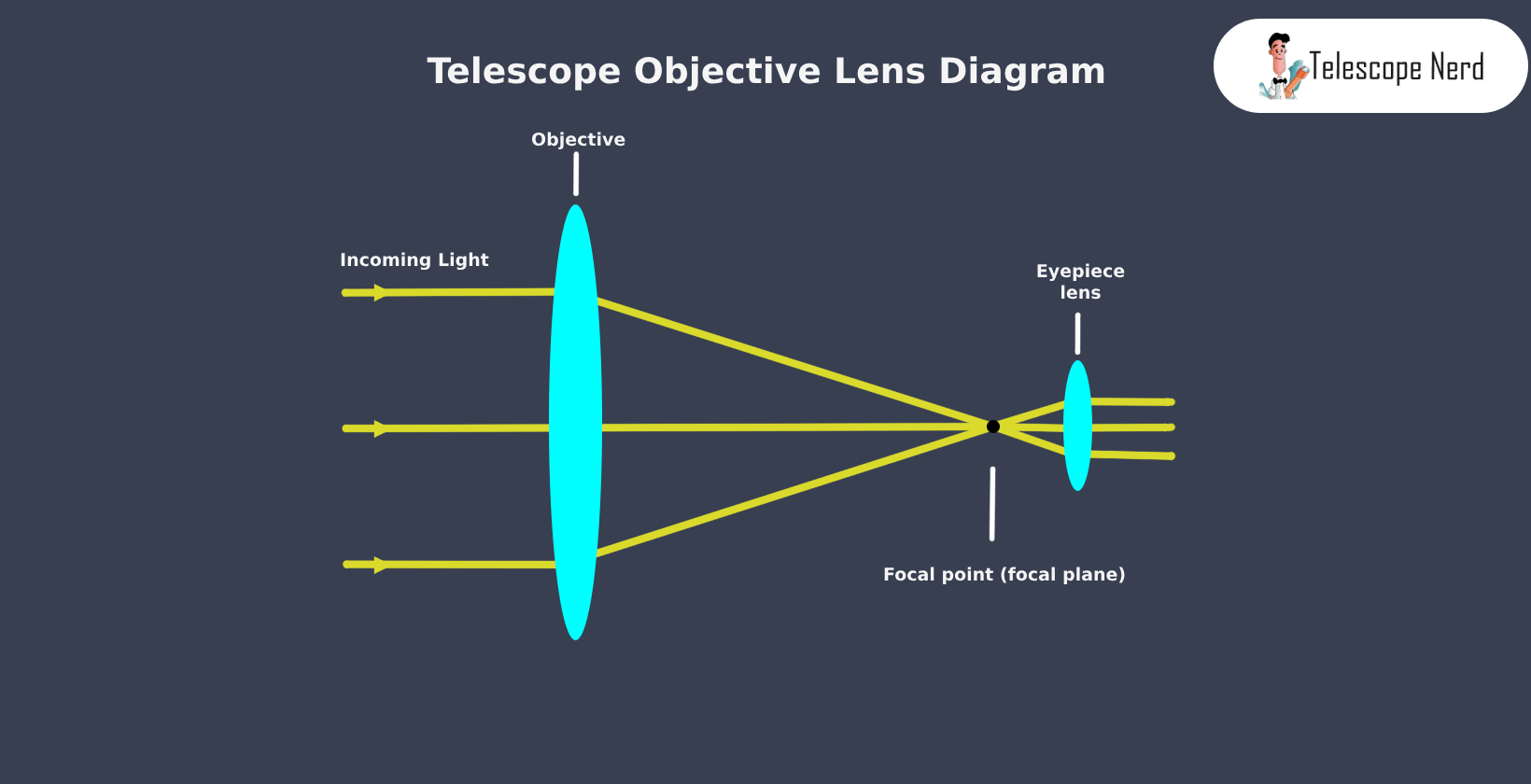
The objective lens directly affects telescope’s performance, including the magnification, light-gathering power and resolution. The curvature of this lens plays a pivotal role in determining the telescope’s focal length. A stronger curvature bends light at a higher angle, causing it to focus at a shorter distance. This results in a shorter focal length because focal length describes the distance from the objective lens to the focal point.
The objective lens of a telescope, integral to the viewing experience, is constructed using a combination of materials. The lens is typically crafted from crown or flint glass, each known for its unique refractive properties. The objective lens is secured within the telescope’s optical tube assembly (OTA). To enhance performance, the surface of the objective lens should be treated with anti-reflective coatings, commonly derived from materials such as magnesium fluoride, to maximize light transmission and minimize unwanted reflections. Each material, combined with its quality and any applied coatings, plays a pivotal role in determining the clarity, brightness, and color accuracy of the images produced by the telescope.
Bestobjective lens telescope
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), a low-coherence interferometry technique, is well established as a non-invasive clinical tool for high resolution ophthalmic imaging of the retina. By using the 1.05 µm central wavelength, instrumentation companies are now developing systems to image deeper through the retina into the blood vessel layer (called the choroid) to diagnose eye diseases and monitor treatment. Developing clinical applications are in Endoscopy, both in the esophagus or in the arteries, and dentistry.
Will Kalif is an amateur astronomer at TelescopeNerd.com. Will is an author of the book "See It With A Small Telescope". Will Kalif has been passionate about telescopes and the wonders of the night sky ever since he received his first telescope as a teenager. And for several decades now he has been making and using his own telescopes and helping other people to also enjoy the various things that can be seen on a dark and starry night.
The objective lens refracts light into the focal point because the lens is thinner at the edges than in the middle. When light passes through the thinner parts, it is refracted at a higher angle than in the middle. This causes light to converge into focus at the same point where it is magnified and observed.
