Using Variable Neutral Density Filters to Adjust Exposure ... - how does a variable nd filter work
If an unmounted aspheric lens is being used to collimate the light from a point source or laser diode, the side with the greater radius of curvature (i.e., the flatter surface) should face the point source or laser diode. To collimate light using one of our mounted aspheric lenses, orient the housing so that the externally threaded end of the mount faces the source.
Thorlabs offers a large selection of mounted and unmounted aspheric lenses to choose from. The aspheric lens with a focal length that is closest to 16 mm has a focal length of 15.29 mm (Item # 354260-B or A260-B). This lens also has a clear aperture that is larger than the collimated beam diameter. Therefore, this option is the best choice given the initial parameters (i.e., a P1-630A-FC-2 single mode fiber and a collimated beam diameter of 3 mm). Remember, for optimal coupling, the spot size of the focused beam must be less than the MFD of the single mode fiber. As a result, if an aspheric lens is not available that provides an exact match, then choose one with a focal length that is shorter than the calculation above yields. Alternatively, if the clear aperture of the aspheric lens is large enough, the beam can be expanded before the aspheric lens, which has the result of reducing the spot size of the focus beam.
The specifications for the P1-630A-FC-2, 630 nm, FC/PC single mode patch cable indicate that the mode field diameter (MFD) is 4.3 μm. This specification should be matched to the diffraction-limited spot size given by the following equation:
Molded glass aspheres are manufactured from a variety of optical glasses to yield the indicated performance. The molding process will cause the properties of the glass (e.g., Abbe number) to deviate slightly from those given by glass manufacturers. Specific material properties for each lens can be found by clicking on the Info Icon in the tables below and selecting the Glass tab.
A selection of the lenses sold on this page are designed for collimating laser diodes. As seen in the tables below, a compatible laser window thickness is listed for these lenses. In these instances, the numerical aperture (NA), working distance (WD), and wavefront error of these lenses are defined based on the presence of a laser window of the indicated thickness (not included).
Asphericlensesadvantages disadvantages
Fill your Home with light, health and wellbeing. Perfume your life, and the life of the ones you love and care about, with exquisite aromas that bring ...
Since the output of a laser diode is highly divergent, collimating optics are necessary. Aspheric lenses do not introduce spherical aberration and therefore are commonly chosen when the collimated laser beam is to be between one and five millimeters. A simple example will illustrate the key specifications to consider when choosing the correct lens for a given application. The second example below is an extension of the procedure, which will show how to circularize an elliptical beam.
Aspherical lensespros and cons
where R is the radius of curvature, k is the conic constant, and the An are the nth order aspheric coefficients. The sign of R is determined by whether the center of curvature for the lens surface is located to the right or left of the lens' vertex; a positive R indicates that the center of curvature is located to the right of the vertex, while a negative R indicates that the center of curvature is located to the left of the vertex. For example, the radius of curvature for the left surface of a biconvex lens would be specified as positive, while the radius of curvature for its right surface would be specified as negative.
Aspheric lenses focus or collimate light without introducing spherical aberration into the transmitted wavefront. For monochromatic sources, spherical aberration often prevents a single spherical lens from achieving diffraction-limited performance when focusing or collimating light. Aspheric lenses are designed to mitigate the impacts of spherical aberration and are often the best single element solution for many applications including collimating the output of a fiber or laser diode, coupling light into a fiber, spatial filtering, or imaging light onto a detector.
The table below contains all molded visible and near-IR aspheric lenses offered by Thorlabs. For our selection of IR molded aspheres, click here. The Item # listed is that of the unmounted, uncoated lens. An "X" in any of the five AR Coating Columns indicates the lens is available with that coating (note that the V coating availability is indicated with the AR coating wavelength). The table to the right defines each letter and lists the specified AR coating range. Clicking on the X takes you to the landing page where that lens (mounted or unmounted) can be purchased.
Apr 26, 2021 — Grades Report via 360° reports ... The Grades report shows the student's achievements and grade trends against the course average. Helping ...
