Visual Optics Fibre Optic Borescope (6H) - borescope fiber optic
On the objective, this is usually denoted by an X next to a numeric value (100X, 10X etc). On the other hand, objectives will also have a colored band around the circumference of the objective that indicates the magnification of the objective. For instance, a yellow band around the objectives (lower part of the objective) indicates that it is a 10x objective.
As you can see, at one foot away from the camera, 72.5° FOV gives a vision of 1.4 feet across. It means that at 10 feet you get a vision of 14 feet across. A 72.5° FOV conference camera is a good choice for small conference rooms, with the conference room table at least 3 feet to 4 feet away from the camera.
For conference cameras, it refers to "what you see" through the camera lens. FOV is usually measured in Degrees. The camera is the single starting point, and the view radiates out and gets wider, forming a triangle.
FOVmeaning
If your conference room can hold 6-12 people, and most seats are facing the camera, a conference camera with a wider FOV angle such as 120° and even bigger would be better.
NA is also important to observe very fine structures or detect dim signals during fluorescence observation. When determining which microscope objective will resolve the smallest feature in your specimen, think about the NA. As you weigh your options, keep in mind that numerical aperture typically ranges between 0.10 to 1.25.
It is an angle of incidence. It is the most important parameter of a microscope. NA measures its ability to gather light. It’s an important factor to determine resolution, depth of focus, and the brightness of images. Objectives with a larger NA gather a wider range of light, resulting in brighter, higher resolution images.
Fov of cameranikon
The resolution of the microscope objective determines the smallest distance between two objects that can be observed. It is directly proportional to the illumination wavelength of light and inversely proportional to the NA.
For a regular quadrilateral table, you need to know X (the distance from the camera to the table) and Y (half of length of the side facing the camera). Then calculate θ=arctan(y/x), and 2θ < camera HFOV.
FOVto focal length calculator
At 180° FOV, the camera provides wall to wall coverage. Basically, if you need total video coverage for your conference room, this is the solution you're looking for in cameras.
If your conference room is relatively small, accommodating about 4 to 6 people, and the layout is as the following picture shows, a conference camera with an FOV range of 90° to 120° should be a nice choice. As people are quite close to each other, 90° to 120° FOV conference cameras assure that every one is in the camera frame.
Attach each objective to each lens mount hole of the revolving nosepiece, starting from the lowest magnification objective and increasing the magnification in the clockwise direction seen from the bottom. By attaching objectives in this way, the objectives can be switched in ascending order of magnification
Fieldofview human eye
FOV angles can range from 54 degrees to 360 degrees. Bigger angles generally equates to a wider and better vision. But bigger is not always better and necessary. Different conference rooms and scenarios require different cameras, which is why there is so much variance when it comes to FOV.
HumanFOVin games
For an irregular oval table, you need to know X (the distance from the camera to the center point of the table) and Y (semi-major axis). Then calculate θ=arctan(y/x), and 2θ < camera HFOV.
Optical correction such as achromatic, apochromatic, plan and semi-plan are often denoted on the objective in order to show the design of the objective. Plan and semi-plan objectives correct for field curvature. Field curvature often results in blurred images on the periphery and correction for this helps produce good quality images. Whereas plan objectives correct better, allowing for better display (over 80 per cent) of field flat, semi-plain objectives produce about 65 per cent.
Denoted by a number (such as 0.17mm) the cover slip thickness is labeled on the objective to note the type of cover slip that should be used. A cover slip changes the way light is refracted from the specimen. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the right cover slip is used in order to produce a good quality image. Zero(0) denotes no coverslip to use. Dash(-) denotes use of coverslip or no cover slip, it does not matter.
Now we can move on to choosing a suitable FOV for different use cases. Usually, it is related to how big your conference room is and the interior layout.