EyepieceTelescope
Although these aberrations negatively impact the telescope’s performance, proper maintenance of the objective lens can mitigate their effects. Dust, smudges, or scratches will degrade the image quality. Regular maintenance along with careful handling will prolong the lens’s life and maintain its performance.
The maintenance of an objective lens in a refractor is easier than a primary mirror in a reflector, due to the delicate nature of mirrors. However, both types of telescopes provide both upsides and downsides.
To prolong the life of an objective lens, it’s crucial to maintain it properly by protecting it from scratches and pollutants, like dust. Dust accumulation not only compromises image clarity but also leads to optical aberrations if not addressed.
Telescope objective lensfocal length
Refracting telescopes use an objective lens as their primary optical component. A refracting telescope, or refractor, operates on the principle of refraction, using an objective lens to gather and bend incoming light. At the front of a reflector, this lens refracts and concentrates the light rays to a focal point inside the telescope.
To maintain the condition of the lens, use a lens cap consistently when the telescope is not in active use. To clean an objective lens, begin with a soft brush or compressed air to delicately remove any loose dust particles. If the lens has more stubborn marks or smudges, use a lens cleaning solution with a microfiber cloth. It’s crucial to remember to apply the solution to the cloth and not directly onto the lens, using gentle, circular motions to avoid potential damage. Excessive or incorrect cleaning methods will inadvertently scratch the lens or harm its protective coating.

The objective lens also affects the brightness and clarity of the image. A lens with a larger diameter collects more light, resulting in brighter and more detailed images. The quality of the lens material and its coatings also influences the clarity and color accuracy by reducing aberrations.
When SWIR wavelengths like 1.04 and 1.31 are used for OCT in tissue, it is because they travel farther in scattering medium than do visible or NIR wavelengths, due to a phenomenon called Raleigh scattering. In one version of OCT, called spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT), linescan cameras capture one line of depth information for each readout cycle (known as an axial line or as an "A-line"). Moving the light probe over the tissue in both X and Y directions capture a 3 dimensional view of the tissue. The Sensors Unlimited line of high speed digital linescan cameras provide the resolution and speed to image up to 150,000 lines per second of 2048 pixels. The speed cuts the time the patient has to hold still while scanning larger 3-D volumes. The pixel count and related spectral resolution enables deeper image capture with the detail that doctors use to make better healthcare decisions.
It’s also important to monitor other components such as the lens mount, where the objective lens is attached to the telescope. The lens mount should be periodically inspected for debris to ensure the telescope focuses optimally. Additionally, the storage environment of the telescope plays a pivotal role in its longevity. A dry environment is paramount to prevent the onset of fungus or moisture damage to the objective lens.
An alternative method using two InGaAs cameras provides full-field optical coherence tomography (FF-OCT) by use of heterodyne techniques. The tissue section is fully illuminated and en-faced imaged to capture the data at one depth. Then, the reference mirror is shifted to add images at successive depths, building the 3-D reconstruction of the tissue block. Sensors Unlimited high-frame rate imaging cameras, such as the SU640SDWH and the video frame-rate high-resolution GA1280JS-15, both enable FF-OCT methods to capture 2-D images at specific depths in one frame capture.
A) A Full-range SD-OCT 3-D image showing front of human eye from eye lashes to below the iris and into the lens, an image of 2048 pixels x 2048 lines x 200 frames covering a volume of 12x18x18 mm. B) Across section of the 3-D image from the top of the cornea through to the bottom of the lens, demonstrating the image depth resulting from the combination of the University of Washington Full-Range FFT technology with the Sensors Unlimited GL2048L camera. Provided by Dr. Ruikang Wang of the BAIL lab at the University
What isobjective lensin microscope
Objective lens telescopefunction
Weight and size constraints arise because crafting large, high-quality lenses is both challenging and heavy, limiting the practical size of refracting telescopes. The process involves shaping and polishing thick glass or other transparent materials to exact specifications, ensuring that the entire lens is free from imperfections. As the diameter of the lens increases, the challenges in manufacturing become exponentially more complex.
Objective lens telescopefor sale

The downsides of using an objective lens are primarily chromatic aberration, weight and size constraints, and potential lens imperfections.
The objective lens is a part of a refracting telescope that collects and focuses light from distant objects. Knowing the design and material of an objective lens is crucial as it influences the telescope’s field of view, magnification, and overall performance.
Some telescopes incorporate multiple lenses in their design, with each lens serving to correct aberrations or enhance the image quality. The choice and combination of lenses influences various factors, including the telescope’s focal length, magnification, and overall performance.
A smaller curvature will cause light to focus further from the objective, increasing the focal length. The increase in focal length will provide more detailed images of distant objects, but it also narrows the field of view. Decreasing the curvature, thus increasing the focal length, will also result in higher magnification.
In refractors, the objective lens is designed to focus different wavelengths of light onto the same plane. While this design leads to chromatic aberrations, where colors don’t converge at the same point, the lens’s precise curvature effectively reduces coma.
Chromatic aberration occurs because objective lenses refract different wavelengths of light at varying angles. This results in a failure to focus all colors to the same convergence point, leading to color fringing around observed objects.
The shape of the objective lens is convex, meaning it bulges outward. This design allows it to act as a converging lens, focusing parallel rays of light to converge at a focal point. The distance from the focal point to the objective lens is called the focal length.
In refracting telescopes, the entire volume of objective lenses must be free from imperfections, as any flaws will lead to image distortion. This is because light must pass through the entire lens uninterrupted, while in reflecting telescopes, only the surface quality is critical for accurate image representation.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500