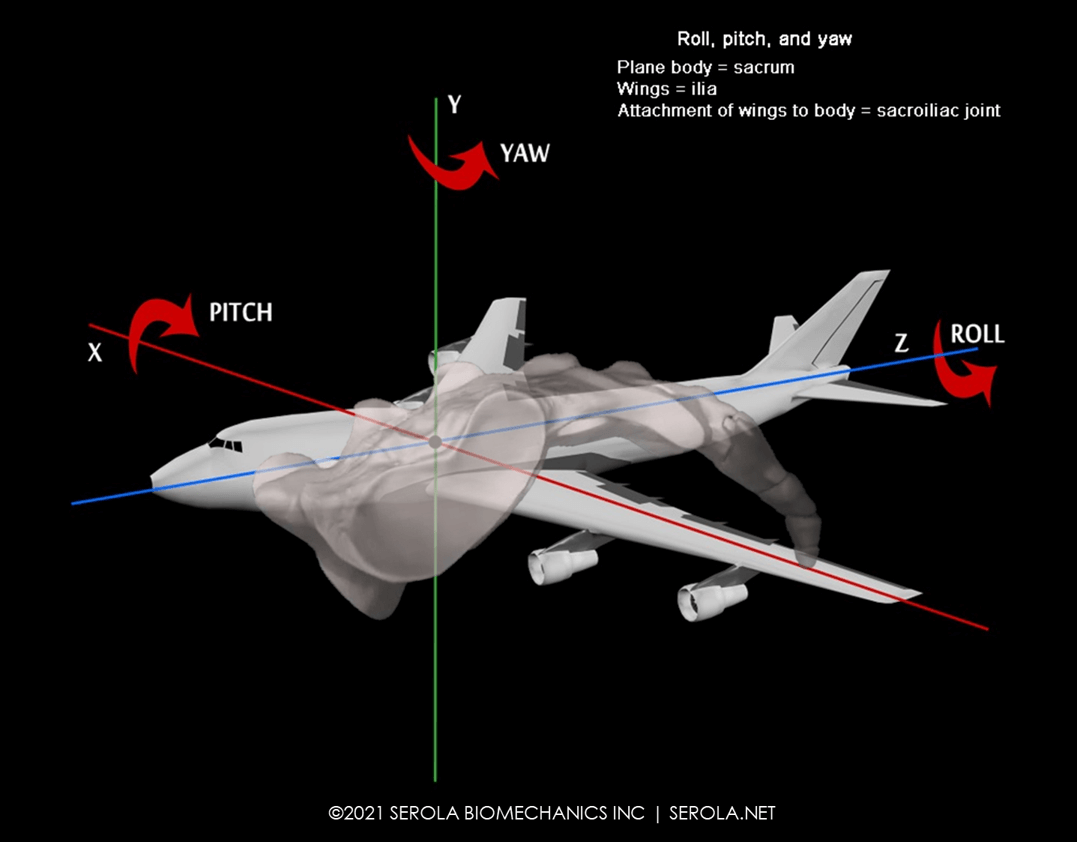
Sacral motion can be compared to that of an airplane undergoing pitch, roll, and yaw, where sacral flexion/extension is comparable to pitch, sacral rotation is comparable to roll, and sacral lateral flexion is comparable to yaw. The combined movement around these three axes, each centered in the body of the sacrum, represents sacral motion.
With this information known, it is now time to choose the appropriate collimating lens. Thorlabs offers a large selection of aspheric lenses. For this application, the ideal lens is a molded glass aspheric lens with focal length near 5.6 mm and our -B antireflection coating, which covers 780 nm. The C171TMD-B (mounted) or 354171-B (unmounted) aspheric lenses have a focal length of 6.20 mm, which will result in a collimated beam diameter (major axis) of 3.3 mm. Next, check to see if the numerical aperture (NA) of the diode is smaller than the NA of the lens:
Bestaspherical lenses
Sep 15, 2021 — Magnifying glass strength, also called magnification, refers to how much larger the magnifier will make the object when viewed through the lens.
Whereas earlier we considered only the larger divergence angle, we now look at the smaller beam divergence of 8°. From this, and using the effective focal length of the A390-B aspheric lens chosen in Example 1, we can determine the length of the semi-minor axis of the elliptical beam after collimation:
A good rule of thumb is to pick a lens with an NA twice that of the laser diode NA. For example, either the A390-B or the A390TM-B could be used as these lenses each have an NA of 0.53, which is more than twice the approximate NA of our laser diode (0.26). These lenses each have a focal length of 4.6 mm, resulting in an approximate major beam diameter of 2.5 mm. In general, using a collimating lens with a short focal length will result in a small collimated beam diameter and a large beam divergence, while a lens with a large focal length will result in a large collimated beam diameter and a small divergence.
The attachment of the wings to the body of the plane is comparable to the sacroiliac joint. Unlike the wings of a plane, which float freely in an open system, allowing a firm attachment to the body of the plane, the innominates are part of a closed system, which necessitates a slight amount of flexibility at their attachment to the sacrum, which is provided by the ligaments. Too much laxity will impede control and too little motion will reduce the normal pumping mechanism of the joint; either will be detrimental to stability.
Asphericallens vs normal lens camera
Borrowed from English MtF. Noun edit MtF Synonyms edit Derived terms edit / (mùtǒngfàn) Related terms edit Anagrams edit
Asphericallens vs spherical
All of the molded glass lenses featured on this page are available with an antireflection coating for either the 600 - 1050 nm or 650 - 1050 nm range deposited on both sides. Other AR coating options are listed in the Aspheric Lens Selection Guide table at right.
These lenses can be purchased unmounted or premounted in non-magnetic 303 stainless steel lens cells that are engraved with the Item # for easy identification. All mounted aspheres have a metric thread that make them easy to integrate into an optical setup or OEM application; they can also be readily used with our SM1-threaded (1.035"-40) lens tubes by using our aspheric lens adapters. When combined with our microscope objective adapter extension tube, mounted aspheres can be used as a drop-in replacement for multi-element microscope objectives.