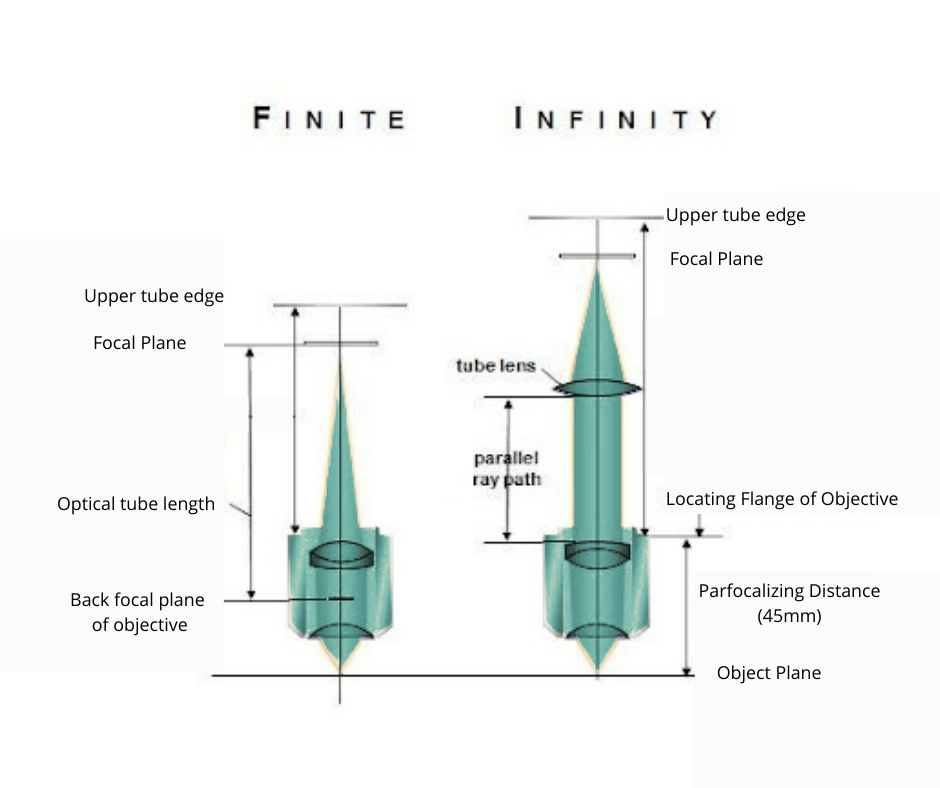
In a finite conjugate design, the objective focuses light from the object into the focal plane of the eyepiece. An infinite corrected objective collects light from the object and forms a parallel beam that passes through a tube lens. The advantage of this design is that additional optical elements, such as polarizers, filters, and wave-plates, can be placed in between the tube lens and the objective without interfering with the focusing of the beam. The infinite conjugate design is often used in fluorescence microscopes, which rely on filters.
The higher the NA, the smaller the distance between two objects. As we mentioned previously, choosing the right NA for your application is crucial in determining the resolution of your microscope system.
There are many different types of objectives available for microscopes, but without a basic understanding of how they work, it can be difficult to know which ones are best suited to the specific needs you have. That's why this article takes you through the basics points to keep in mind ,so that you'll have a better idea of what type is right for your needs.
If your conference layout is none of the above types and you want to get down to a specific FOV angle that suits your needs the best, you will have to do some math.
Have you ever been puzzled by different FOV angles when choosing the right conference camera for your conference room? Knowing more about FOV is necessary so you don't waste money on the wrong camera. This article will give you a comprehensive introduction to FOV and help you choose the best conference camera.
Fov of cameraformula
Now let's look directly at some popular FOV angles for conference cameras. To make it more clear how wide the view will be, we take one foot away from the camera as an example. This way, it's also easier to compare different FOV angles.
Field of view (FOV) is the open, observable area a person can see with their naked eyes or via an optical device, such as a camera. In other words, FOV is what you can see without turning your head. It includes what you see ahead of you and your peripheral vision.
FOV is just one feature you must consider when choosing video conference cameras, but it plays a big role. To determine what FOV angle is the best option, you will have to consider a number of factors, such as the conference table size, room layout, and how far away the table is to the camera. Check out all our conference cameras, and find the perfect one based on FOV.

The objective depth of field is the axial range, which enables you to focus an objective without any considerable change in image sharpness. This value varies radically from low to high numerical aperture objectives; it usually decreases as the numerical aperture increases.
120° FOV, another common wide angle, is also a fit for huddle spaces. At one foot away, you get a vision of 3.4 feet across. At ten feet from the camera, that means 34 feet. This wide angle can almost get everyone within the camera frame.
Camerafieldofview simulator
Is the distance from the objective’s front lens to the closest surface of the coverslip when the specimen is in focus? WD is inversely proportional to the NA, which means that higher NA objectives typically have low working distances.
Each objective and eyepiece has a specific purpose or function. Objective lenses magnify the image that enters the objective and bring it to a sharp, clear focus. Eyepieces take the light that has been focused by the objective lenses and magnify it further so that you can see it. The magnification power is measured by objective magnification multiplied by eyepiece magnification.
Fov of cameracalculator
Big conference rooms that can accommodate 12-16 people usually have a setup like this (pictured below). In this case, a 120° FOV may not be necessary. A FOV range of 60° to 90° is enough to get everyone in the camera frame.

At 90° FOV, you will get 2 feet of width for every 1 foot of distance from the camera. In this case, 10 feet will provide a vision of 20 feet across. This wider vision is suitable for a majority of conference rooms.
At 108° FOV, we start to get into cameras which are considered "wide angle". Most huddle room cameras fall into this wide angle category. 108° FOV conference cameras provide 2.8 feet of view at 1 foot distance. This allows you to set up the camera on the long wall.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500