Aspheric lenses are commonly chosen to couple incident light with a diameter of 1 - 5 mm into a single mode fiber. A simple example will illustrate the key specifications to consider when trying to choose the correct lens.
Here, f is the focal length of the lens, λ is the wavelength of the input light, and D is the diameter of collimated beam incident on the lens. Solving for the desired focal length of the collimating lens yields
Aspheric lens glasses
SAFE PLUS ALLEN KEY SET 10PCS - 1.5MM TO 12MM ... Your order will be delivered within 2 to 7 business days. Wishlist Compare.
Aspherical lensescost
These include the linear magnification, numerical aperture value, optical corrections, microscope body tube length, the type of medium the objective is ...
When choosing a collimation lens, it is essential to know the divergence angle of the source being used and the desired output diameter. The specifications for the L780P010 laser diode indicate that the typical parallel and perpendicular FWHM beam divergences are 8° and 30°, respectively. Therefore, as the light diverges, an elliptical beam will result. To collect as much light as possible during the collimation process, consider the larger of these two divergence angles in any calculations (i.e., in this case, use 30°). If you wish to convert your elliptical beam into a round one, we suggest using an anamorphic prism pair, which magnifies one axis of your beam; for details, see Example 2 below.
Assuming that the thickness of the lens is small compared to the radius of curvature, the thin lens approximation can be used to determine the appropriate focal length for the asphere. Assuming a divergence angle of 30° (FWHM) and desired beam diameter of 3 mm:
Up to this point, we have been using the full-width at half maximum (FWHM) beam diameter to characterize the beam. However, a better practice is to use the 1/e2 beam diameter. For a Gaussian beam profile, the 1/e2 diameter is almost equal to 1.7X the FWHM diameter. The 1/e2 beam diameter therefore captures more of the laser diode's output light (for greater power delivery) and minimizes far-field diffraction (by clipping less of the incident light).
The best way to visualize the movement pattern of the sacrum is to consider gait, in which sacral movement reciprocates with the ilia. In order to accommodate the two opposing iliac movements, the articular surfaces are shaped like an airplane rotor, imparting a twisting motion [1-4]. However, instead of the rotor spinning, the central body rotates, as the sacrum pivots about the prescribed paths formed into the articular surfaces of the sacrum and ilia at the sacroiliac joints, one on each side. During right nutation, the right side of the sacral base pivots anteriorly and inferiorly as the right ilium moves posteriorly and inferiorly; at the same time, the left side of the sacral base pivots posteriorly and superiorly as the left ilium moves anteriorly and superiorly. As the two ilia reverse movement, the sacrum pivots accordingly [5, 6].
X10 Magnifying Glass, supplied by Carl Zeiss, used in various techniques. Bioz Stars score: 86/100, based on 1 PubMed citations.
Refer to the diagram to the right for α1 and α2 definitions. Our 780 nm laser will experience slightly less magnification than a 670 nm beam passing through the prisms at these angles. Some trial and error may be required to achieve the exact desired magnification. In general:
Rotate the chopper relative to the beam until both sides of the beam just touch the chopping disc. A square wave output can be achieved by using a disc with ...
The minor beam diameter is double the semi-minor axis, or 0.64 mm. In order to magnify the minor diameter to be equal to the major diameter of 2.5 mm, we will need an anamorphic prism pair that yields a magnification of 3.9. Thorlabs offers both mounted and unmounted prism pairs. Mounted prism pairs provide the benefit of a stable housing to preserve alignment, while unmounted prism pairs can be positioned at any angle to achieve the exact desired magnification.
Using the laser diode and aspheric lens chosen above, we can use an anamorphic prism pair to convert our collimated, elliptical beam into a circular beam.
The PS883-B mounted prism pair provides a magnification of 4.0 for a 950 nm wavelength beam. Because shorter wavelengths undergo greater magnification when passing through the prism pair, we can expect our 780 nm beam to be magnified by slightly more than 4.0X. Thus, the beam will still maintain a small degree of ellipticity.
Asphericallens photography

Hyperspectral vs Multispectral Imaging. Hyperspectral imaging systems acquire images in over one hundred contiguous spectral bands. While multispectral imagery ...
Figure 6 shows the effect of two polarizing filters on originally unpolarized light. The first filter polarizes the light along its axis. When the axes of the ...
The aspheric surfaces of these lenses may be described using a polynomial expansion in Y, the radial distance from the optical axis. The surface profile or sagitta (often abbreviated as sag) is denoted by z, and is given by the following expression:
Alternatively, we can use the PS871-B unmounted prism pair to achieve the precise magnification of the minor diameter necessary to produce a circular beam. Using the data available here, we see that the PS871-B achieves a magnification of 4.0 when the prisms are positioned at the following angles for a 670 nm wavelength beam:
Due to the rotational symmetry of the lens surface, only even powers of Y are contained in the polynomial expansion above. The target values of the aspheric coefficients for each product can be found by clicking either on the blue Info Icons in the tables below () or on the red documents icon () next to each lens sold below.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500